Uncovering the Jewel of Southeast Asia: Exploring the Geography of East Timor
Related Articles: Uncovering the Jewel of Southeast Asia: Exploring the Geography of East Timor
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Uncovering the Jewel of Southeast Asia: Exploring the Geography of East Timor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Uncovering the Jewel of Southeast Asia: Exploring the Geography of East Timor

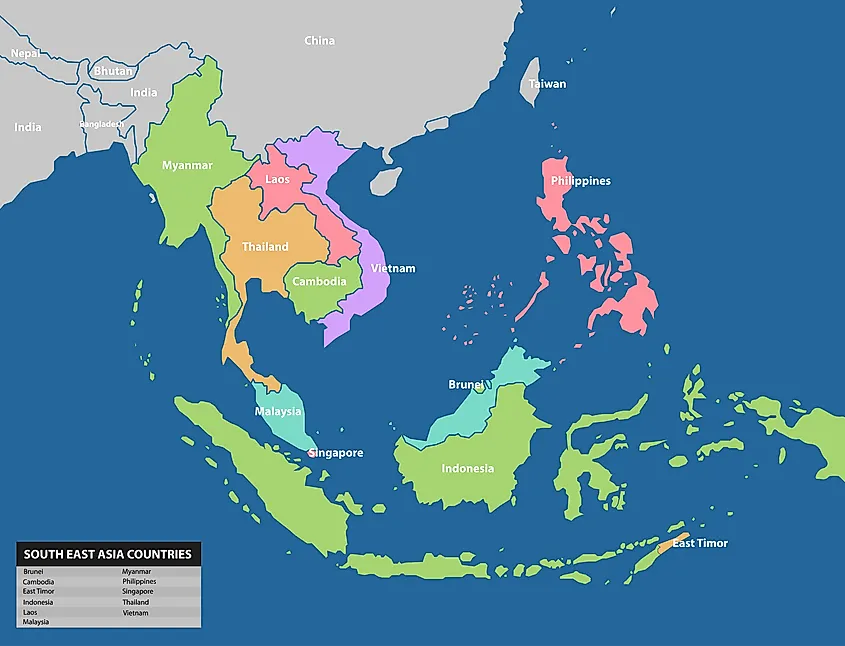
East Timor, officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is a nation nestled in the heart of Southeast Asia. Its unique geographical location, a small island nation situated north of Australia, makes it a fascinating case study in island geography and a crucial player in the regional geopolitical landscape.
A Nation Defined by its Location:
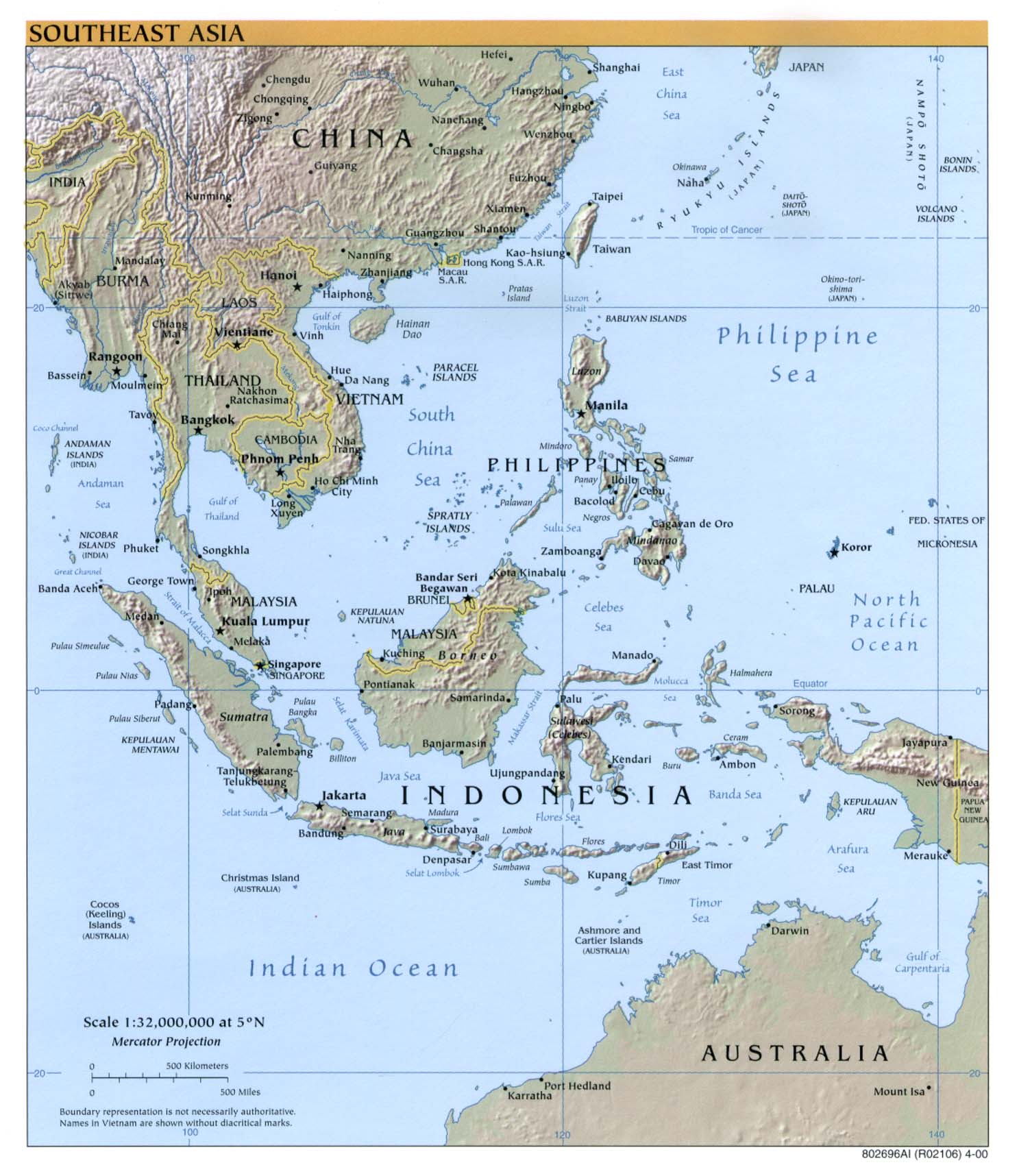
East Timor’s geographical coordinates are 8.55° S, 125.57° E. The nation consists of two distinct parts: the eastern half of the island of Timor, which it shares with Indonesia, and the small island of Atauro. This strategic location places East Timor at a crossroads between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, impacting its climate, biodiversity, and cultural influences.
The Timor Sea: A Vital Maritime Connection:
The Timor Sea, located between East Timor and Australia, is a vital body of water for the nation. It is a rich source of marine life, boasting diverse coral reefs and a thriving fishing industry. The sea also holds significant potential for oil and gas exploration, making it a key economic resource for East Timor.
Island Geography: A Unique Landscape:
East Timor’s landscape is characterized by rugged mountains, fertile valleys, and a coastline dotted with stunning beaches. The highest point, Mount Ramelau, reaches 2,963 meters, offering breathtaking views and showcasing the island’s dramatic topography. The island’s diverse terrain supports a range of ecosystems, including rainforests, savannas, and coastal wetlands, adding to its rich biodiversity.
A Tapestry of Cultural Influences:
East Timor’s geographical location has been instrumental in shaping its vibrant culture. Its proximity to Indonesia and its historical ties to Portugal have resulted in a unique blend of Asian and European influences. This cultural tapestry is reflected in the nation’s music, art, language, and cuisine, making it a fascinating destination for cultural exploration.
Navigating the Geopolitical Landscape:
East Timor’s position in Southeast Asia has also played a significant role in its political history. The nation gained independence in 2002 after a long struggle against Indonesian rule, and its location continues to influence its regional relationships. East Timor’s commitment to regional cooperation and its growing economic ties with its neighbors are shaping its future in the dynamic geopolitical landscape of Southeast Asia.
