Tracing the Threads of History: The Silk Road on the World Map
Related Articles: Tracing the Threads of History: The Silk Road on the World Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Tracing the Threads of History: The Silk Road on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tracing the Threads of History: The Silk Road on the World Map
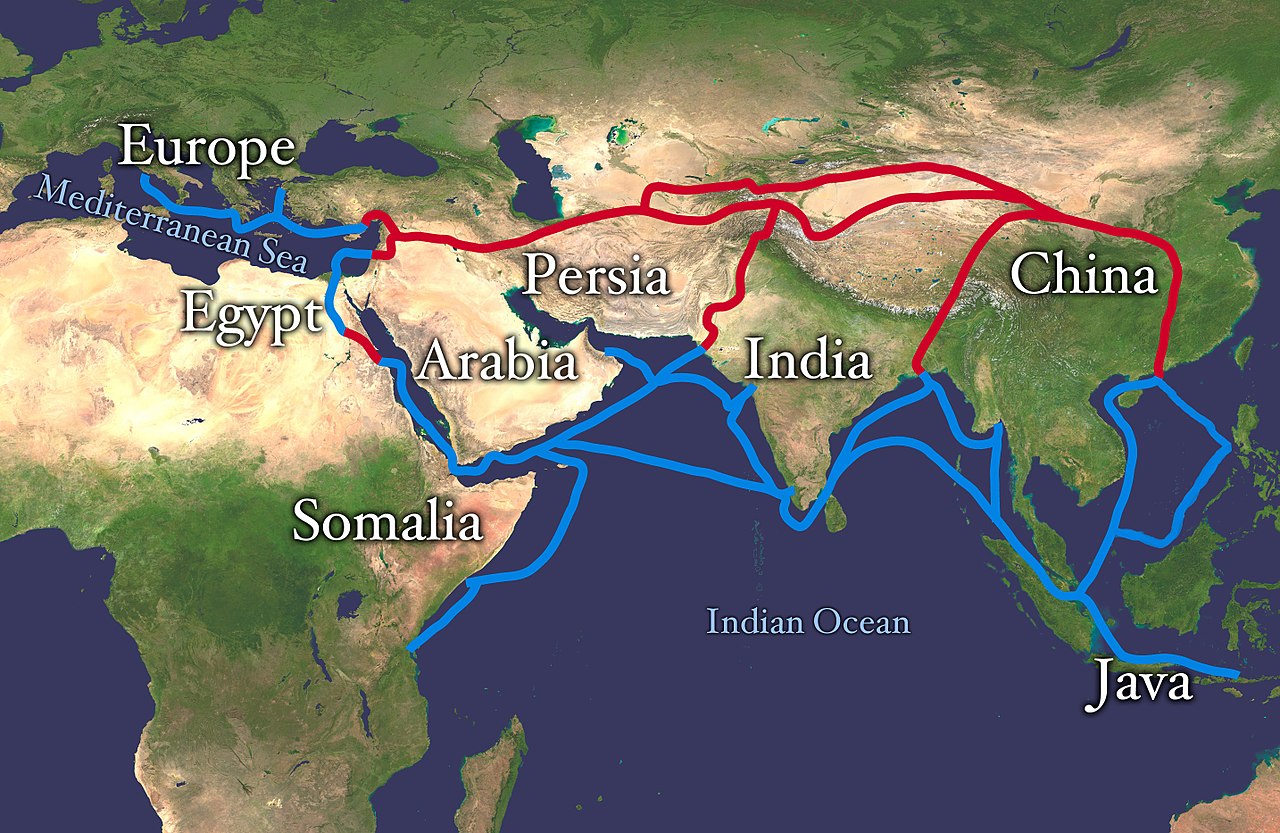
The Silk Road, a network of ancient trade routes that spanned Eurasia for over 1,500 years, stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of the human world. Its impact on history, culture, and global economies is undeniable, leaving an enduring mark on the world map. Understanding the Silk Road’s geographical reach and its significance requires a nuanced approach, exploring its intricate routes, diverse cultural exchanges, and lasting legacies.
