The Crucial Role of the GM 4-Bar MAP Sensor in Engine Management
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of the GM 4-Bar MAP Sensor in Engine Management
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of the GM 4-Bar MAP Sensor in Engine Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Role of the GM 4-Bar MAP Sensor in Engine Management

The automotive landscape is a complex tapestry of intricate systems working in unison to deliver power and efficiency. Among these systems, the engine management system plays a vital role, orchestrating the delicate balance of fuel and air to ensure optimal combustion. At the heart of this system lies a critical sensor: the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor. In General Motors vehicles, a specific type of MAP sensor, known as the 4-bar MAP sensor, plays a crucial role in determining engine load and influencing fuel delivery, ignition timing, and other critical engine parameters.
Understanding the Function of the 4-Bar MAP Sensor
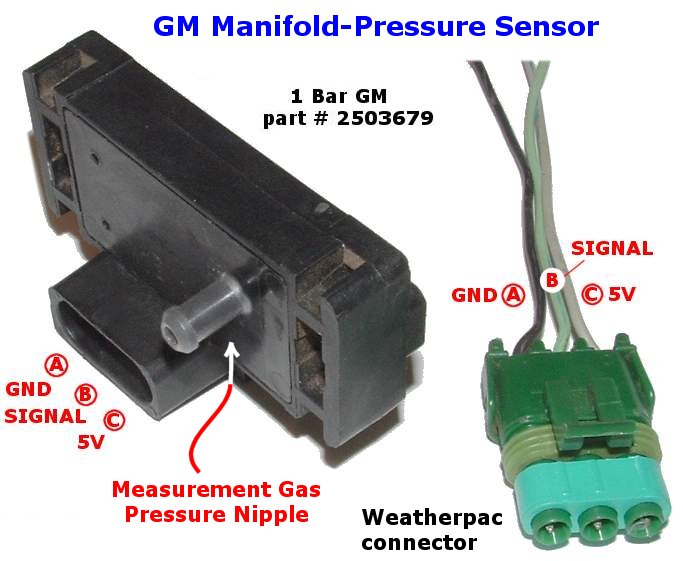
The 4-bar MAP sensor is a vital component in modern automotive engines. It acts as a transducer, converting pressure variations within the intake manifold into an electrical signal that the engine control module (ECM) can interpret. This signal provides the ECM with real-time information about the amount of air entering the engine, a crucial parameter for determining engine load.
How the 4-Bar MAP Sensor Works
The 4-bar MAP sensor operates on the principle of piezoresistive technology. It consists of a silicon diaphragm with a thin layer of piezoresistive material. When pressure changes within the intake manifold, the diaphragm deflects, altering the resistance of the piezoresistive material. This change in resistance is translated into an electrical signal that is proportional to the pressure difference.
Significance of the 4-Bar MAP Sensor in Engine Management
The 4-bar MAP sensor plays a pivotal role in several aspects of engine management:
- Fuel Delivery: The ECM uses the pressure readings from the 4-bar MAP sensor to calculate the amount of fuel required for optimal combustion. By accurately determining engine load, the ECM can adjust fuel injection timing and duration, ensuring a precise fuel-air mixture for efficient combustion.
- Ignition Timing: The MAP sensor data also influences ignition timing. The ECM uses the pressure readings to optimize spark advance, ensuring optimal combustion and reducing emissions.
- Engine Performance: The 4-bar MAP sensor contributes significantly to overall engine performance. By providing accurate information about engine load, the ECM can fine-tune fuel delivery and ignition timing, resulting in improved fuel efficiency, smoother engine operation, and increased power output.
- Emissions Control: The 4-bar MAP sensor plays a crucial role in emissions control. By ensuring precise fuel-air mixtures, the sensor helps reduce harmful emissions such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and oxides of nitrogen.
Common Issues Associated with the 4-Bar MAP Sensor
Like any electronic component, the 4-bar MAP sensor can experience malfunctions. Common problems include:
- Vacuum Leaks: A vacuum leak in the intake manifold can lead to inaccurate pressure readings, affecting engine performance and fuel economy.
- Sensor Failure: The sensor itself can fail due to age, wear, or environmental factors. This can result in erratic engine operation, poor fuel economy, and increased emissions.
- Electrical Problems: Issues with the sensor’s wiring or connection to the ECM can also cause malfunctions.
Symptoms of a Faulty 4-Bar MAP Sensor
Several symptoms can indicate a faulty 4-bar MAP sensor:
- Rough Idle: The engine may idle erratically or stall, especially at low engine speeds.
- Hesitation or Stalling: The engine may hesitate or stall during acceleration.
- Poor Fuel Economy: The vehicle may experience a decrease in fuel efficiency.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light may illuminate, accompanied by a corresponding diagnostic trouble code (DTC) related to the MAP sensor.
- Increased Emissions: The engine may produce excessive emissions, leading to a failure in emissions tests.
Diagnosing and Replacing a Faulty 4-Bar MAP Sensor
If you suspect a faulty 4-bar MAP sensor, it’s crucial to diagnose the issue accurately before attempting any repairs. A qualified mechanic can use a scan tool to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes and perform a thorough inspection of the sensor and its associated wiring.
Replacing a faulty 4-bar MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward process. However, it’s essential to use a genuine OEM part or a high-quality aftermarket replacement to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
FAQs about the GM 4-Bar MAP Sensor
Q: What are the common causes of a faulty 4-bar MAP sensor?
A: Common causes include age, wear, exposure to extreme temperatures, contamination, electrical problems, and vacuum leaks.
Q: How can I test a 4-bar MAP sensor?
A: A qualified mechanic can use a scan tool to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes and perform a pressure test to assess the sensor’s functionality.
Q: Can I replace a 4-bar MAP sensor myself?
A: While replacing a 4-bar MAP sensor is relatively simple, it’s recommended to have a qualified mechanic perform the replacement to ensure proper installation and avoid potential complications.
Q: What are the signs of a faulty 4-bar MAP sensor?
A: Common signs include rough idling, hesitation or stalling during acceleration, poor fuel economy, check engine light illumination, and increased emissions.
Q: How often should I replace my 4-bar MAP sensor?
A: There is no set timeframe for replacing a 4-bar MAP sensor. It’s recommended to replace it if it fails or shows signs of wear and tear.
Tips for Maintaining the 4-Bar MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Regular vehicle maintenance, including oil changes and air filter replacements, can help prevent contamination and extend the lifespan of the sensor.
- Avoid Excessive Engine Revving: Excessive engine revving can create excessive pressure fluctuations, potentially stressing the sensor.
- Inspect for Vacuum Leaks: Regularly inspect the intake manifold and associated hoses for any signs of leaks that could affect sensor accuracy.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing the sensor, use a genuine OEM part or a high-quality aftermarket replacement to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
The GM 4-bar MAP sensor is a critical component in modern automotive engine management systems. Its accurate readings play a pivotal role in optimizing fuel delivery, ignition timing, and overall engine performance. By understanding the function, importance, and potential issues associated with this sensor, drivers can ensure their vehicle operates efficiently, reliably, and with reduced emissions. Regular maintenance, prompt diagnosis of any issues, and the use of quality replacement parts are key to maintaining the optimal functionality of the 4-bar MAP sensor and ensuring a smooth and efficient driving experience.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of the GM 4-Bar MAP Sensor in Engine Management. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!