The Power of Mapping: Exploring the World through Cartography
Related Articles: The Power of Mapping: Exploring the World through Cartography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Mapping: Exploring the World through Cartography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Mapping: Exploring the World through Cartography

Maps, those intricate representations of our planet, have been instrumental in shaping human understanding and facilitating exploration for centuries. From ancient cave paintings to modern digital globes, mapping has evolved into a powerful tool, enabling us to navigate, analyze, and understand the world around us. This article delves into the multifaceted world of map publishing, examining its history, significance, and the profound impact it has on various fields.
A Brief History of Map Publishing
The genesis of map publishing can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Early maps, often etched on stone, clay tablets, or papyrus, served as rudimentary navigational aids and visual representations of known territories. The Egyptians, for instance, meticulously documented their vast empire through detailed maps, while ancient Greek cartographers like Ptolemy made significant contributions to the understanding of geography.
The invention of the printing press in the 15th century revolutionized map production. Mass printing allowed for the dissemination of maps to a wider audience, fostering exploration and scientific advancements. The Age of Exploration, fueled by the desire to map uncharted territories, witnessed a surge in map publishing, with explorers like Christopher Columbus and Ferdinand Magellan relying on maps to guide their voyages.
The Evolution of Map Publishing in the Digital Age
The 20th century ushered in a new era of map publishing, marked by the advent of aerial photography, satellite imagery, and computer technology. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) emerged as a powerful tool for creating and managing spatial data, revolutionizing the way maps are created and used.
Digital map publishing, with its ability to integrate data from diverse sources, has transformed the field. Online mapping platforms, such as Google Maps and OpenStreetMap, have become indispensable for navigation, travel planning, and location-based services. These platforms leverage real-time data, user contributions, and advanced algorithms to provide interactive and dynamic mapping experiences.
The Importance of Map Publishing: A Multifaceted Impact
Map publishing plays a vital role in numerous fields, contributing to a wide range of activities and applications. Here are some key areas where mapping proves its significance:
-
Navigation and Transportation: Maps are essential for navigating our surroundings, be it on foot, by car, or by air. From road maps and GPS systems to online navigation apps, mapping technologies guide us through unfamiliar territories, optimize routes, and enhance our understanding of spatial relationships.
-
Urban Planning and Development: Mapping is indispensable for urban planning, enabling architects, planners, and engineers to analyze urban landscapes, identify infrastructure needs, and design sustainable urban environments. Maps are used to visualize population density, traffic flow, and resource allocation, facilitating informed decision-making in urban development.
-
Environmental Management and Conservation: Mapping plays a crucial role in environmental monitoring and conservation efforts. Geospatial data collected through satellite imagery, aerial photography, and ground-based surveys allows scientists to analyze deforestation rates, monitor biodiversity, and track climate change impacts. Maps are used to identify areas requiring conservation efforts, manage natural resources, and mitigate environmental risks.
-
Disaster Response and Emergency Management: In the aftermath of natural disasters or emergencies, maps are critical for coordinating relief efforts, providing information on affected areas, and facilitating the delivery of aid. Maps help emergency responders assess the situation, identify evacuation routes, and allocate resources effectively.
-
Education and Research: Maps are invaluable tools for education and research, fostering understanding of geography, history, and various scientific disciplines. By visualizing complex data and spatial relationships, maps enhance learning experiences, facilitate data analysis, and support research endeavors.
-
Business and Marketing: Map publishing is essential for businesses, enabling them to understand customer demographics, analyze market trends, and target specific audiences. Location-based marketing strategies, such as proximity targeting and geofencing, leverage mapping technologies to reach potential customers effectively.
FAQs on Map Publishing
Q: What are the different types of maps published?
A: Maps are diverse in their purpose and presentation. Common types include:
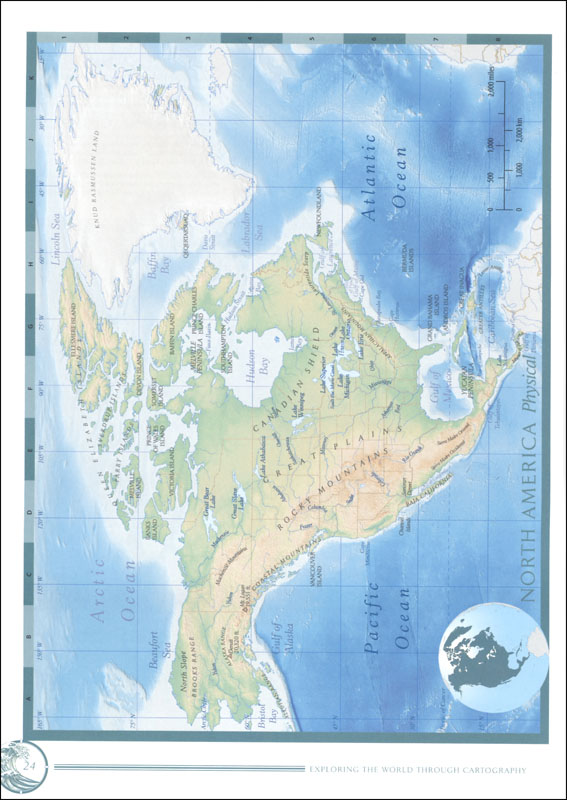
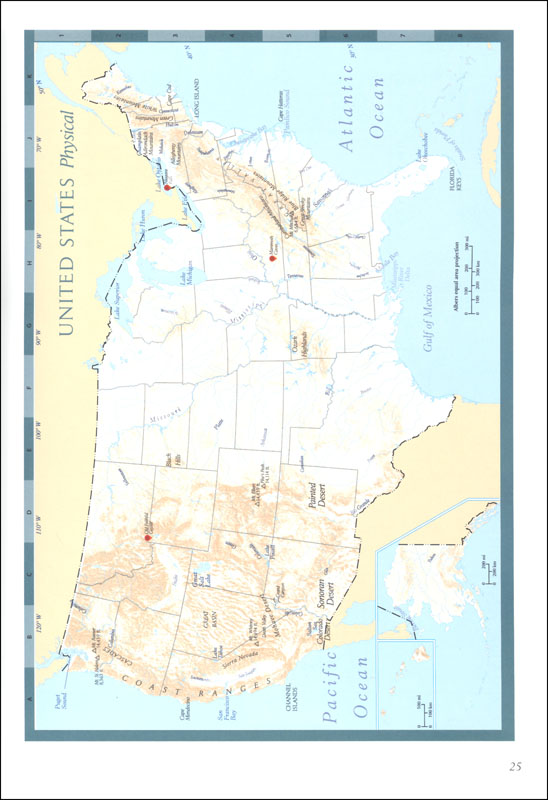
- Topographic maps: Depict terrain features, elevations, and physical landmarks.
