The Ever-Evolving Canvas: Understanding the World Map Through Time
Related Articles: The Ever-Evolving Canvas: Understanding the World Map Through Time
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Ever-Evolving Canvas: Understanding the World Map Through Time. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ever-Evolving Canvas: Understanding the World Map Through Time

The world map, a seemingly static image, is in reality a dynamic representation of our planet’s ever-shifting political, social, and geographical landscape. It is a powerful tool for understanding history, current events, and the interconnectedness of our world. Each year, subtle or dramatic changes occur, altering the map’s contours and influencing our perception of the globe.
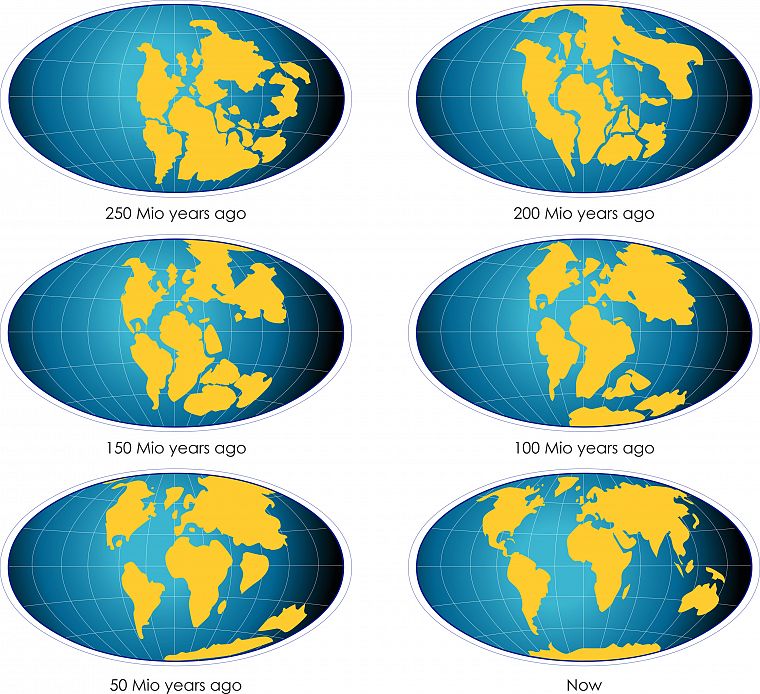
Tracing the Evolution of the World Map
To grasp the significance of the annual changes on the world map, it is essential to understand its historical evolution. The first known world maps were rudimentary, often based on mythical accounts and limited exploration. As maritime voyages and scientific advancements progressed, the map’s accuracy improved, reflecting a growing understanding of the Earth’s shape and geography.
The Impact of Political Shifts
The most visible changes on the world map are often triggered by political events. The collapse of empires, the rise of new nations, border disputes, and territorial acquisitions all leave their mark on the global landscape.
- The Fall of Empires: The disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991 resulted in the formation of 15 new independent nations, redrawing the political map of Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
- The Birth of New Nations: The independence of South Sudan in 2011, the culmination of a long struggle for self-determination, added a new country to the world map.
- Border Disputes: Ongoing territorial disputes, such as those between India and China in the Himalayas, are reflected in the map as areas of contention and potential instability.
- Territorial Acquisitions: The annexation of Crimea by Russia in 2014 sparked international controversy and altered the political map of Eastern Europe.
The Influence of Social and Cultural Transformations
Beyond politics, social and cultural shifts also leave their imprint on the world map. The rise of globalization, migration patterns, and cultural exchange influence the map’s representation of human activity and interconnectedness.
- Globalization: The increasing interconnectedness of the world through trade, communication, and travel is evident in the map’s emphasis on global networks and transportation routes.
- Migration Patterns: The movement of people across borders, driven by economic opportunity, conflict, or climate change, is reflected in the map’s depiction of population density and distribution.
- Cultural Exchange: The spread of languages, religions, and cultural practices across the globe is reflected in the map’s representation of cultural diversity.
The Importance of the World Map in a Changing World
The world map serves as a vital tool for understanding the dynamics of our planet. It helps us:
- Visualize Global Interconnectedness: The map highlights the relationships between countries, continents, and regions, demonstrating the interconnectedness of our world.
- Analyze Political and Social Trends: By tracking changes over time, the map allows for the analysis of global trends, such as the rise of democracy, the growth of megacities, or the impact of climate change.
- Facilitate International Cooperation: The map fosters a shared understanding of the global landscape, facilitating communication and collaboration between nations.
- Educate and Inform: The world map serves as a powerful educational tool, fostering geographical literacy and promoting awareness of global issues.
FAQs: Understanding the World Map’s Dynamic Nature
Q: How often is the world map updated?
A: The world map is constantly evolving, with changes occurring on a daily, weekly, or yearly basis. Major updates are typically made in response to significant political events, such as the creation of new nations or the redrawing of borders.
Q: What are the most common types of changes on the world map?
A: The most frequent changes include:
- New countries: The formation of new nations, often through independence movements or the dissolution of existing states.
- Border adjustments: Changes in borders due to territorial acquisitions, disputes, or agreements between countries.
- Name changes: The renaming of countries, cities, or regions for political, cultural, or historical reasons.
- Geographic updates: Changes in physical features, such as the discovery of new islands or the alteration of coastlines due to climate change.
Q: Are there any standardized guidelines for updating the world map?
A: There is no single governing body that dictates how the world map should be updated. However, reputable mapmakers generally follow established principles of accuracy, objectivity, and clarity. They rely on official sources, such as the United Nations, national governments, and international organizations, to ensure the map’s reliability.
Q: How do technological advancements impact the world map?
A: Technological advancements, such as satellite imagery and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), have revolutionized mapmaking. These tools provide more accurate and detailed data, allowing for the creation of dynamic and interactive maps that can be updated in real-time.
Tips for Interpreting the World Map
- Consider the map’s projection: The shape of the world map is determined by its projection, which can influence the relative size and shape of countries. Understanding the projection used is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- Pay attention to the map’s scale: The scale of the map indicates the ratio between the map’s distance and the actual distance on the Earth’s surface. Maps with different scales can provide varying levels of detail.
- Analyze the map’s symbols and colors: The map’s symbols and colors convey information about population density, geographical features, political boundaries, or economic activity. Understanding these conventions is essential for interpreting the map’s data.
- Compare maps from different time periods: Comparing maps from different years can reveal historical trends, political shifts, or the impact of environmental changes.
Conclusion: The World Map as a Window to Our Planet
The world map is not just a static image; it is a dynamic and evolving representation of our planet’s complex and interconnected reality. By understanding the forces that shape the world map, we can gain valuable insights into the history, politics, and social dynamics of our world. The map serves as a vital tool for education, analysis, and collaboration, fostering a deeper understanding of our global community and the challenges we face together.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ever-Evolving Canvas: Understanding the World Map Through Time. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!