Navigating the Unseen Dangers: Understanding Yellowstone’s Geothermal Hazards
Related Articles: Navigating the Unseen Dangers: Understanding Yellowstone’s Geothermal Hazards
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Unseen Dangers: Understanding Yellowstone’s Geothermal Hazards. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Unseen Dangers: Understanding Yellowstone’s Geothermal Hazards
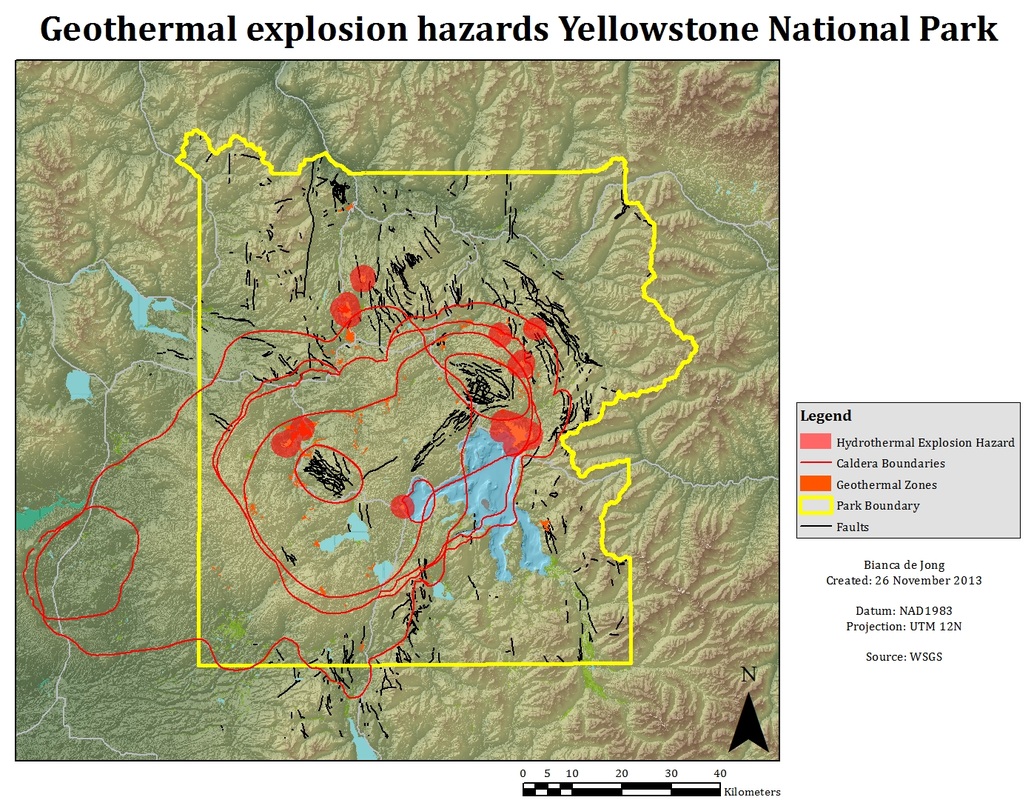
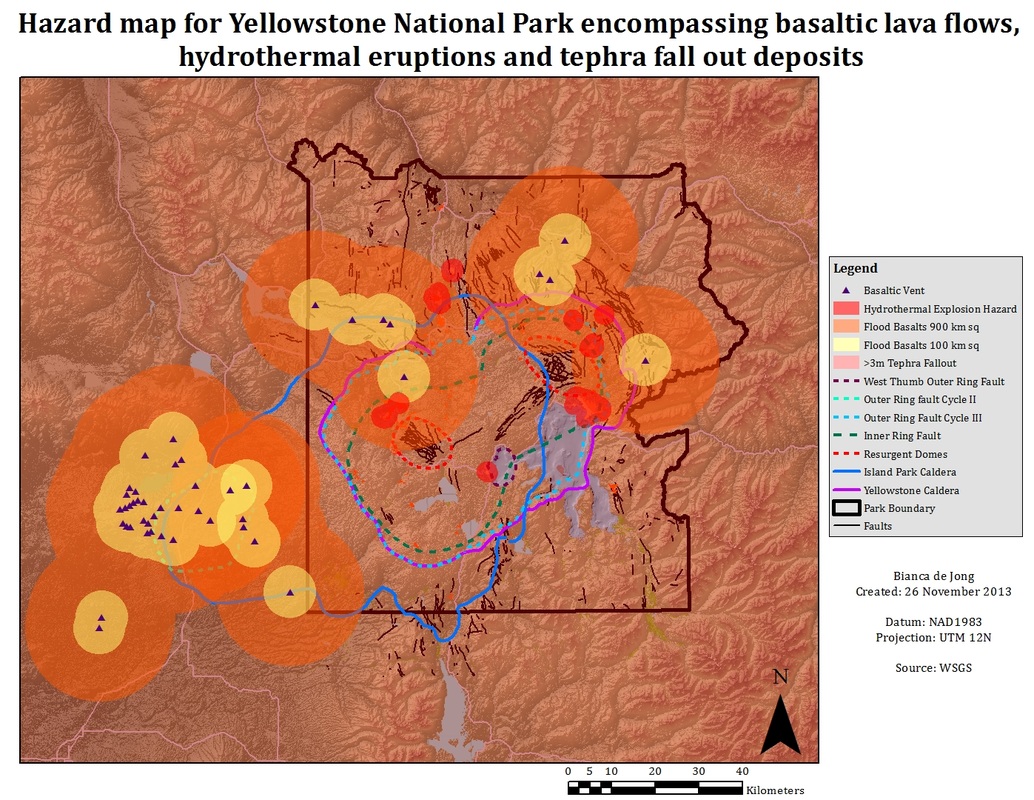
Yellowstone National Park, a breathtaking landscape of geysers, hot springs, and volcanic wonders, is also home to a hidden network of geothermal hazards. These hazards, while often concealed beneath the surface, pose a significant threat to visitors and researchers alike. Understanding the distribution of these hazards is crucial for ensuring the safety of park visitors and for managing the delicate ecological balance of the region.
The Concept of a "Death Zone"
The term "death zone" is a colloquial term used to describe areas within Yellowstone National Park where geothermal activity is particularly intense and potentially dangerous. It is important to note that this term is not an official designation used by park authorities. The concept of a "death zone" is often misinterpreted as a clearly defined area on a map, but the reality is more nuanced.
Geothermal activity in Yellowstone is dynamic and constantly evolving. Hot springs can shift, new vents can open, and ground temperatures can fluctuate. Therefore, the location and intensity of geothermal hazards are not fixed. Instead, the "death zone" encompasses a broad range of areas where the risk of severe injury or death from geothermal activity is significantly elevated.
Mapping Geothermal Hazards
To manage the risks associated with geothermal activity, park officials and researchers employ a variety of methods to map and monitor these hazards. These methods include:
- Ground-based surveys: Researchers use specialized instruments to measure ground temperatures, gas emissions, and soil composition. These measurements help identify areas with elevated geothermal activity.
- Remote sensing: Aerial and satellite imagery provide a broader perspective on the distribution of thermal features. This data is used to identify areas with altered vegetation or changes in soil composition, which can indicate the presence of geothermal activity.
- Geochemical analysis: Analyzing the composition of water and gases emitted from geothermal features provides insights into the underlying geological processes and the potential hazards associated with those features.
- Historical records: Studying historical accounts of accidents and injuries related to geothermal activity helps identify areas with a history of incidents.
The Importance of Understanding Geothermal Hazards
The information gathered from these mapping efforts is essential for:
- Visitor safety: Understanding the location and intensity of geothermal hazards allows park officials to implement safety measures, such as establishing designated trails, erecting warning signs, and providing educational materials.
- Resource management: By identifying areas with high geothermal activity, park officials can better manage the use of resources, such as water and energy, and protect sensitive ecosystems.