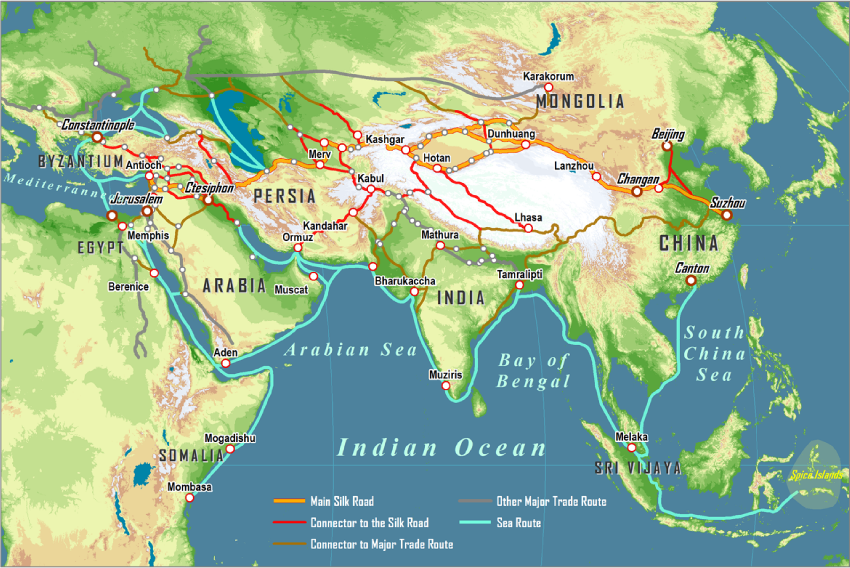
Mapping the Silk Road: A Network of Routes
The term "Silk Road" is a modern construct, a collective name for a series of interconnected routes that evolved over centuries. These routes, primarily land-based, connected the East and West, traversing vast distances and diverse landscapes. While the Silk Road is often associated with the trade of silk from China to the Roman Empire, it facilitated a far wider exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices.
Key Routes and Geographical Significance:
- The Northern Route: This route, often called the "Classic Silk Road," traversed Central Asia, connecting major cities like Xi’an (China), Samarkand (Uzbekistan), and Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul). It crossed challenging terrains like the Gobi Desert and the Pamir Mountains, requiring advanced logistical skills and cultural understanding.
- The Southern Route: This route, skirting the Himalayas, connected India, Pakistan, and Central Asia. It played a crucial role in the exchange of spices, textiles, and religious ideas.
- The Maritime Silk Road: While primarily land-based, the Silk Road also encompassed maritime routes. These routes connected China, Southeast Asia, India, and the Middle East, facilitating trade in goods like porcelain, spices, and precious stones.
Beyond Silk: The Breadth of Exchange
The Silk Road’s impact transcends the mere exchange of goods. It facilitated a vibrant exchange of ideas, technologies, and religious beliefs, shaping the cultural landscape of Eurasia.
- Cultural Exchange: The Silk Road fostered intercultural dialogue, with the exchange of artistic motifs, architectural styles, and literary traditions. The spread of Buddhism from India to China, the adoption of Persian papermaking techniques in China, and the influence of Greek philosophy on Islamic thought are all testaments to this cultural exchange.
- Technological Diffusion: The Silk Road facilitated the transmission of knowledge and technology. The spread of gunpowder from China, the adoption of Arabic numerals in Europe, and the transmission of medical practices from India to the West are examples of this technological diffusion.
- Religious Transmission: The Silk Road played a crucial role in the spread of major religions. Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, and Zoroastrianism all traveled along these routes, influencing the religious landscape of Eurasia.
The Silk Road’s Legacy: A Lasting Impact
The Silk Road, though largely inactive by the 15th century, continues to exert a powerful influence on the world map. Its impact on trade routes, cultural exchange, and global interconnectedness remains evident today.
- Trade and Globalisation: The Silk Road’s legacy is visible in the modern globalized world, where trade networks connect continents and economies. The concept of interconnectedness and cultural exchange, central to the Silk Road, continues to drive global economic growth and cultural understanding.
- Cultural Diversity: The Silk Road’s legacy is evident in the rich cultural diversity of Eurasia. The intermingling of languages, traditions, and beliefs along these routes continues to shape the cultural landscape of the region.
