Understanding Alabama’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Fault Lines
Related Articles: Understanding Alabama’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Fault Lines
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Alabama’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Fault Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Alabama’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Fault Lines
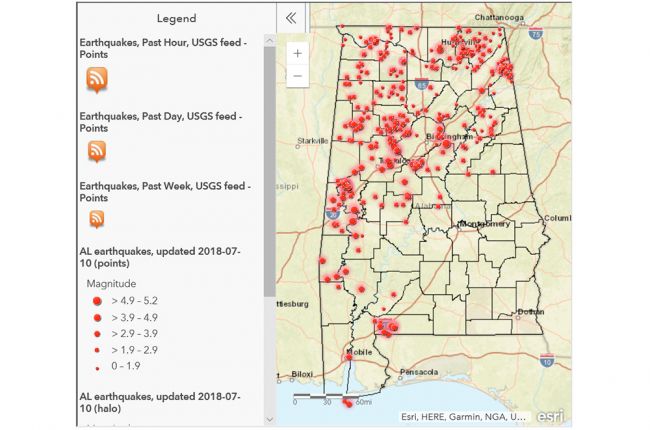
Alabama, often perceived as a relatively stable region, is not immune to the forces of tectonic activity. While earthquakes in the state are generally less frequent and less intense compared to regions like California, the presence of fault lines underscores the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust beneath Alabama’s surface. This article delves into the intricacies of Alabama’s fault lines, exploring their geographical distribution, geological significance, and potential impact on the state.
Unveiling Alabama’s Fault Lines: A Geographical Perspective
Alabama’s fault lines, representing zones of weakness in the Earth’s crust, are primarily concentrated in the northern and central portions of the state. These fault systems are remnants of past tectonic activity, reflecting the ongoing process of continental drift and the relentless forces shaping our planet.
The Appalachian Thrust Belt: A Legacy of Mountain Building
The most prominent fault system in Alabama is the Appalachian Thrust Belt, a vast geological structure extending across the eastern United States. This belt is a testament to the collision of tectonic plates millions of years ago, resulting in the formation of the Appalachian Mountains. Within Alabama, the thrust belt is characterized by a series of thrust faults, where older rocks are pushed over younger rocks. These faults are primarily located in the northern part of the state, extending from the Tennessee border into northeast Alabama.
The Reelfoot Rift: A Zone of Extensional Stress
Another significant fault system in Alabama is the Reelfoot Rift, a zone of extensional stress that runs through the central part of the state. This rift, formed millions of years ago, is associated with the separation of tectonic plates. It is characterized by normal faults, where blocks of the Earth’s crust move downward relative to each other. The Reelfoot Rift is responsible for the creation of the Mississippi Embayment, a geological depression that extends into northern Alabama.
The Birmingham Fault System: A Localized Zone of Activity
The Birmingham Fault System, located in central Alabama, is a series of smaller faults that are associated with the Appalachian Thrust Belt and the Reelfoot Rift. These faults are generally less prominent than the major fault systems, but they still represent zones of potential seismic activity.
The Impact of Fault Lines on Alabama: A Geological Perspective
While Alabama’s fault lines are not directly responsible for the frequent and powerful earthquakes experienced in other parts of the world, they still play a crucial role in shaping the state’s geological landscape. These fault lines influence:
- Geological formations: Fault lines can create diverse geological formations, including mountains, valleys, and plateaus. The Appalachian Thrust Belt, for example, has played a significant role in shaping the topography of northern Alabama.
- Groundwater resources: Fault lines can create pathways for groundwater movement, influencing the availability of water resources in certain regions.
- Mineral deposits: Fault zones can act as conduits for mineral-rich fluids, leading to the formation of mineral deposits.
- Seismic activity: While Alabama experiences relatively infrequent earthquakes, the presence of fault lines indicates the potential for seismic activity.
