The Superconducting Super Collider: A Journey Through Time and Space
Related Articles: The Superconducting Super Collider: A Journey Through Time and Space
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Superconducting Super Collider: A Journey Through Time and Space. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Superconducting Super Collider: A Journey Through Time and Space
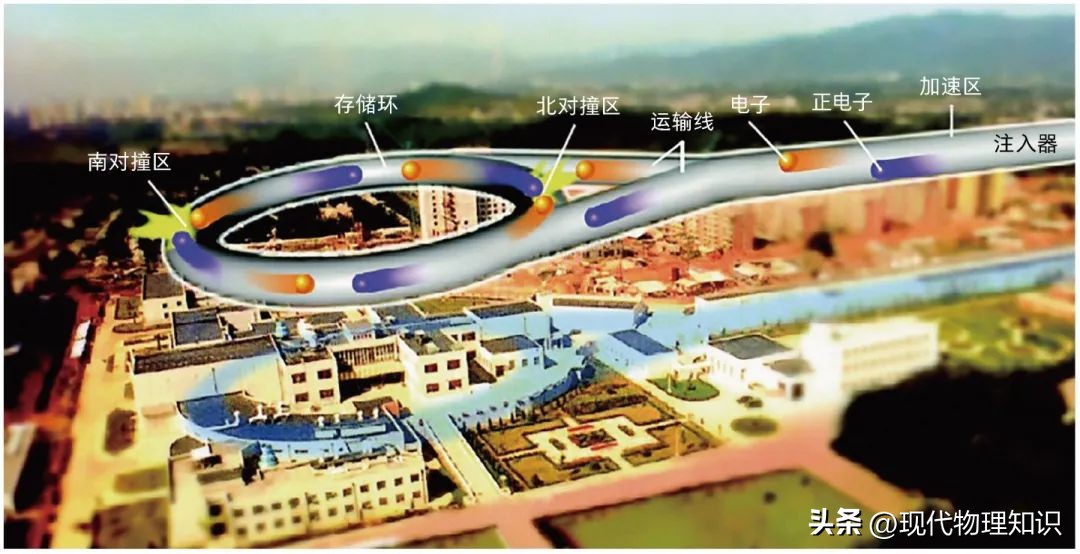
The Superconducting Super Collider (SSC), a project that captivated the scientific community in the late 20th century, was envisioned as a monumental leap forward in particle physics research. This ambitious undertaking, planned for construction in Texas, aimed to unlock the secrets of the universe by smashing particles together at unprecedented energies. While the project ultimately faced cancellation, its legacy continues to resonate within the scientific world.
A Monumental Undertaking:
The SSC was conceived as a circular tunnel spanning 54 miles (87 kilometers) in circumference, buried deep beneath the Texas landscape. This colossal structure would have housed a ring of superconducting magnets, capable of accelerating protons to nearly the speed of light. These high-energy protons would then collide, generating a shower of particles that scientists could analyze to unravel the fundamental building blocks of matter and the forces that govern their interactions.
The Promise of Discovery:
The SSC held immense promise for advancing our understanding of the universe. It was expected to shed light on several key areas, including:
- The Higgs Boson: The SSC was designed to definitively discover the Higgs boson, a fundamental particle responsible for giving mass to other particles.
- Supersymmetry: The SSC could have provided evidence for supersymmetry, a theoretical framework that proposes a deeper symmetry in nature, predicting the existence of partner particles for each known particle.
- New Physics Beyond the Standard Model: The immense energies achievable at the SSC could have revealed new particles and forces beyond the known Standard Model of particle physics, potentially leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the universe.
The SSC Map: A Blueprint for Exploration:
The SSC map, a detailed representation of the proposed collider’s layout, was meticulously crafted by engineers and physicists. It depicted the tunnel’s trajectory, the locations of the magnets, the interaction points where collisions would occur, and the surrounding infrastructure. This map served as a blueprint for the construction and operation of the collider, guiding the project from its initial conceptualization to its eventual cancellation.
The Cancellation and its Aftermath:
Despite the SSC’s immense scientific potential, the project faced significant challenges. Budgetary concerns, political uncertainties, and scientific priorities shifted, ultimately leading to its cancellation in 1993. The project’s termination left a profound impact on the field of particle physics, prompting a reassessment of priorities and funding strategies for large-scale scientific endeavors.
The Legacy of the SSC:
Although the SSC was never completed, its legacy lives on. The project’s cancellation prompted the development of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN, which ultimately succeeded in discovering the Higgs boson. The SSC’s influence can be seen in the technological advancements and scientific insights gained during its development.
The SSC: A Journey Through Time and Space:
The Superconducting Super Collider stands as a testament to human ambition and the pursuit of scientific discovery. While its construction never reached completion, its legacy continues to inspire future generations of scientists and engineers. The SSC map, a blueprint for a journey through time and space, serves as a reminder of the profound questions that drive scientific exploration and the enduring quest for knowledge.
FAQs
1. What was the purpose of the Superconducting Super Collider?
The SSC was designed to collide protons at extremely high energies, enabling scientists to study the fundamental building blocks of matter and the forces that govern their interactions. Its primary goals included discovering the Higgs boson, exploring supersymmetry, and potentially revealing new physics beyond the Standard Model.
2. Why was the SSC cancelled?
The cancellation of the SSC was due to a combination of factors, including escalating costs, political uncertainties, and shifting scientific priorities. Budgetary concerns and the emergence of competing scientific projects contributed to the project’s demise.
3. What impact did the SSC’s cancellation have on particle physics?
The SSC’s cancellation prompted a reassessment of priorities and funding strategies for large-scale scientific endeavors. It also led to the development of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN, which ultimately achieved many of the scientific goals envisioned for the SSC.
4. What are some of the lasting legacies of the SSC?
The SSC’s legacy includes technological advancements in superconducting magnets, particle detectors, and data analysis. It also spurred advancements in accelerator physics and the development of new theoretical models in particle physics.
5. What are some of the key features of the SSC map?
The SSC map depicted the proposed collider’s layout, including the tunnel’s trajectory, the locations of the magnets, the interaction points for collisions, and the surrounding infrastructure. It served as a blueprint for the project’s construction and operation.
Tips for Understanding the SSC Map:
- Focus on the key elements: Pay attention to the tunnel’s trajectory, the location of the magnets, and the interaction points where collisions would occur.
- Consider the scale: The SSC’s immense size is crucial to understanding its scientific potential.
- Visualize the process: Imagine the protons accelerating through the tunnel, colliding at the interaction points, and generating a shower of particles.
Conclusion:
The Superconducting Super Collider, despite its unfinished journey, stands as a testament to human ambition and the relentless pursuit of scientific discovery. Its cancellation marked a turning point in the history of particle physics, highlighting the challenges and complexities of funding large-scale scientific endeavors. Yet, its legacy continues to inspire future generations of scientists and engineers, reminding us of the boundless potential for unraveling the universe’s mysteries. The SSC map, a blueprint for a journey through time and space, serves as a poignant reminder of the enduring quest for knowledge and the insatiable human curiosity that drives scientific exploration.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Superconducting Super Collider: A Journey Through Time and Space. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!