- Historical Significance: The Silk Road stands as a testament to the human spirit’s ability to overcome geographical barriers and forge connections across vast distances. Its story continues to inspire scholars, historians, and travelers, offering insights into the interconnectedness of the human world.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What was the primary purpose of the Silk Road?
The Silk Road served as a network of trade routes, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices between the East and West.
2. What goods were traded on the Silk Road?
The Silk Road witnessed the exchange of a vast array of goods, including silk, spices, textiles, precious stones, porcelain, horses, and even slaves.
3. What role did the Silk Road play in the spread of religions?
The Silk Road facilitated the transmission of major religions like Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, and Zoroastrianism, influencing the religious landscape of Eurasia.
4. How did the Silk Road contribute to cultural exchange?
The Silk Road fostered intercultural dialogue, leading to the exchange of artistic motifs, architectural styles, and literary traditions, shaping the cultural landscape of Eurasia.
5. What were the challenges faced by travelers on the Silk Road?
Travelers on the Silk Road faced numerous challenges, including harsh weather conditions, banditry, disease, and cultural differences.
6. How did the Silk Road influence modern trade and globalisation?
The Silk Road’s legacy is evident in the modern globalized world, where trade networks connect continents and economies, highlighting the concept of interconnectedness and cultural exchange.
7. What are some of the lasting impacts of the Silk Road?
The Silk Road’s lasting impacts include its contribution to cultural diversity, the spread of knowledge and technology, and its role as a testament to the human spirit’s ability to overcome geographical barriers.
Tips for Understanding the Silk Road:
- Study the maps: Visualizing the Silk Road’s routes on a map provides valuable context for understanding its geographical reach and cultural connections.
- Explore historical sources: Documents, archaeological evidence, and travelers’ accounts provide insights into the daily lives, trade practices, and cultural exchanges along the Silk Road.
