The Andes: A Mountainous Backbone Shaping South America
Related Articles: The Andes: A Mountainous Backbone Shaping South America
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Andes: A Mountainous Backbone Shaping South America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Andes: A Mountainous Backbone Shaping South America

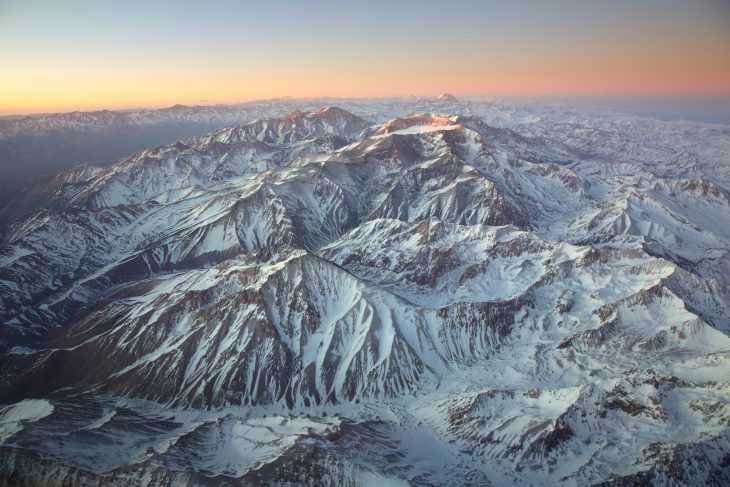
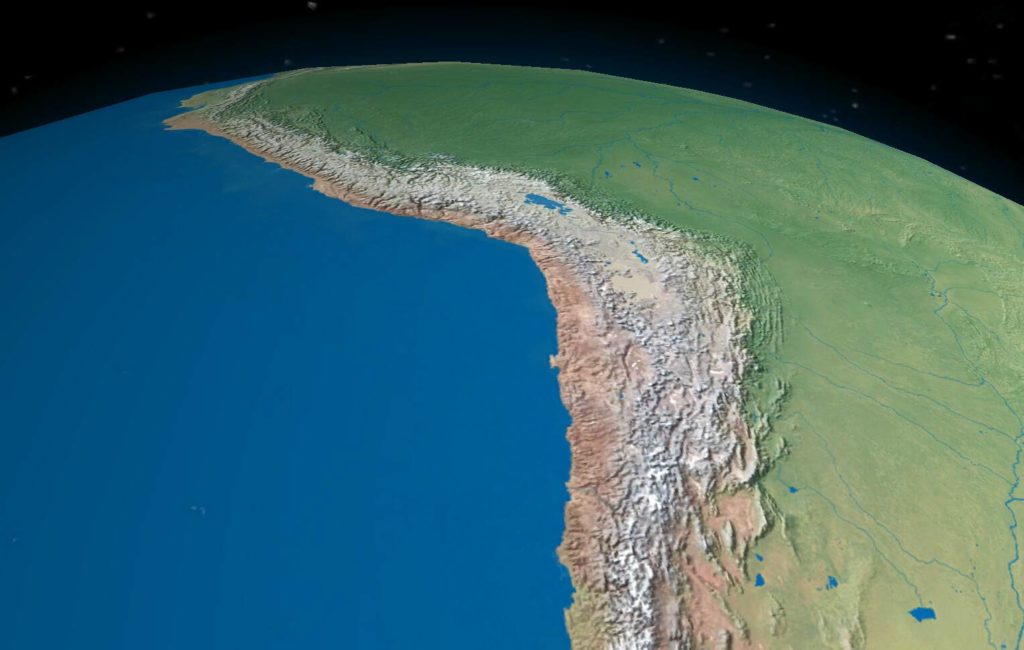
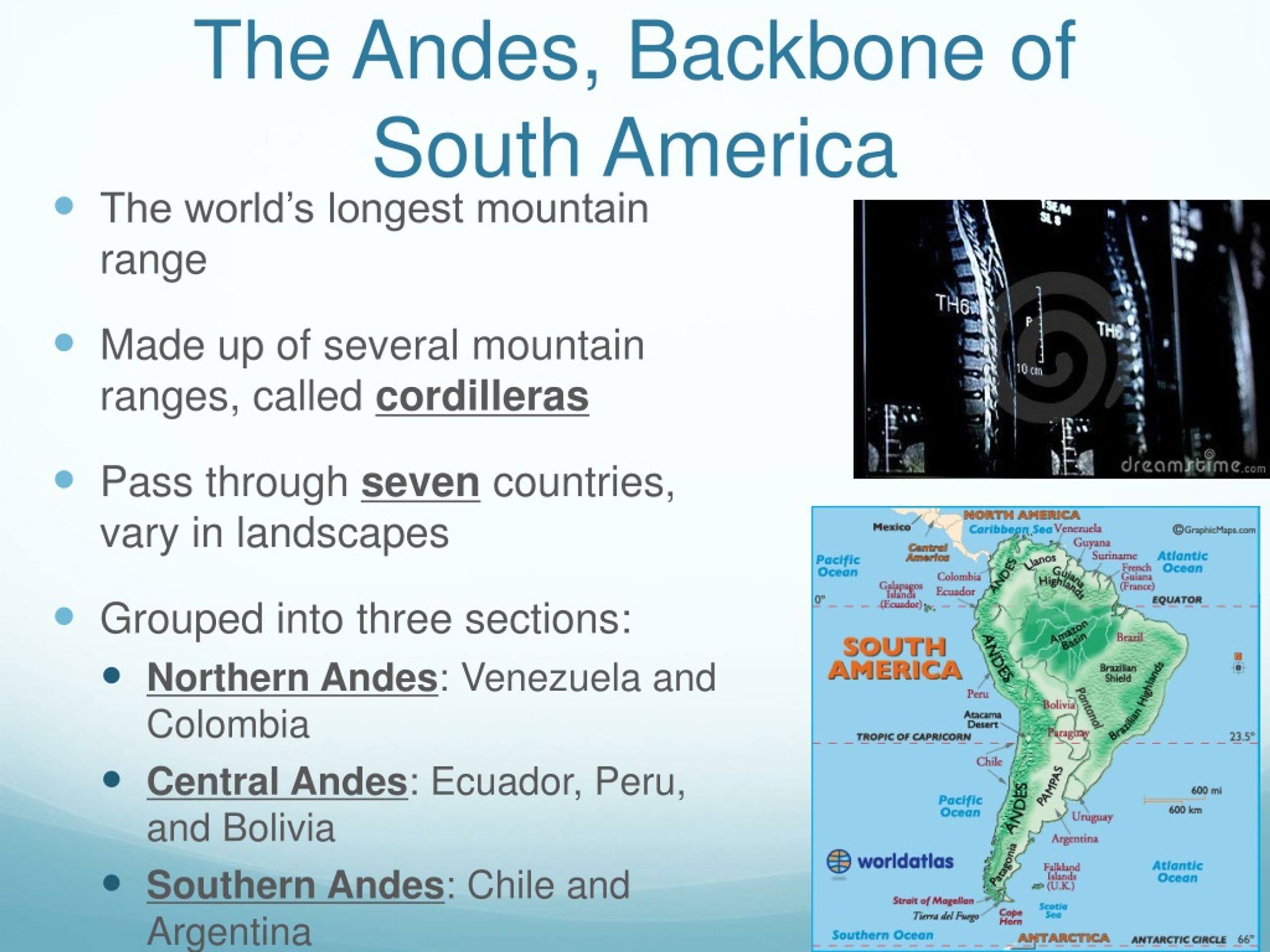
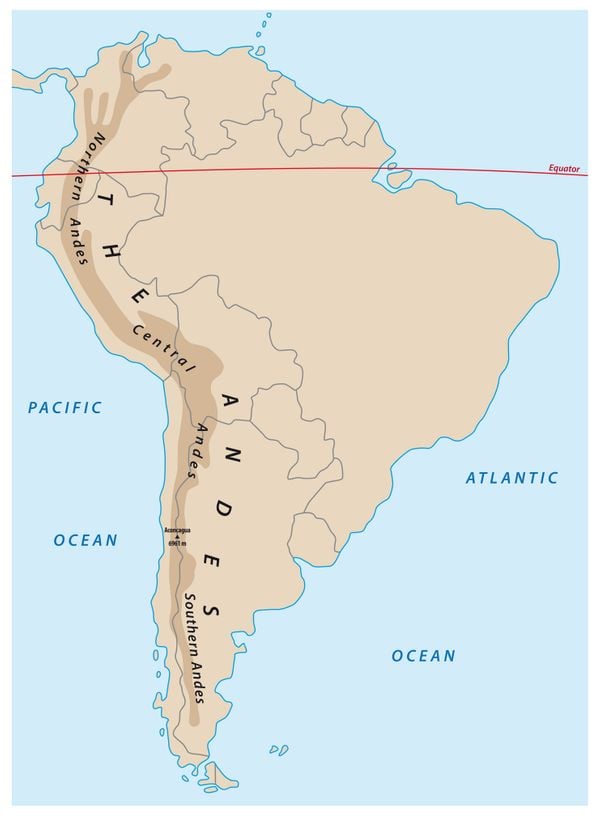
The Andes Mountains, a majestic chain of towering peaks, volcanoes, and glaciers, form the backbone of South America. Stretching over 7,000 kilometers (4,350 miles) from the northern tip of Venezuela to the southern tip of Chile, the Andes are the longest mountain range in the world. This colossal mountain system profoundly influences the geography, climate, and cultural landscapes of the continent, making it a subject of immense interest to geographers, geologists, and anyone seeking to understand the intricate tapestry of South America.
