Navigating the Waters of Green Bay: A Comprehensive Guide to the Lake’s Geography and Importance
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters of Green Bay: A Comprehensive Guide to the Lake’s Geography and Importance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters of Green Bay: A Comprehensive Guide to the Lake’s Geography and Importance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Waters of Green Bay: A Comprehensive Guide to the Lake’s Geography and Importance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Waters of Green Bay: A Comprehensive Guide to the Lake’s Geography and Importance
- 3.1 Delving into the Depths: A Geographic Overview
- 3.2 The Vital Role of Green Bay: A Multifaceted Importance
- 3.3 Navigating the Waters of Knowledge: FAQs about Green Bay
- 3.4 Charting a Course for the Future: Tips for Exploring Green Bay
- 3.5 Conclusion: A Legacy of Water, Life, and Culture
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Waters of Green Bay: A Comprehensive Guide to the Lake’s Geography and Importance
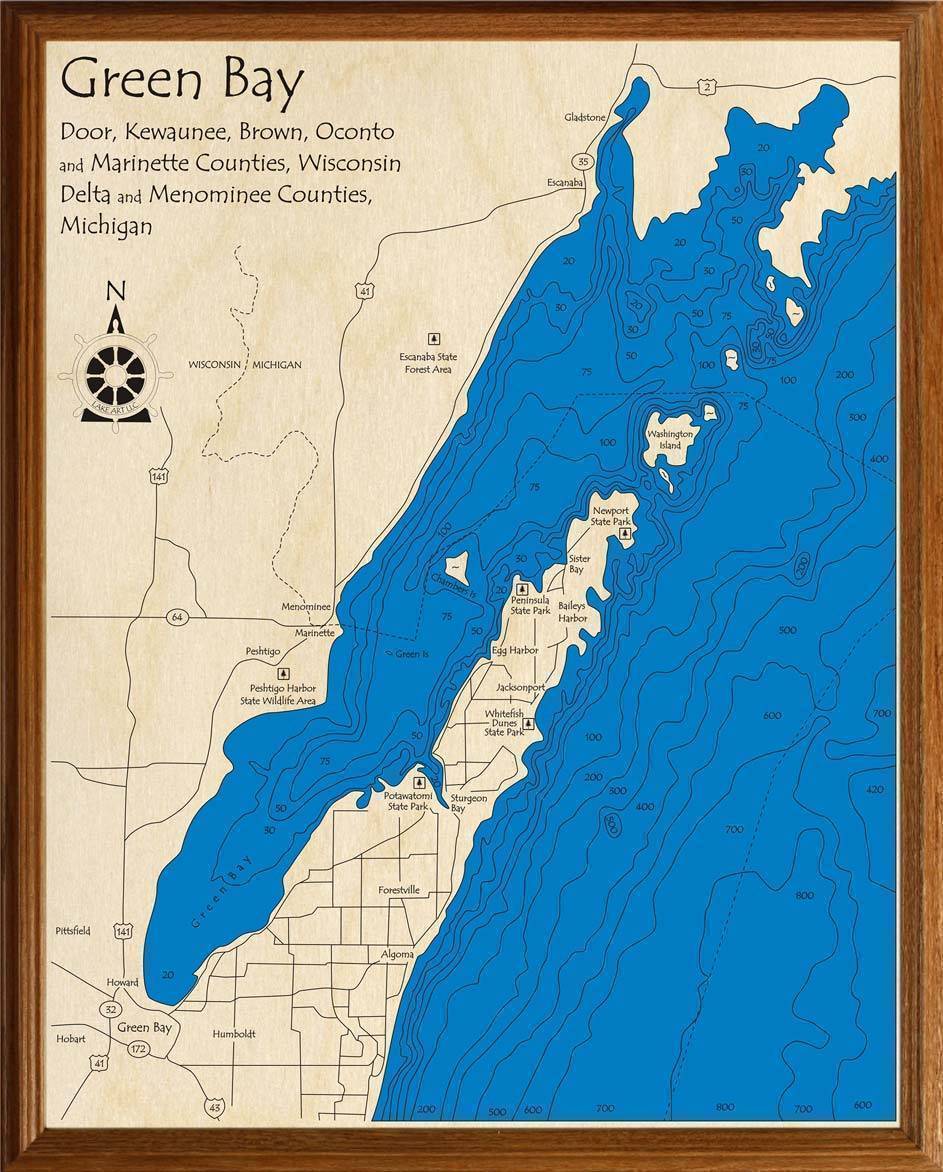
Green Bay, a prominent body of water within Lake Michigan, holds a unique place in the Great Lakes ecosystem. It is not simply a bay but a semi-enclosed body of water with its own distinct characteristics, influencing the surrounding region’s ecology, economy, and cultural identity. Understanding the geography of Green Bay through the lens of its map provides invaluable insights into its complexities and significance.
Delving into the Depths: A Geographic Overview
Green Bay’s map reveals a body of water approximately 115 miles long and 20 miles wide at its widest point. Its shape resembles a long, narrow finger extending south from Lake Michigan, creating a distinct geographic feature. The bay’s perimeter encompasses over 400 miles of coastline, encompassing the shores of Wisconsin and Michigan.