- Road maps: Show roads, highways, and other transportation networks.
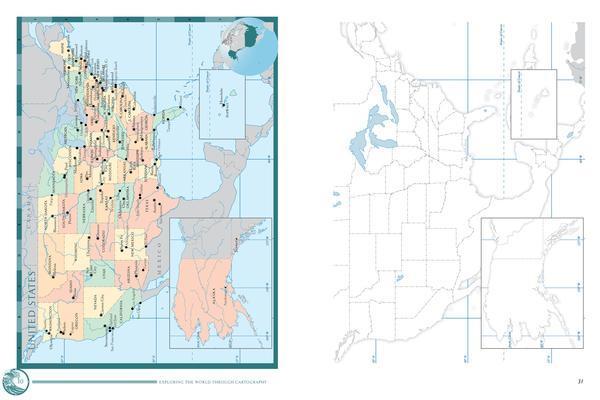
- Political maps: Highlight boundaries of countries, states, and other administrative divisions.
- Thematic maps: Illustrate specific themes, such as population density, climate patterns, or economic activity.
- Nautical charts: Designed for navigation at sea, providing information on depths, currents, and navigational hazards.
- Aerial maps: Created from aerial photographs, offering detailed views of landscapes.
Q: How are maps created and published?
A: The process of map creation and publication involves several stages:
- Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, ground surveys, and digital databases.
- Data Processing: Analyzing and transforming raw data into a format suitable for map production.
- Map Design: Creating a visual representation of the data, choosing appropriate symbols, colors, and projections.
- Map Production: Printing or digitally publishing the map, ensuring accuracy and clarity.
- Map Distribution: Making the map available to the public through various channels, such as online platforms, printed publications, or physical stores.
Q: What are the key elements of a good map?
A: A well-designed map should possess the following characteristics:
- Accuracy: The map should accurately represent the geographical features and data it portrays.
- Clarity: Clear and concise symbols, labels, and legends to convey information effectively.
- Relevance: The map should be tailored to its intended purpose, providing relevant information to the user.
- Aesthetics: Visually appealing and aesthetically pleasing design to enhance engagement and understanding.
Q: What are the future trends in map publishing?
A: The future of map publishing is characterized by:
- Increased integration with other technologies: Maps will be seamlessly integrated with other technologies, such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence.
- Real-time data and dynamic mapping: Maps will increasingly rely on real-time data, providing users with up-to-date information on traffic conditions, weather patterns, and other dynamic events.
- Personalization and customization: Users will have greater control over map content and presentation, enabling them to customize maps based on their specific needs and preferences.
- Data visualization and storytelling: Maps will play a more prominent role in data visualization, enabling users to explore and understand complex data sets through interactive and engaging visual narratives.
Tips for Effective Map Publishing
- Define your target audience: Identify the intended users of the map and tailor its content and design to their needs and understanding.
- Choose an appropriate projection: Select a map projection that minimizes distortion and accurately represents the geographical area of interest.
- Use clear and concise symbols and labels: Ensure that symbols and labels are easily recognizable and convey information effectively.
- Employ a visually appealing design: Use color, contrast, and typography to create a visually appealing and engaging map.
- Include a legend and scale: Provide a clear legend to explain symbols and a scale to indicate distances.
- Test your map: Thoroughly test the map for accuracy, clarity, and usability before publishing.
Conclusion: The Enduring Power of Maps
Maps, in their various forms, remain indispensable tools for navigating, understanding, and interacting with the world. From ancient cave paintings to digital globes, mapping has evolved into a powerful and versatile technology, impacting numerous fields and facilitating human progress. As technology continues to advance, map publishing will continue to evolve, offering new possibilities for exploration, analysis, and understanding our complex and ever-changing planet.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Mapping: Exploring the World through Cartography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!