Understanding the Seismic Risk in Alabama: A Scientific Perspective
While Alabama is not considered a high-risk earthquake zone, the presence of fault lines underscores the need for ongoing seismic monitoring and preparedness. The Alabama Geological Survey (AGS) plays a vital role in understanding and mitigating seismic risks within the state. The AGS maintains a network of seismic stations that continuously monitor ground motion, providing valuable data for research and hazard assessment.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about Alabama’s Fault Lines
1. What is the largest earthquake ever recorded in Alabama?
The largest earthquake recorded in Alabama was a magnitude 5.1 event that occurred near Decatur in 1811. This earthquake, while relatively weak compared to events in other parts of the world, caused significant damage to buildings and infrastructure in the region.
2. Are there any active fault lines in Alabama?
While the vast majority of Alabama’s fault lines are considered inactive, there is evidence of occasional seismic activity along certain fault zones. The Birmingham Fault System, for example, has been associated with minor earthquakes in recent years.
3. How often do earthquakes occur in Alabama?
Earthquakes in Alabama are relatively infrequent, with most events being small and undetectable by humans. The AGS typically records several minor earthquakes each year, but significant events are rare.
4. What is the risk of a major earthquake in Alabama?
The risk of a major earthquake in Alabama is considered low, but not negligible. The state’s fault lines, while generally inactive, have the potential to generate earthquakes, although the likelihood of a large-scale event is low.
5. What should I do if I experience an earthquake in Alabama?
If you experience an earthquake, it is important to remain calm and follow safety guidelines. Seek shelter under a sturdy piece of furniture or in a doorway. Stay away from windows and avoid using elevators. Once the shaking has stopped, check for injuries and damage.
Tips for Residents: Being Prepared for Seismic Activity
- Educate yourself: Familiarize yourself with the potential seismic risks in your area.
- Develop an emergency plan: Create a plan for your family to follow in the event of an earthquake.
- Secure your home: Secure heavy objects that could fall and cause injury during an earthquake.
- Prepare an emergency kit: Assemble a kit containing essential supplies, such as food, water, first aid, and a flashlight.
- Stay informed: Stay updated on earthquake warnings and safety guidelines from official sources.
Conclusion: Navigating Alabama’s Seismic Landscape
While Alabama’s seismic landscape is generally stable, the presence of fault lines reminds us of the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust. Understanding the geological processes that have shaped Alabama’s fault lines is crucial for assessing seismic risks and developing effective preparedness strategies. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, residents can enhance their safety and resilience in the face of potential seismic activity.

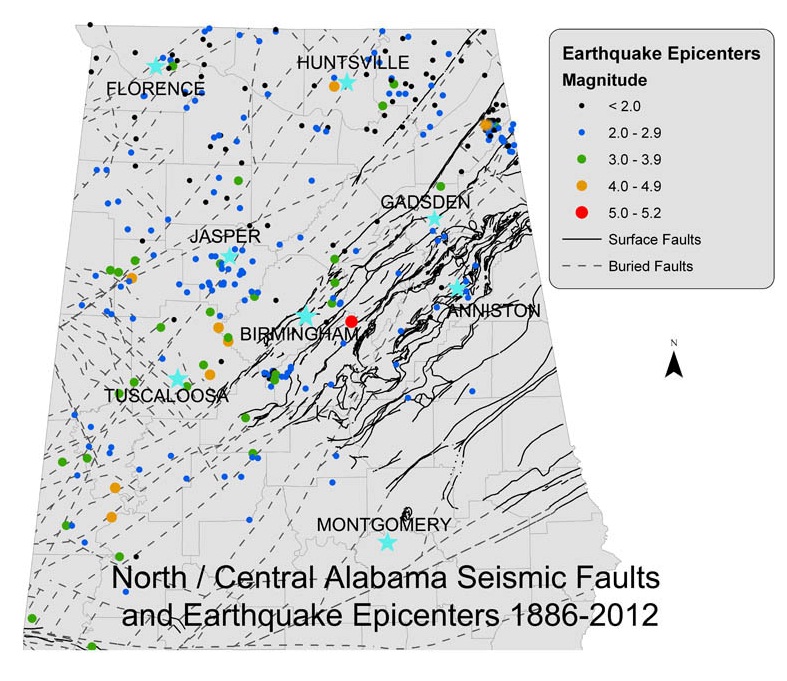






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Alabama’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Fault Lines. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!