The Iroquois Confederacy: A Map of Power and Resilience
Related Articles: The Iroquois Confederacy: A Map of Power and Resilience
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Iroquois Confederacy: A Map of Power and Resilience. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Iroquois Confederacy: A Map of Power and Resilience

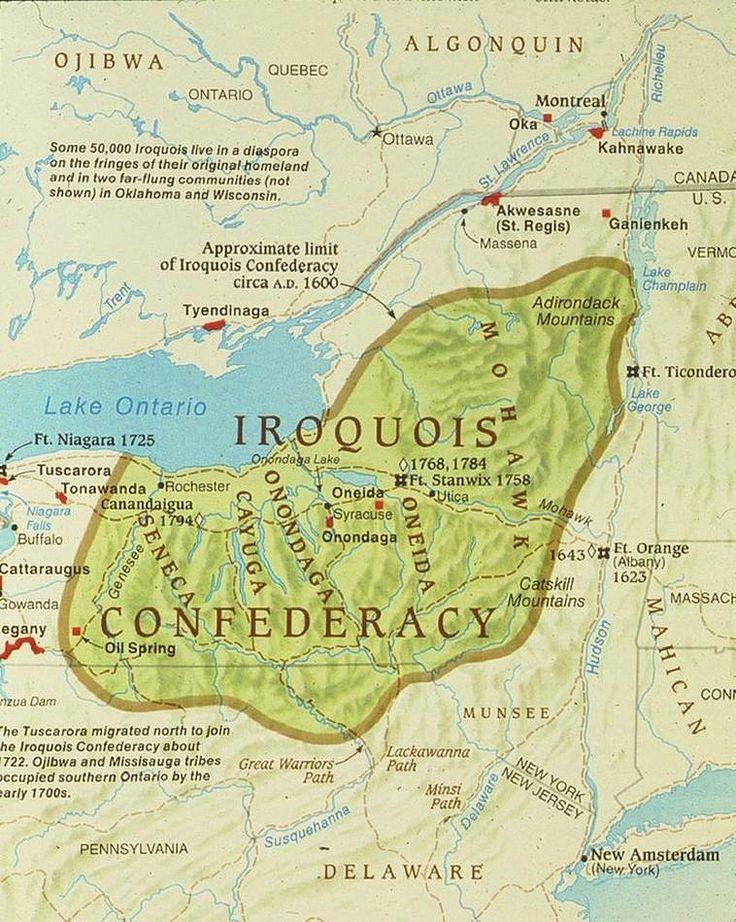
The Iroquois Confederacy, also known as the Haudenosaunee, stands as a testament to Indigenous resilience and political ingenuity. This powerful alliance of six distinct nations – the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca, and Tuscarora – held sway over a vast territory in what is now the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. Understanding the Iroquois territory map, its evolution, and its significance is crucial to comprehending the complex history of this region and the enduring legacy of the Haudenosaunee people.
A Shifting Landscape: Tracing the Iroquois Territory
The Iroquois territory map is not static; it reflects the dynamic history of the Haudenosaunee people, marked by alliances, conflicts, and shifts in political power.
