The Global Distribution of Wolves: A Map of Resilience and Survival
Related Articles: The Global Distribution of Wolves: A Map of Resilience and Survival
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Global Distribution of Wolves: A Map of Resilience and Survival. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Global Distribution of Wolves: A Map of Resilience and Survival
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Global Distribution of Wolves: A Map of Resilience and Survival
- 3.1 A Global Perspective: Understanding the Distribution of Wolves
- 3.2 Factors Influencing Wolf Distribution: A Complex Interplay
- 3.3 The Importance of Wolves in the Ecosystem: A Cornerstone of Biodiversity
- 3.4 Conservation Challenges and Opportunities: Protecting a Vital Species
- 3.5 FAQs about the Global Distribution of Wolves: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding the Global Distribution of Wolves: A Practical Guide
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Future of Wolves: A Call to Action
- 4 Closure
The Global Distribution of Wolves: A Map of Resilience and Survival
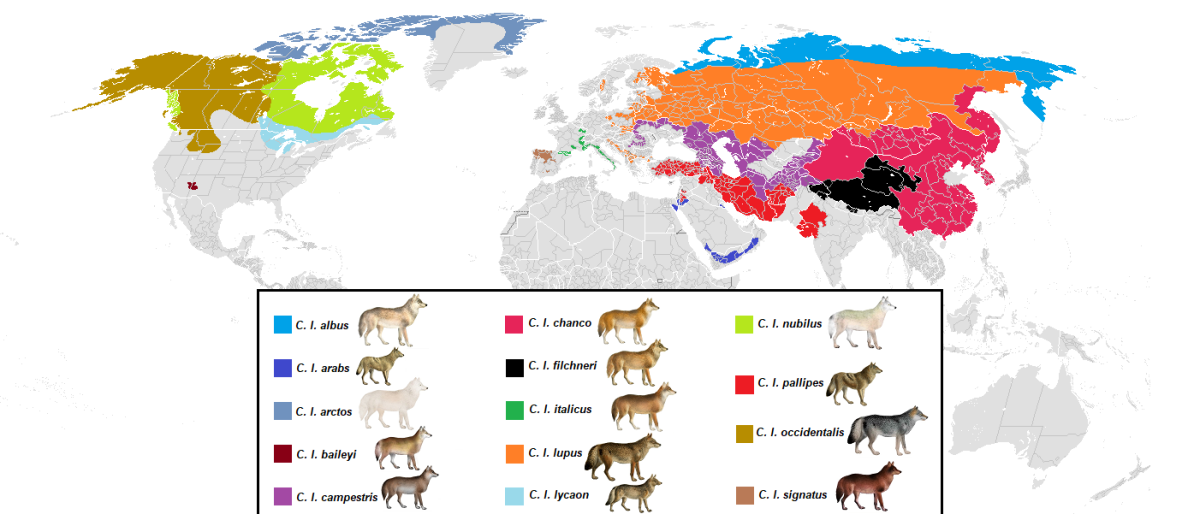
Wolves, apex predators with a rich history and enduring cultural significance, are found across a vast swathe of the globe. Their presence is a testament to the intricate web of life that sustains our planet, highlighting the importance of ecological balance and the interconnectedness of ecosystems. This article explores the current global distribution of wolves, delving into the factors that influence their presence and the significance of their role in the natural world.