- Scientific research: Mapping geothermal hazards provides valuable data for scientists studying the complex geological processes that drive volcanic activity and geothermal energy.
Navigating the Landscape Safely
While the concept of a "death zone" can be a useful tool for understanding the potential risks, it is crucial to remember that geothermal activity is unpredictable and can manifest in various ways. To navigate the park safely, visitors should:
- Stay on designated trails: Trails are carefully planned to avoid areas with high geothermal activity.
- Respect warning signs: Warning signs are placed in areas with known geothermal hazards. Do not ignore these signs.
- Avoid areas with hot springs, geysers, and fumaroles: These features are often associated with elevated temperatures and toxic gases.
- Be aware of the potential for hidden hazards: Even areas that appear safe can have hidden geothermal features.
- Report any unusual observations: If you notice any changes in the landscape, such as new vents or altered vegetation, report them to park officials immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions about Yellowstone’s Geothermal Hazards
Q: Are there specific "death zones" marked on maps?
A: No, there are no officially designated "death zones" marked on maps. The concept of a "death zone" is a general term used to describe areas with a high risk of geothermal hazards.
Q: How can I identify areas with high geothermal activity?
A: Areas with high geothermal activity are often characterized by:
- Hot springs and geysers: These features release hot water and steam.
- Fumaroles: These vents release steam and gases.
- Mud pots: These bubbling pools of mud are formed by hot water interacting with soil.
- Altered vegetation: Geothermal activity can affect the growth of plants.
Q: What are the risks associated with geothermal activity?
A: The risks associated with geothermal activity include:
- Burns: Hot water and steam can cause severe burns.
- Asphyxiation: Gases released from geothermal features can be toxic.
- Falling rocks and debris: Geothermal activity can cause rocks and debris to fall.
- Earthquakes: Geothermal activity can trigger earthquakes.
Q: What should I do if I encounter a geothermal hazard?
A: If you encounter a geothermal hazard, you should:
- Stay calm and assess the situation.
- Move away from the hazard immediately.
- Report the incident to park officials.
Tips for Staying Safe in Yellowstone
- Plan your trip carefully: Research the areas you plan to visit and familiarize yourself with the potential risks.
- Check weather conditions: Geothermal activity can be amplified by weather events.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can increase the risk of heat exhaustion.
- Wear appropriate footwear: Sturdy shoes are essential for navigating uneven terrain.
- Bring a map and compass: This will help you stay oriented and avoid getting lost.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Pay attention to the landscape and any changes in the environment.
- Respect the environment: Do not disturb or alter any natural features.
Conclusion
While Yellowstone National Park is a breathtaking and awe-inspiring destination, it is important to remember that it is also a dynamic and unpredictable environment. Understanding the risks associated with geothermal activity is crucial for ensuring the safety of visitors and for preserving the park’s unique natural wonders. By following safety guidelines, visitors can enjoy their experience while minimizing the risk of injury or death.