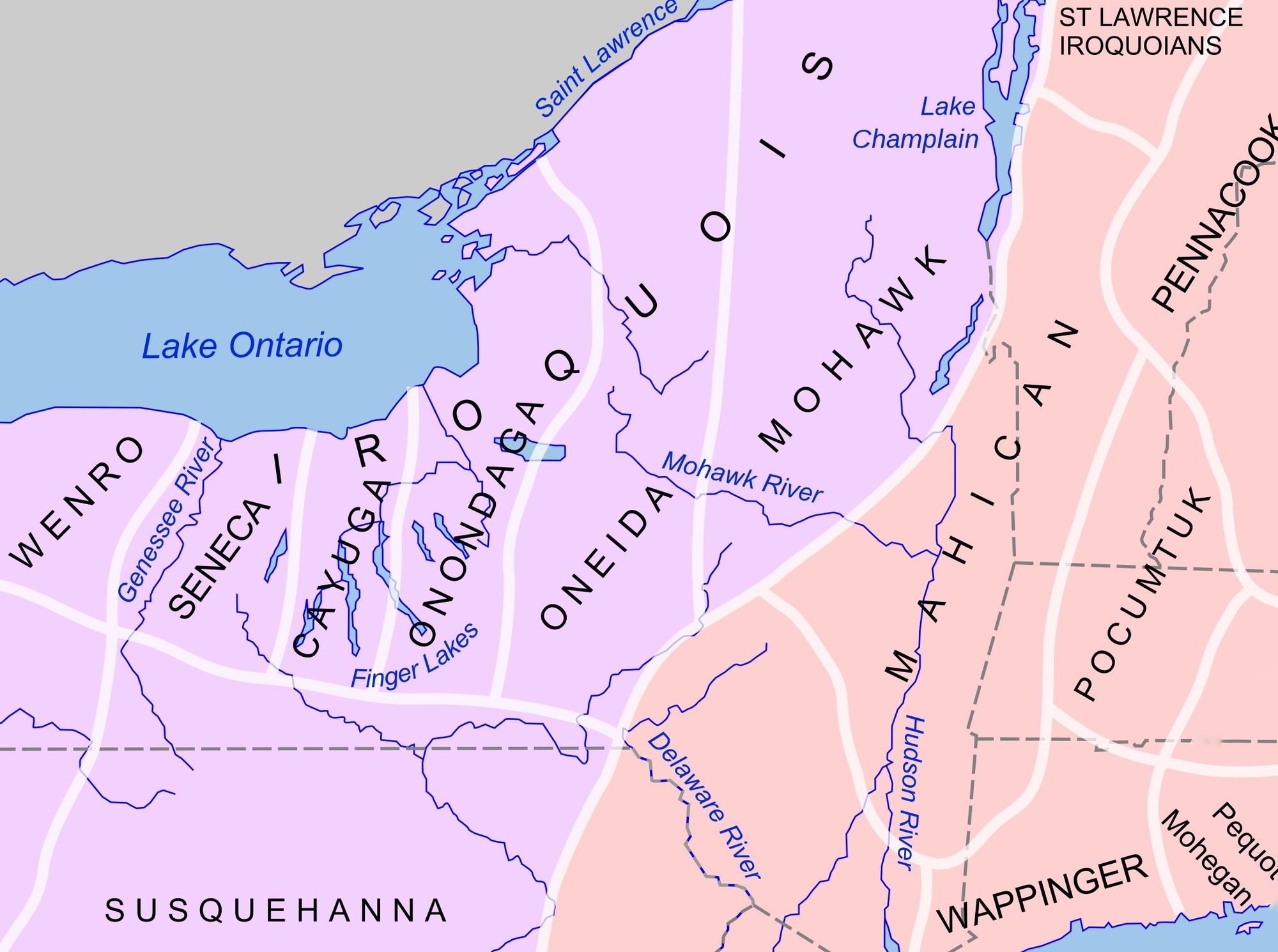
- Early Origins: The Iroquois Confederacy emerged around the 15th century, initially encompassing territories centered around the Finger Lakes region of New York State. The Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca nations formed the core of this alliance, with each nation maintaining its own sovereignty and governance.
- The Tuscarora Addition: In the early 18th century, the Tuscarora Nation, originally residing in North Carolina, joined the Confederacy after facing persecution and displacement. This addition expanded the Iroquois territory southward, extending the Confederacy’s influence and solidifying their position as a formidable force in the region.
- Colonial Expansion and Displacement: The arrival of European colonists in the 17th century brought significant changes to the Iroquois territory. European settlement, driven by land acquisition and resource extraction, encroached upon traditional Haudenosaunee lands. Treaties, often negotiated under duress, resulted in the cession of vast tracts of land, leading to a gradual reduction of the Iroquois territory.
- The Impact of the American Revolution: The American Revolution further impacted the Iroquois territory. The Haudenosaunee nations were divided in their allegiance, with some siding with the British and others with the Americans. The aftermath of the war saw the Iroquois territory further diminished, with the loss of land and the displacement of many Haudenosaunee people.
Beyond Borders: The Significance of the Iroquois Territory Map
The Iroquois territory map is more than a geographical representation; it embodies the Haudenosaunee people’s political prowess, their enduring cultural identity, and their resilience in the face of adversity.