- Visit Silk Road cities: Traveling to cities like Xi’an, Samarkand, and Istanbul offers a tangible experience of the Silk Road’s legacy, allowing you to witness its architectural, cultural, and historical influence.
- Engage with cultural exhibits: Museums and exhibitions dedicated to the Silk Road provide valuable insights into the trade, art, and culture of this historic network.
Conclusion:
The Silk Road, a network of ancient trade routes, stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of the human world. Its impact on trade, culture, and global economies is undeniable, leaving an enduring mark on the world map. Understanding its geographical reach, diverse cultural exchanges, and lasting legacies allows us to appreciate the intricate web of human interaction that shaped our world. The Silk Road’s story continues to inspire, reminding us of the power of human connection and the enduring legacy of cultural exchange across time and space.

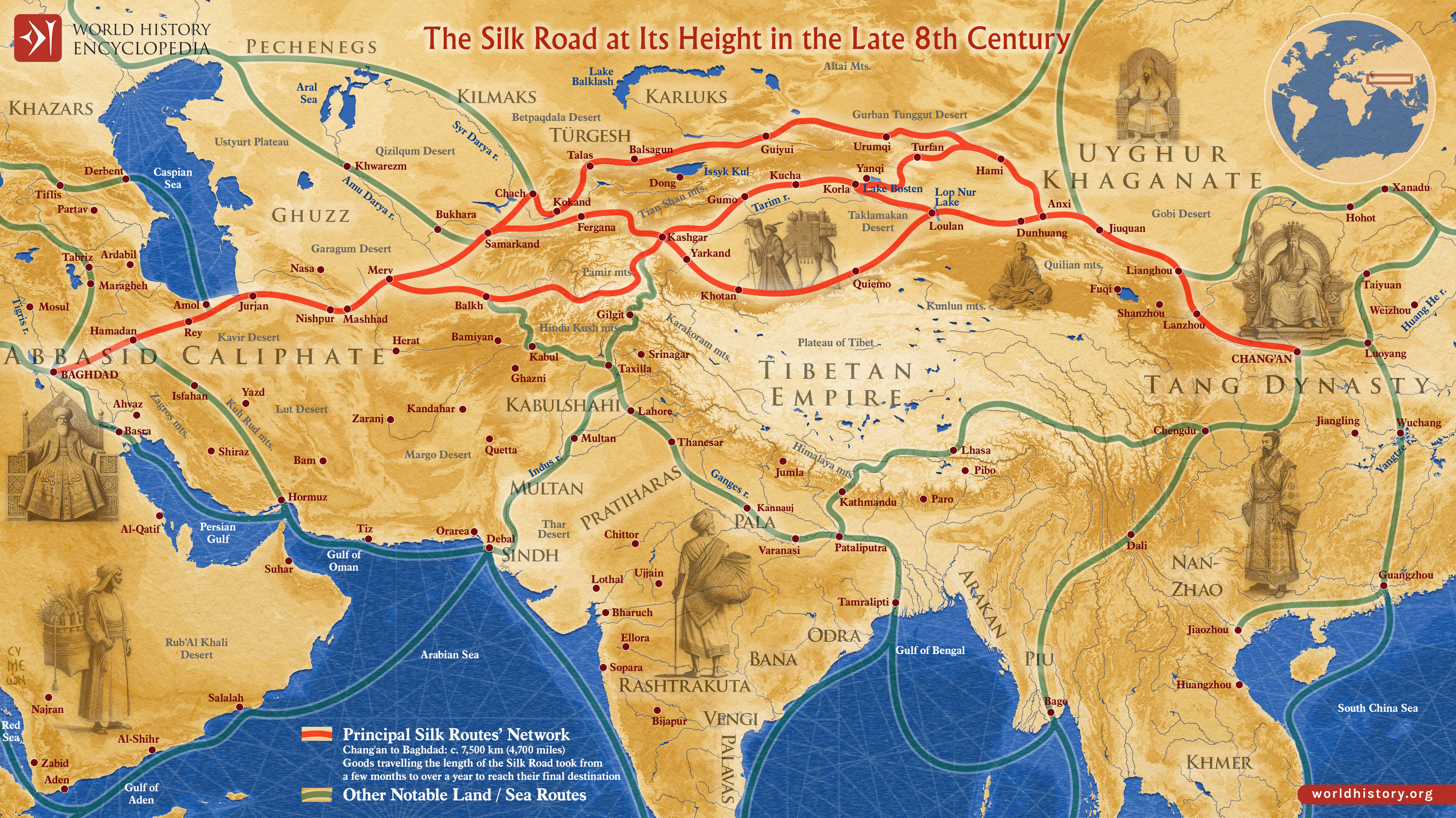
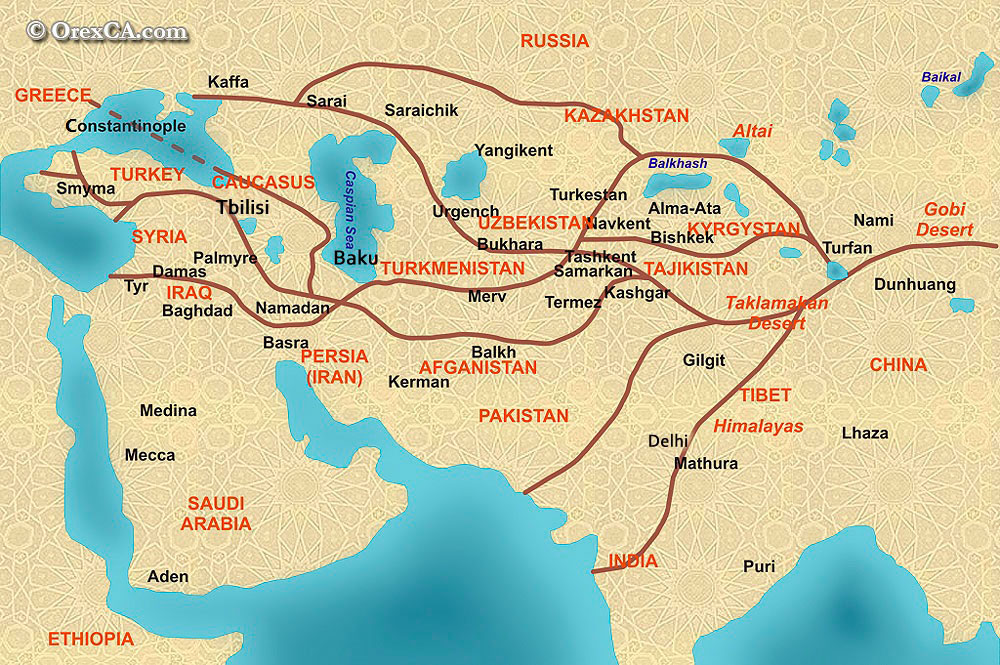

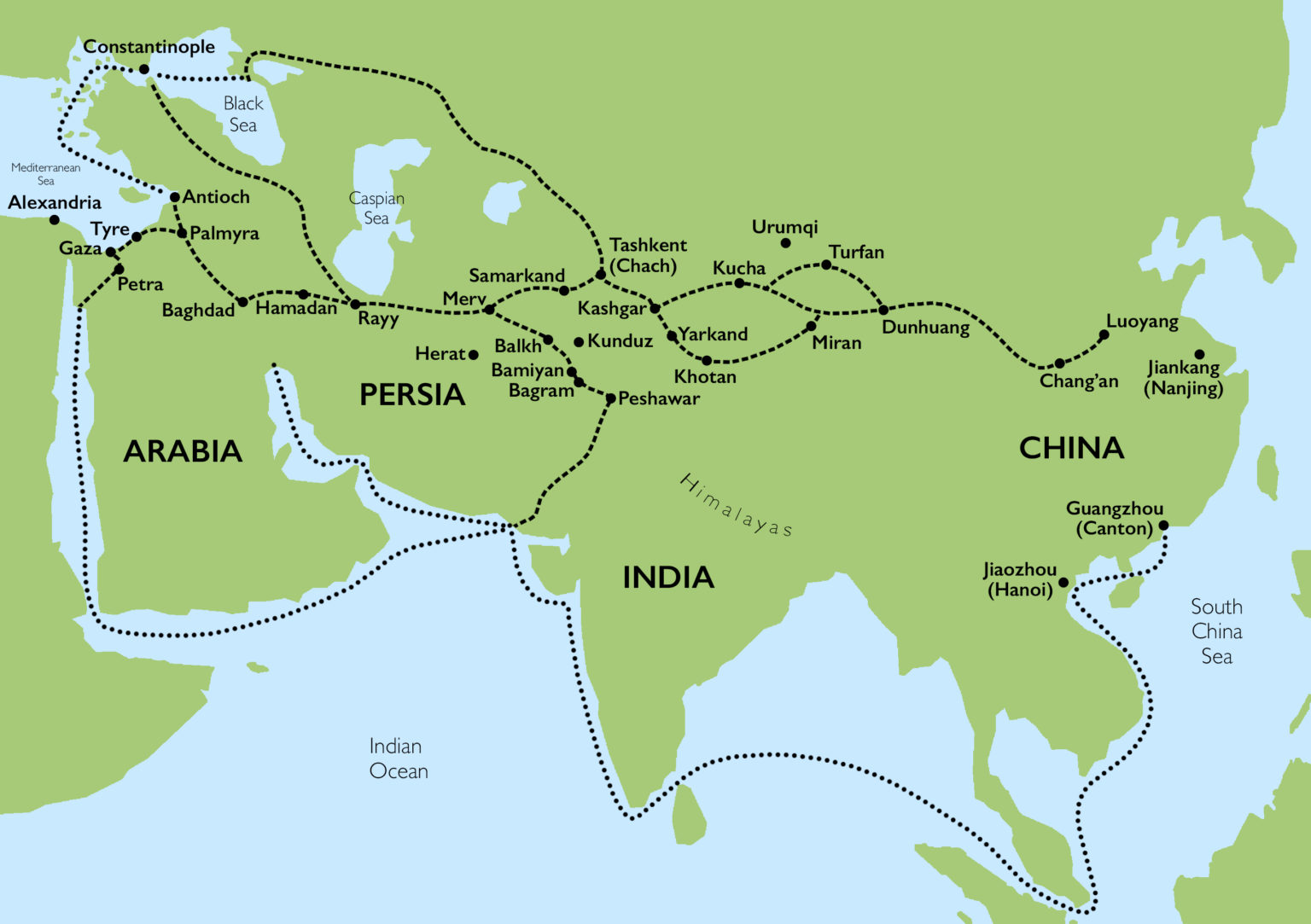


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tracing the Threads of History: The Silk Road on the World Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!