A Global Perspective: Understanding the Distribution of Wolves
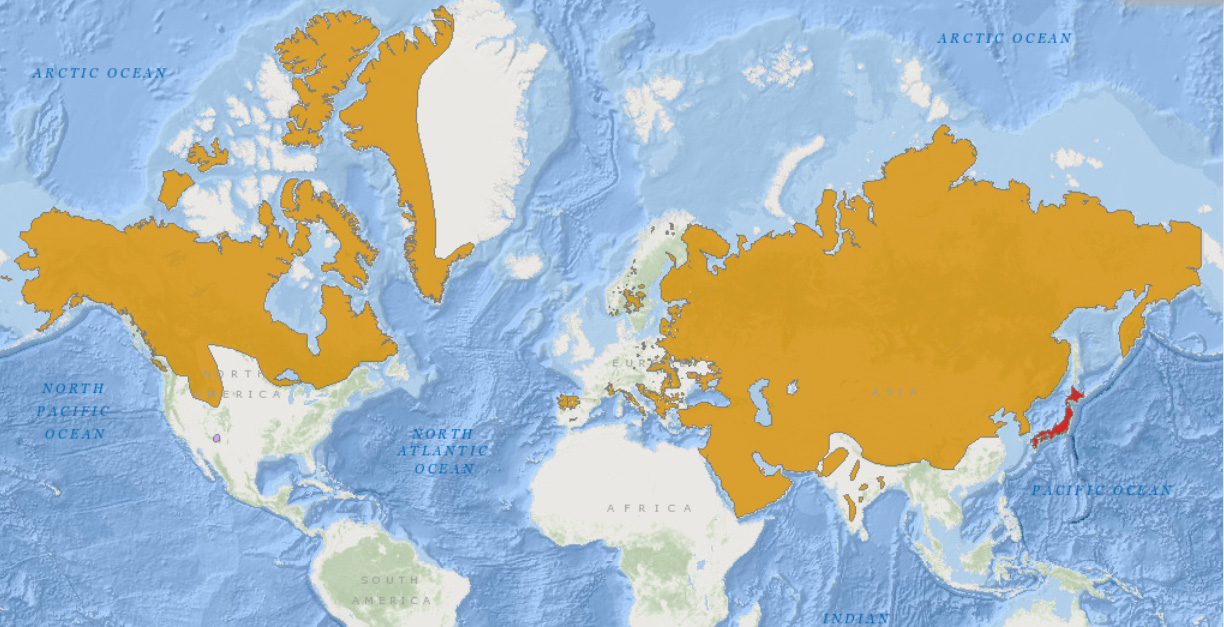
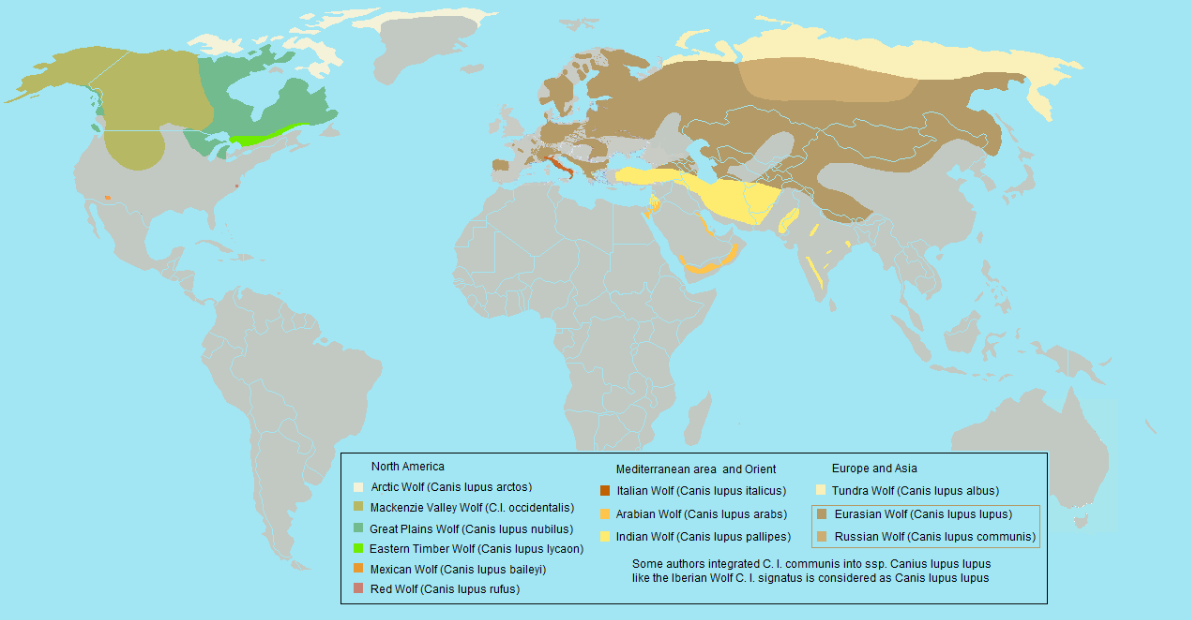
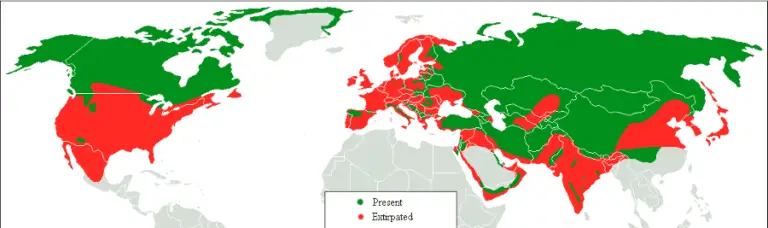
The world map of wolf distribution reveals a fascinating story of resilience and adaptation. While once inhabiting a far broader range, wolves have faced significant challenges due to human activity, including habitat loss, hunting, and persecution. Despite these pressures, they have persisted in diverse environments, from the frozen tundras of the Arctic to the temperate forests of Europe and the rugged mountains of Asia.
North America: The North American continent boasts a robust wolf population, with their range extending from Alaska and Canada to the northern United States. The iconic gray wolf, a symbol of wilderness and resilience, thrives in these vast landscapes. However, their presence in the contiguous United States is fragmented, with populations concentrated in the Rocky Mountains, the Great Lakes region, and the northern states.
Europe: Wolves are found in various parts of Europe, with populations concentrated in Eastern Europe, Scandinavia, and the Iberian Peninsula. The Carpathian Mountains, the Alps, and the Pyrenees serve as important refuges for these elusive predators. While wolf numbers have been steadily increasing in many European countries, they still face challenges from habitat fragmentation and human-wildlife conflict.