Beyond the Map: Understanding East Timor’s Significance
East Timor’s geographical location is more than just a matter of latitude and longitude. It is a defining characteristic that shapes its history, culture, and future. The nation’s strategic location, its rich natural resources, and its unique cultural tapestry make it a significant player in Southeast Asia and a fascinating study of island geography.
Frequently Asked Questions about East Timor’s Location:
Q: Is East Timor part of Indonesia?
A: East Timor is an independent nation, not part of Indonesia. While the two countries share the island of Timor, East Timor gained its independence in 2002 after a long struggle.
Q: What is the capital of East Timor?
A: The capital of East Timor is Dili, located on the northern coast of the island.
Q: What languages are spoken in East Timor?
A: The official languages of East Timor are Tetum and Portuguese. However, a variety of other languages are also spoken, including Indonesian and English.
Q: What is the climate like in East Timor?
A: East Timor experiences a tropical monsoon climate, with a wet season from November to April and a dry season from May to October.
Q: What are the major industries in East Timor?
A: The major industries in East Timor include agriculture, fishing, tourism, and oil and gas exploration.
Tips for Visiting East Timor:
- Plan your trip during the dry season: The best time to visit East Timor is during the dry season (May to October), when the weather is pleasant and there is less rainfall.
- Respect local customs: East Timor is a predominantly Catholic country, and it is important to be respectful of local customs and traditions.
- Learn some Tetum phrases: Even a few basic Tetum phrases can go a long way in making your trip more enjoyable.
- Explore the diverse landscape: From the rugged mountains to the stunning beaches, East Timor offers a wide range of landscapes to explore.
- Sample the local cuisine: East Timor’s cuisine is a delicious blend of Asian and Portuguese influences.
Conclusion:
East Timor’s geographical location is a testament to its unique history, culture, and potential. It stands as a beacon of resilience and a testament to the power of self-determination. Its location on the world map is not merely a point on a grid; it is a vital link in the tapestry of Southeast Asia, a symbol of cultural diversity, and a testament to the enduring spirit of an island nation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Uncovering the Jewel of Southeast Asia: Exploring the Geography of East Timor. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!