Charting a New Africa: A Comprehensive Look at the African Union Map
Related Articles: Charting a New Africa: A Comprehensive Look at the African Union Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting a New Africa: A Comprehensive Look at the African Union Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting a New Africa: A Comprehensive Look at the African Union Map

The African Union (AU) map is more than just a geographical representation; it is a powerful symbol of unity, cooperation, and shared destiny. It embodies the aspirations of a continent striving for peace, development, and a brighter future for its people. This article will explore the multifaceted significance of the AU map, delving into its historical context, political implications, economic benefits, and the challenges it continues to face.
A Union Forged in Unity:
The AU map represents the culmination of decades of Pan-Africanism, a movement advocating for the unity and liberation of African people. Following the wave of independence movements in the 1960s, the Organization of African Unity (OAU) was established in 1963. This organization, while a significant step forward, lacked the capacity to effectively address the continent’s complex challenges. Recognizing the need for a more robust institution, the AU was formed in 2002, replacing the OAU with a renewed focus on peace, security, and development.
The Geographical Landscape:
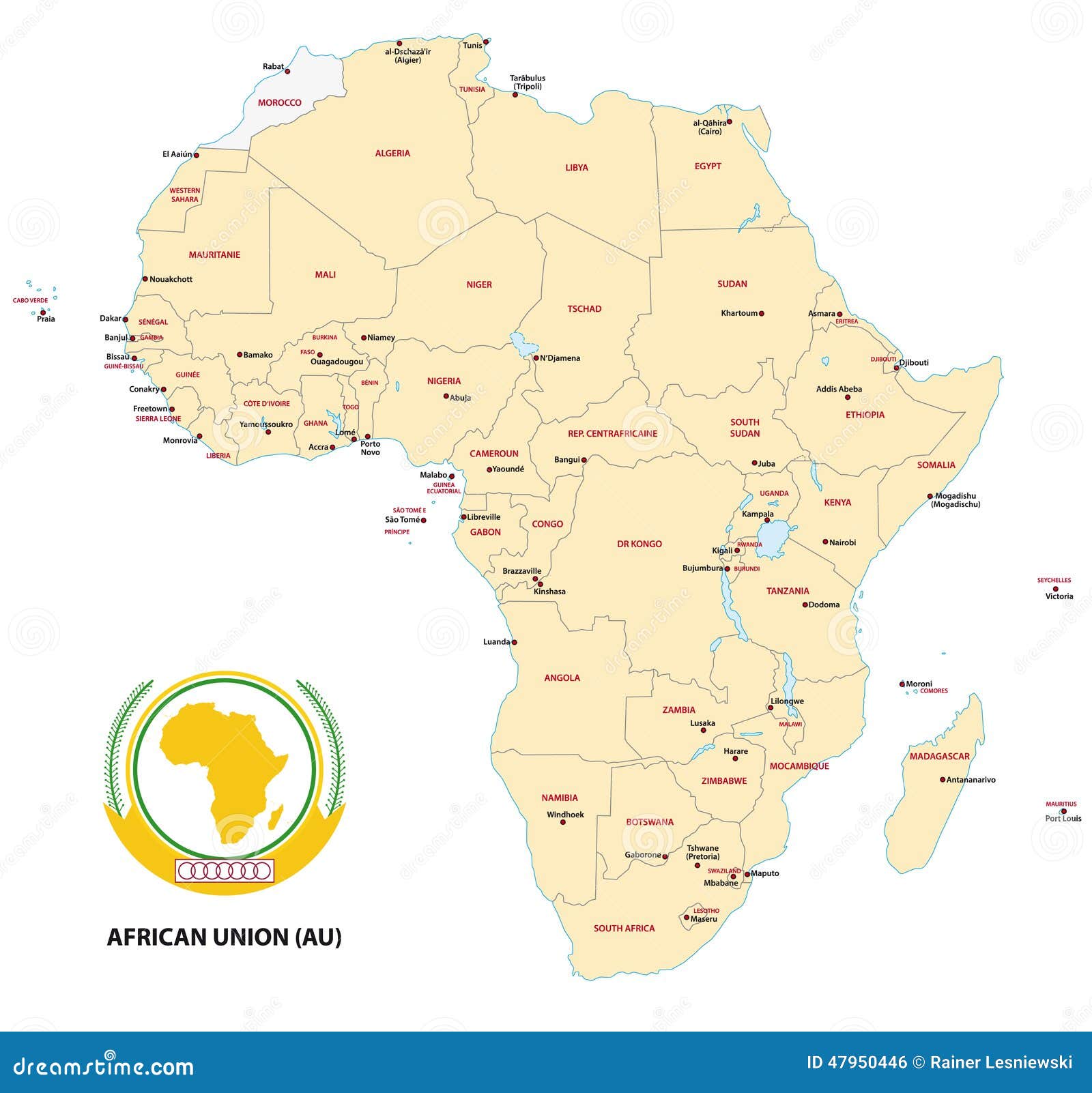
The AU map encompasses 54 independent African states, covering a vast and diverse continent. It stretches from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Cape of Good Hope in the south, and from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Indian Ocean in the east. This geographical diversity is reflected in the map’s intricate tapestry of landscapes, cultures, languages, and economies.