A Geological Marvel:
The Andes are a result of a complex interplay of tectonic forces. They were formed by the collision of the Nazca and South American tectonic plates, a process known as subduction. As the denser Nazca plate dives beneath the South American plate, it melts, generating magma that rises to the surface, creating volcanoes and ultimately shaping the towering peaks that define the Andes.
This ongoing geological activity makes the Andes a region of significant seismic and volcanic activity. The region experiences frequent earthquakes, and numerous active volcanoes dot the mountain range, reminding us of the dynamic forces shaping the earth’s surface.
A Diverse Landscape:
The Andes are not a uniform entity. The vast mountain range encompasses a remarkable diversity of landscapes, from snow-capped peaks to lush valleys, arid deserts to vibrant rainforests.
-
High Peaks and Glaciers: The Andes are home to some of the world’s highest peaks, including Aconcagua (6,961 meters or 22,838 feet) in Argentina, the highest peak outside of Asia. The mountains are also characterized by extensive glaciers, which play a crucial role in providing water to surrounding regions.
-
Valleys and Plateaus: The Andes are interspersed with valleys, some of which are fertile and support significant populations. The Altiplano, a high plateau located in Bolivia and Peru, is one of the most notable examples. This plateau is characterized by its high altitude, arid climate, and unique ecosystem.
-
Deserts and Rainforests: The Andes also feature contrasting climates, ranging from arid deserts like the Atacama Desert in Chile to lush rainforests in the Amazon Basin. This diversity is influenced by factors such as altitude, latitude, and proximity to the Pacific Ocean.
A Cradle of Cultures:
The Andes have been home to diverse indigenous cultures for millennia. The Inca Empire, with its impressive cities and sophisticated agricultural systems, flourished in the Andes region. The legacy of these ancient civilizations is still visible today in the region’s architecture, languages, and traditions.
The Andes continue to be a vibrant cultural landscape, with indigenous communities maintaining their distinct traditions and languages. The region also boasts a rich tapestry of modern cultures, influenced by European colonization and the blending of indigenous and European traditions.
The Importance of the Andes:
The Andes are not merely a geographical feature; they are a vital part of South America’s identity and well-being.
-
Water Resources: The Andes act as a water tower for the continent, providing water for millions of people. Glaciers in the Andes are a crucial source of water for irrigation, drinking water, and hydroelectric power generation.
-
Biodiversity: The Andes are home to a remarkable diversity of flora and fauna, including many endemic species found nowhere else in the world. The region is a biodiversity hotspot, with unique ecosystems ranging from high-altitude grasslands to cloud forests.
-
Tourism: The Andes are a major tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world who come to experience the region’s stunning landscapes, rich culture, and adventure opportunities.
-
Economic Importance: The Andes are also an important source of minerals, including copper, silver, and gold. Mining is a significant economic activity in the region, but it also raises concerns about environmental sustainability.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Andes face a number of challenges, including climate change, deforestation, and mining activities. These challenges threaten the region’s ecosystems, biodiversity, and the livelihoods of its people.
-
Climate Change: Climate change is impacting the Andes in significant ways, leading to glacier melt, changes in precipitation patterns, and increased risk of natural disasters such as landslides and floods.
-
Deforestation: Deforestation is a major problem in the Andes, driven by factors such as agriculture, logging, and mining. This loss of forest cover has negative consequences for biodiversity, water resources, and climate regulation.
-
Mining: Mining activities in the Andes can have significant environmental and social impacts. The extraction of minerals often involves the use of harmful chemicals, leading to pollution and land degradation.
Despite these challenges, the Andes also present significant opportunities for sustainable development.
-
Ecotourism: The region’s unique landscapes and biodiversity offer tremendous potential for ecotourism, which can generate economic benefits while protecting the environment.
-
Renewable Energy: The Andes have significant potential for renewable energy generation, particularly from hydropower and solar power.