A Deeper Dive into the Bay’s Features:
- The Door Peninsula: This prominent landmass extends south from the northern tip of the bay, forming a natural barrier between Green Bay and Lake Michigan. The peninsula’s unique geography significantly influences water circulation and salinity levels within the bay.
- Fox River: This major tributary flows into Green Bay from the west, contributing significantly to the bay’s water volume and carrying sediment from the surrounding watershed.
- The Bay’s Islands: Numerous islands dot Green Bay, providing valuable habitat for various wildlife species and offering scenic beauty to the region.
- The Bay’s Depths: The water depth in Green Bay varies considerably, ranging from shallow areas near the shore to deeper regions exceeding 100 feet. This depth variation influences the bay’s ecosystem and supports diverse aquatic life.
The Vital Role of Green Bay: A Multifaceted Importance
Green Bay’s map not only depicts its physical characteristics but also highlights its crucial role in the region’s ecosystem, economy, and cultural identity.
Environmental Significance:
- Habitat for Diverse Species: Green Bay serves as a critical habitat for numerous fish species, including walleye, muskellunge, and whitefish. It also provides vital nesting grounds for migratory birds and supports a diverse population of aquatic plants and invertebrates.
- A Vital Link in the Great Lakes Ecosystem: Green Bay acts as a crucial link in the Great Lakes ecosystem, receiving water from Lake Michigan and influencing the water quality and circulation patterns within the entire system.
- Impact on Water Quality: The bay’s water quality is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including agricultural runoff, industrial discharge, and urban development. Monitoring the bay’s water quality is essential for protecting its ecosystem and ensuring the health of its inhabitants.
Economic Importance:
- Tourism and Recreation: Green Bay’s scenic beauty and recreational opportunities draw visitors from around the world, contributing significantly to the local economy.
- Commercial Fishing: The bay has a long history of commercial fishing, providing livelihoods for many residents and supplying seafood to regional and national markets.
- Shipping and Transportation: The bay serves as a vital waterway for shipping and transportation, connecting the region to the rest of the Great Lakes and beyond.
Cultural Significance:
- Native American Heritage: Green Bay holds significant cultural importance for numerous Native American tribes, who have inhabited the region for centuries. The bay’s rich history and cultural traditions are deeply intertwined with the lives of these indigenous communities.
- Regional Identity: Green Bay is a source of pride and identity for the surrounding communities, inspiring art, literature, and folklore that celebrate the bay’s beauty and significance.
Navigating the Waters of Knowledge: FAQs about Green Bay
1. What are the primary threats to Green Bay’s ecosystem?
Green Bay faces numerous threats, including agricultural runoff, industrial pollution, invasive species, and climate change. These factors can lead to water quality degradation, habitat loss, and disruptions to the bay’s delicate ecosystem.
2. How is Green Bay’s water quality monitored?
Various organizations, including government agencies and research institutions, monitor Green Bay’s water quality through regular sampling and analysis. These efforts provide valuable data to understand the bay’s health and identify potential issues.
3. What measures are being taken to protect Green Bay’s ecosystem?
Several initiatives are underway to protect Green Bay’s ecosystem, including efforts to reduce agricultural runoff, improve wastewater treatment, and control invasive species. Collaborative efforts between government agencies, research institutions, and local communities are crucial for the success of these initiatives.
4. What are the best ways to enjoy Green Bay’s recreational opportunities?
Green Bay offers a wide range of recreational activities, from fishing and boating to hiking and birdwatching. Exploring the bay’s numerous parks, beaches, and islands provides unique opportunities to experience its natural beauty and engage in outdoor activities.
5. How can individuals contribute to the protection of Green Bay?
Individuals can contribute to Green Bay’s protection by practicing sustainable land management practices, reducing their use of fertilizers and pesticides, supporting local initiatives focused on environmental conservation, and advocating for policies that prioritize the bay’s health.
Charting a Course for the Future: Tips for Exploring Green Bay
- Explore the Bay’s Islands: Visit the numerous islands within Green Bay, offering unique opportunities to observe wildlife, enjoy scenic views, and experience the bay’s natural beauty.
- Discover the Bay’s History: Explore the rich history of Green Bay by visiting museums, historical sites, and cultural centers that showcase the region’s past and its connection to the bay.
- Engage in Responsible Recreation: Practice responsible recreation by adhering to fishing regulations, disposing of waste properly, and minimizing disturbance to wildlife habitats.
- Support Local Conservation Efforts: Support organizations dedicated to protecting Green Bay’s ecosystem through donations, volunteering, and advocacy.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Learn about the importance of Green Bay’s ecosystem and share your knowledge with others to promote awareness and inspire action.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Water, Life, and Culture
The map of Green Bay serves as a visual testament to the interconnectedness of geography, ecology, and culture. It underscores the bay’s vital role in the Great Lakes ecosystem, its economic significance to the region, and its cultural importance to the surrounding communities. By understanding the complexities of Green Bay’s geography and appreciating its multifaceted importance, we can better navigate the waters of knowledge and foster a sustainable future for this vital resource.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters of Green Bay: A Comprehensive Guide to the Lake’s Geography and Importance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!