Asia: Asia holds a significant wolf population, with species like the Indian wolf, the Tibetan wolf, and the Mongolian wolf inhabiting diverse habitats. From the steppes of Central Asia to the Himalayan highlands, these wolves play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. However, their presence is threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and human encroachment.
Africa: Africa is home to the African wild dog, often mistaken for a wolf due to its similar appearance and social structure. However, true wolves are not native to the African continent.
Factors Influencing Wolf Distribution: A Complex Interplay
The distribution of wolves is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Habitat Availability: Wolves require vast, undisturbed landscapes with sufficient prey populations to sustain their needs. This includes areas with diverse vegetation, suitable denning sites, and ample water sources.
- Prey Availability: Wolves are highly adaptable predators, with their diets varying based on local prey availability. They primarily prey on large ungulates like deer, elk, moose, and caribou, but also consume smaller mammals, birds, and carrion.
- Human Impact: Human activities like habitat fragmentation, hunting, and persecution have significantly impacted wolf populations. Their presence in areas with high human density is often limited, leading to fragmented populations and increased vulnerability.
- Climate Change: Climate change poses a significant threat to wolves, altering their prey base, affecting habitat conditions, and potentially leading to range shifts.
The Importance of Wolves in the Ecosystem: A Cornerstone of Biodiversity
Wolves play a crucial role in maintaining the health and stability of their ecosystems. They are apex predators, meaning they occupy the top of the food chain, and their presence has a cascading effect on the populations of other species.
- Regulation of Prey Populations: Wolves help regulate prey populations, preventing overgrazing and maintaining the balance of vegetation. This, in turn, benefits other species that rely on these habitats.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: By influencing prey populations, wolves indirectly contribute to biodiversity. Their presence can lead to a greater diversity of plant and animal species, promoting a more resilient ecosystem.
- Ecosystem Health: Wolves are indicators of ecosystem health. Their presence signifies a healthy and balanced ecosystem, while their absence can signal environmental degradation or disruption.
Conservation Challenges and Opportunities: Protecting a Vital Species
Wolves face numerous challenges, including habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and climate change. These threats require concerted efforts to ensure their long-term survival.
- Habitat Conservation: Protecting and restoring wolf habitat is paramount to their survival. This includes creating wildlife corridors to connect fragmented populations, minimizing human encroachment, and promoting sustainable land management practices.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict Mitigation: Addressing human-wildlife conflict is crucial to ensure the coexistence of wolves and humans. This involves promoting livestock protection measures, educating communities about wolf behavior, and fostering responsible land use practices.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Addressing the impacts of climate change on wolf populations is essential. This includes monitoring the effects of climate change on prey populations, adapting management strategies to changing conditions, and promoting research on climate change adaptation.
FAQs about the Global Distribution of Wolves: Addressing Common Queries
Q: What is the current status of wolves globally?
A: While wolf populations have rebounded in some areas, they remain threatened globally. Factors like habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and climate change continue to pose challenges to their survival.
Q: Are wolves a threat to humans?
A: Wolves are generally wary of humans and avoid contact. Attacks on humans are extremely rare. However, it is important to respect their space and take necessary precautions when encountering them in the wild.
Q: Can wolves be domesticated?
A: Wolves are not domesticated animals. While some individuals may exhibit a higher degree of tolerance towards humans, they retain their wild instincts and are not suitable as pets.
Q: What is the role of wolves in mythology and folklore?
A: Wolves have played a significant role in mythology and folklore across cultures. They are often depicted as symbols of power, wisdom, and loyalty, but also as figures of fear and mystery.
Q: What can I do to help protect wolves?
A: You can support wolf conservation by supporting organizations dedicated to their protection, advocating for responsible land management practices, and educating others about the importance of wolves in the ecosystem.
Tips for Understanding the Global Distribution of Wolves: A Practical Guide
- Explore Online Resources: Websites like the International Wolf Center, the Wolf Conservation Center, and the IUCN Red List provide valuable information on wolf distribution, conservation efforts, and research findings.
- Consult Geographic Maps: Utilize online mapping tools like Google Maps to visualize wolf distribution across different regions and identify key areas of their presence.
- Engage with Conservation Organizations: Connect with local and international conservation organizations dedicated to wolf conservation. They can provide insights into ongoing projects, volunteer opportunities, and educational resources.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of current research and news related to wolf conservation. This will help you understand the challenges and opportunities facing these fascinating creatures.
Conclusion: The Future of Wolves: A Call to Action
The global distribution of wolves highlights their resilience and adaptability, but also underscores the challenges they face in a rapidly changing world. Their survival depends on our collective efforts to protect their habitats, mitigate human-wildlife conflict, and address the impacts of climate change. By understanding their importance in the ecosystem and taking action to ensure their future, we can contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the health of our planet.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Global Distribution of Wolves: A Map of Resilience and Survival. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!