-
Conservation Efforts: There are numerous conservation efforts underway in the Andes, aimed at protecting the region’s biodiversity, managing water resources, and promoting sustainable development.
Conclusion:
The Andes are a majestic and dynamic mountain range that plays a crucial role in the geography, climate, and culture of South America. They are a testament to the Earth’s geological forces, a cradle of ancient civilizations, and a vital source of water, biodiversity, and economic activity. Understanding the Andes is essential for appreciating the intricate tapestry of South America and for addressing the challenges and opportunities facing this vital region.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the Andes Mountains?
The Andes Mountains are the longest mountain range in the world, stretching over 7,000 kilometers (4,350 miles) along the western edge of South America. They are formed by the collision of the Nazca and South American tectonic plates.
2. How were the Andes formed?
The Andes were formed by the process of subduction, where the denser Nazca tectonic plate dives beneath the South American plate. This process generates magma that rises to the surface, creating volcanoes and ultimately shaping the towering peaks that define the Andes.
3. What is the highest peak in the Andes?
The highest peak in the Andes is Aconcagua, located in Argentina, which reaches a height of 6,961 meters (22,838 feet).
4. What are some of the unique features of the Andes?
The Andes are characterized by a wide range of features, including:
- High peaks and glaciers: The Andes are home to some of the world’s highest peaks and extensive glaciers.
- Valleys and plateaus: The Andes are interspersed with valleys and plateaus, including the Altiplano, a high plateau located in Bolivia and Peru.
- Deserts and rainforests: The Andes feature contrasting climates, ranging from arid deserts to lush rainforests.
5. What is the cultural significance of the Andes?
The Andes have been home to diverse indigenous cultures for millennia. The Inca Empire, with its impressive cities and sophisticated agricultural systems, flourished in the Andes region. The legacy of these ancient civilizations is still visible today in the region’s architecture, languages, and traditions.
6. Why are the Andes important?
The Andes are vital to South America’s identity and well-being. They provide:
- Water resources: The Andes act as a water tower for the continent, providing water for millions of people.
- Biodiversity: The Andes are home to a remarkable diversity of flora and fauna, including many endemic species.
- Tourism: The Andes are a major tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world.
- Economic importance: The Andes are an important source of minerals, including copper, silver, and gold.
7. What are some of the challenges facing the Andes?
The Andes face a number of challenges, including:
- Climate change: Climate change is impacting the Andes in significant ways, leading to glacier melt, changes in precipitation patterns, and increased risk of natural disasters.
- Deforestation: Deforestation is a major problem in the Andes, driven by factors such as agriculture, logging, and mining.
- Mining: Mining activities in the Andes can have significant environmental and social impacts.
8. What are some of the opportunities for sustainable development in the Andes?
The Andes present significant opportunities for sustainable development, including:
- Ecotourism: The region’s unique landscapes and biodiversity offer tremendous potential for ecotourism.
- Renewable energy: The Andes have significant potential for renewable energy generation, particularly from hydropower and solar power.
- Conservation efforts: There are numerous conservation efforts underway in the Andes, aimed at protecting the region’s biodiversity, managing water resources, and promoting sustainable development.
Tips for Exploring the Andes
- Plan your trip carefully: The Andes are a vast and diverse region, so it’s important to plan your trip carefully, taking into account your interests, budget, and time constraints.
- Choose the right season: The best time to visit the Andes depends on your interests and the specific region you plan to visit. Some areas are best visited during the dry season, while others are more enjoyable during the wet season.
- Respect local cultures: The Andes are home to diverse indigenous cultures, so it’s important to respect local customs and traditions.
- Be prepared for altitude: The Andes are a high-altitude region, so it’s important to acclimatize gradually and be aware of the potential effects of altitude sickness.
- Pack appropriately: The weather in the Andes can be unpredictable, so it’s important to pack for a range of conditions, including cold, wet, and sunny weather.
- Be environmentally conscious: The Andes are a fragile ecosystem, so it’s important to be environmentally conscious and minimize your impact on the environment.
- Consider a guided tour: A guided tour can help you make the most of your trip and learn more about the region’s history, culture, and natural wonders.
Conclusion
The Andes Mountains are a testament to the Earth’s geological forces and the resilience of human civilizations. They are a vital part of South America’s identity and well-being, offering stunning landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and opportunities for sustainable development. As we continue to explore and learn from this majestic mountain range, we can appreciate its profound influence on the continent and work towards its responsible stewardship for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Andes: A Mountainous Backbone Shaping South America. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!