Political Significance:
The AU map embodies a vision of a united Africa, where member states work collectively to address shared challenges and pursue common goals. The organization’s charter outlines a commitment to:
- Peace and Security: Promoting peace and stability through conflict resolution, peacekeeping operations, and addressing root causes of conflict.
- Economic Development: Fostering regional integration, promoting trade, and attracting foreign investment to boost economic growth.
- Human Rights and Democracy: Upholding human rights, promoting democracy, and good governance, ensuring the rule of law and equal opportunities for all citizens.
- Social Development: Addressing social issues such as poverty, hunger, disease, and illiteracy, ensuring access to education, healthcare, and basic necessities.
Economic Benefits:
The AU map signifies the continent’s potential for economic growth and prosperity. By fostering regional integration, the AU aims to create a single market for goods and services, reducing trade barriers and facilitating cross-border trade. This has the potential to unlock new opportunities for businesses, stimulate investment, and create jobs. The AU also seeks to promote infrastructure development, connecting countries through roads, railways, and energy grids, thereby facilitating trade and economic activity.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its significant progress, the AU faces numerous challenges in realizing its vision. These include:
- Conflict and Instability: The continent continues to grapple with armed conflicts, political instability, and humanitarian crises, hindering development and progress.
- Poverty and Inequality: Poverty and inequality remain significant challenges, with a large portion of the population living in poverty and lacking access to basic services.
- Governance and Corruption: Weak governance, corruption, and lack of accountability undermine development efforts and erode public trust in institutions.
- Climate Change: The continent is highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including droughts, floods, and desertification, posing significant threats to food security, water resources, and human health.
The Importance of the AU Map:
The AU map symbolizes the aspirations and potential of the African continent. It represents a commitment to a shared destiny, a collective effort to overcome challenges and build a better future for all Africans. By fostering cooperation, promoting peace, and driving development, the AU aims to create a more prosperous, stable, and inclusive Africa.
FAQs
Q1: What is the purpose of the African Union map?
The AU map serves as a visual representation of the continent’s unity, outlining the geographical boundaries of its 54 member states. It embodies the organization’s vision of a united Africa working towards peace, security, and development.
Q2: What are the key objectives of the African Union?
The AU aims to promote peace, security, and stability; drive economic development and integration; uphold human rights and democracy; and ensure social development and progress for all Africans.
Q3: How does the AU map contribute to economic development?
The AU map facilitates regional integration, reducing trade barriers and promoting cross-border trade, thereby boosting economic growth and creating job opportunities. It also supports infrastructure development, connecting countries and facilitating trade and investment.
Q4: What are some of the challenges facing the African Union?
The AU faces challenges such as ongoing conflicts, poverty and inequality, weak governance, corruption, and the impacts of climate change, which hinder its progress towards achieving its objectives.
Q5: What is the future of the African Union?
The future of the AU depends on its ability to effectively address the challenges it faces, strengthen its institutions, and implement its programs. The organization’s success hinges on the commitment of its member states to working together and upholding the principles enshrined in its charter.
Tips for Understanding the AU Map:
- Explore the map’s historical context: Understanding the origins of the AU and the Pan-African movement provides valuable insights into the map’s significance.
- Focus on the political and economic dimensions: Analyze the map’s implications for regional integration, trade, and development, considering the challenges and opportunities it presents.
- Consider the map’s social and cultural aspects: Explore the diversity of cultures, languages, and traditions represented on the map, appreciating the continent’s rich heritage.
- Engage with the map’s symbolism: The AU map is more than just a geographical representation; it embodies the aspirations of a continent striving for unity, peace, and progress.
Conclusion
The African Union map is a powerful symbol of the continent’s aspirations and potential. It represents a vision of a united Africa, working together to overcome challenges and build a brighter future for all its people. While the journey towards achieving this vision is fraught with challenges, the AU’s commitment to peace, development, and unity offers hope for a more prosperous, stable, and inclusive Africa. By fostering cooperation, promoting good governance, and addressing the root causes of conflict, the AU can pave the way for a brighter future for the continent and its people.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting a New Africa: A Comprehensive Look at the African Union Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!