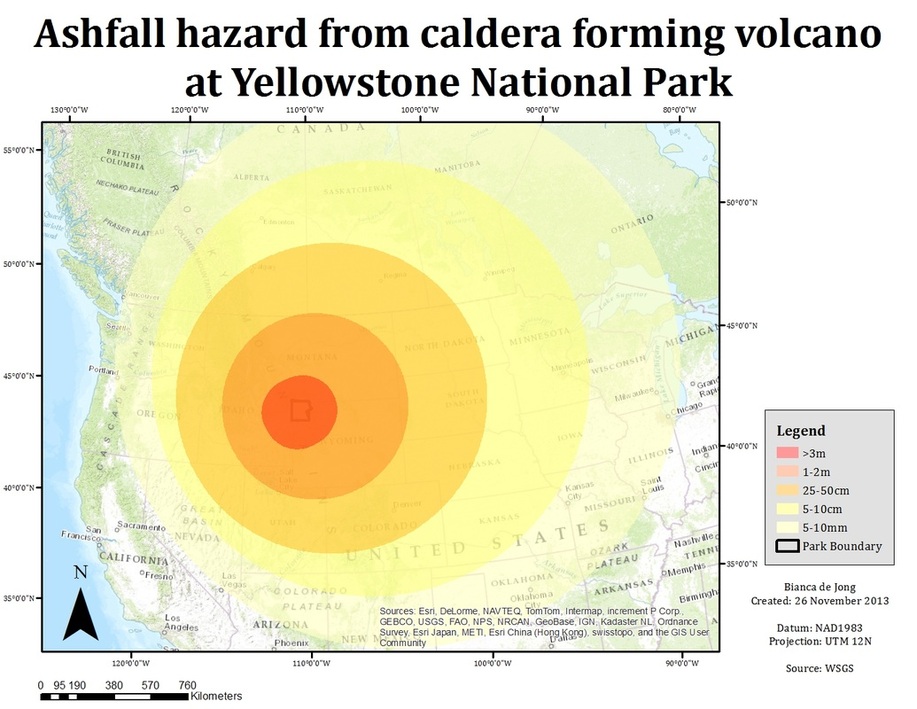
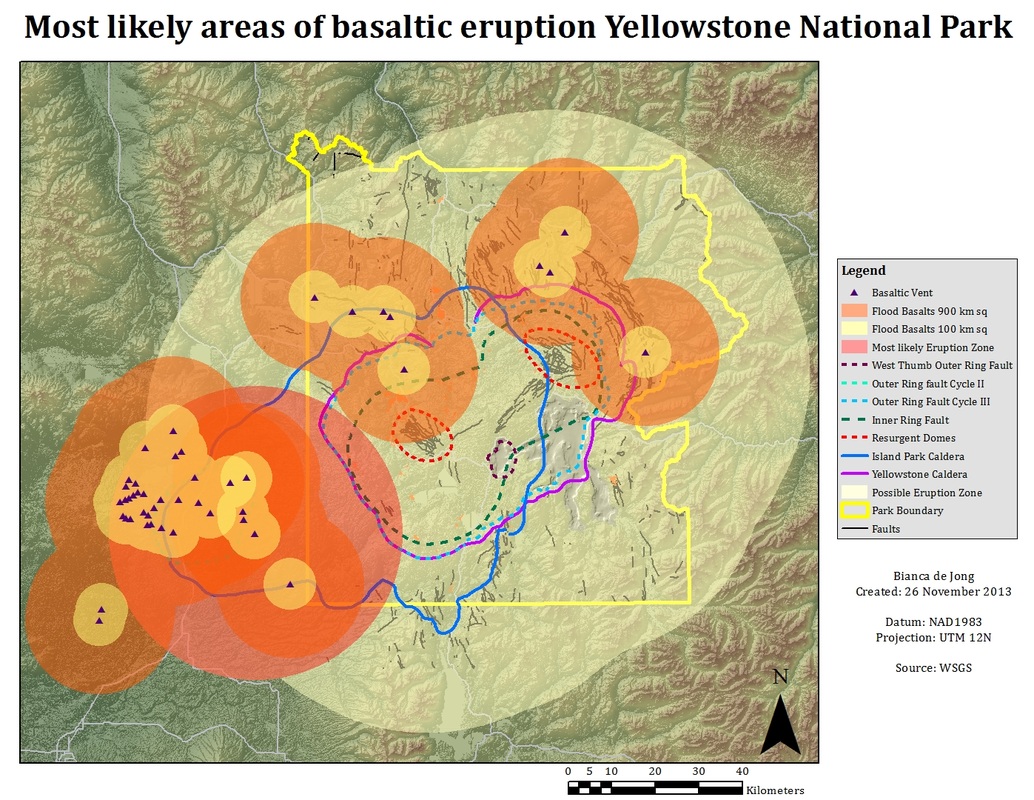

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Unseen Dangers: Understanding Yellowstone’s Geothermal Hazards. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!