- Political Innovation: The Iroquois Confederacy represented a unique and sophisticated form of governance, characterized by a system of checks and balances, a grand council, and a system of rotating leadership. The Iroquois Confederacy’s political structure served as a model for the American Founding Fathers, influencing the development of the U.S. Constitution.
- Cultural Identity: The Iroquois territory was not simply a geographical space; it was a tapestry of cultural practices, traditions, and beliefs. The Haudenosaunee people’s connection to their land was deeply intertwined with their cultural identity, and their territory served as a stage for their rich cultural expressions, including storytelling, ceremonies, and artistic traditions.
- Resilience and Adaptation: Despite the challenges they faced, including colonial encroachment and displacement, the Haudenosaunee people demonstrated remarkable resilience. They adapted to changing circumstances, preserving their cultural heritage and continuing to advocate for their rights and sovereignty.
The Iroquois Territory Map Today: A Legacy of Resistance
The Iroquois territory map today is a reminder of the Haudenosaunee people’s enduring legacy and their ongoing struggle for self-determination.
- Contemporary Haudenosaunee Territories: While the Iroquois territory has been significantly reduced over time, Haudenosaunee communities continue to reside in their ancestral lands, maintaining their cultural traditions and advocating for their sovereignty.
- Land Claims and Recognition: The Haudenosaunee people continue to assert their land claims and fight for recognition of their inherent rights. This struggle is rooted in their historical connection to their territory and their commitment to preserving their cultural heritage.
- The Iroquois Confederacy’s Enduring Influence: The Iroquois Confederacy’s legacy continues to inspire and inform contemporary movements for Indigenous rights and self-determination. The Haudenosaunee people’s story of resilience, political ingenuity, and cultural preservation offers valuable lessons for contemporary society.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Iroquois Territory
1. What are the major geographical features of the Iroquois territory?
The Iroquois territory encompasses a diverse range of landscapes, including the fertile valleys of the Mohawk River, the Finger Lakes region of New York State, and the Appalachian Mountains.
2. How did the Iroquois Confederacy manage its territory?
The Iroquois Confederacy employed a decentralized system of governance, with each nation maintaining its own internal affairs while working together on matters of common concern. The Grand Council, composed of representatives from each nation, served as the primary decision-making body.
3. How did the Iroquois Confederacy interact with other Indigenous nations?
The Iroquois Confederacy engaged in a complex web of alliances, trade partnerships, and rivalries with other Indigenous nations. They played a significant role in the regional power dynamics of the Northeast, often serving as mediators or engaging in conflict to secure their interests.
4. What were the major economic activities of the Iroquois people?
The Iroquois people practiced a mixed economy, relying on agriculture, hunting, fishing, and trade. They cultivated corn, beans, and squash, hunted deer and other game, and traded goods such as furs, tools, and crafts with other Indigenous nations and European colonists.
5. How did the Iroquois territory change after the American Revolution?
The American Revolution significantly altered the Iroquois territory, leading to the loss of land and the displacement of many Haudenosaunee people. The Treaty of Fort Stanwix in 1784 ceded a significant portion of Iroquois territory to the United States, further reducing their land holdings.
Tips for Understanding the Iroquois Territory Map
- Study historical maps: Examine historical maps of the Iroquois territory to trace its evolution over time.
- Consult primary sources: Explore historical accounts and documents written by Haudenosaunee people to gain firsthand insights into their experiences and perspectives.
- Engage with contemporary Haudenosaunee communities: Connect with contemporary Haudenosaunee communities to learn about their ongoing efforts to preserve their culture and advocate for their rights.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Strength and Resilience
The Iroquois territory map is a powerful symbol of the Haudenosaunee people’s history, culture, and resilience. It represents not only a geographical space but also a testament to their political ingenuity, their cultural richness, and their ongoing struggle for self-determination. Understanding the Iroquois territory map is essential to comprehending the complex history of the Northeast and the enduring legacy of the Haudenosaunee people. Their story serves as a reminder of the importance of Indigenous sovereignty, cultural preservation, and the ongoing fight for justice and recognition.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Iroquois Confederacy: A Map of Power and Resilience. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!