Understanding the Indiana House of Representatives District Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Indiana House of Representatives District Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Indiana House of Representatives District Map: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Indiana House of Representatives District Map: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Indiana House of Representatives District Map: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Importance of District Maps
- 3.2 Historical Context: The Evolution of Indiana’s District Map
- 3.3 Key Features of the Indiana House of Representatives District Map
- 3.4 The Redistricting Process: A Complex and Political Undertaking
- 3.5 Understanding the Map: Tools and Resources
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.7 Tips for Engaging with the Redistricting Process
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Indiana House of Representatives District Map: A Comprehensive Guide
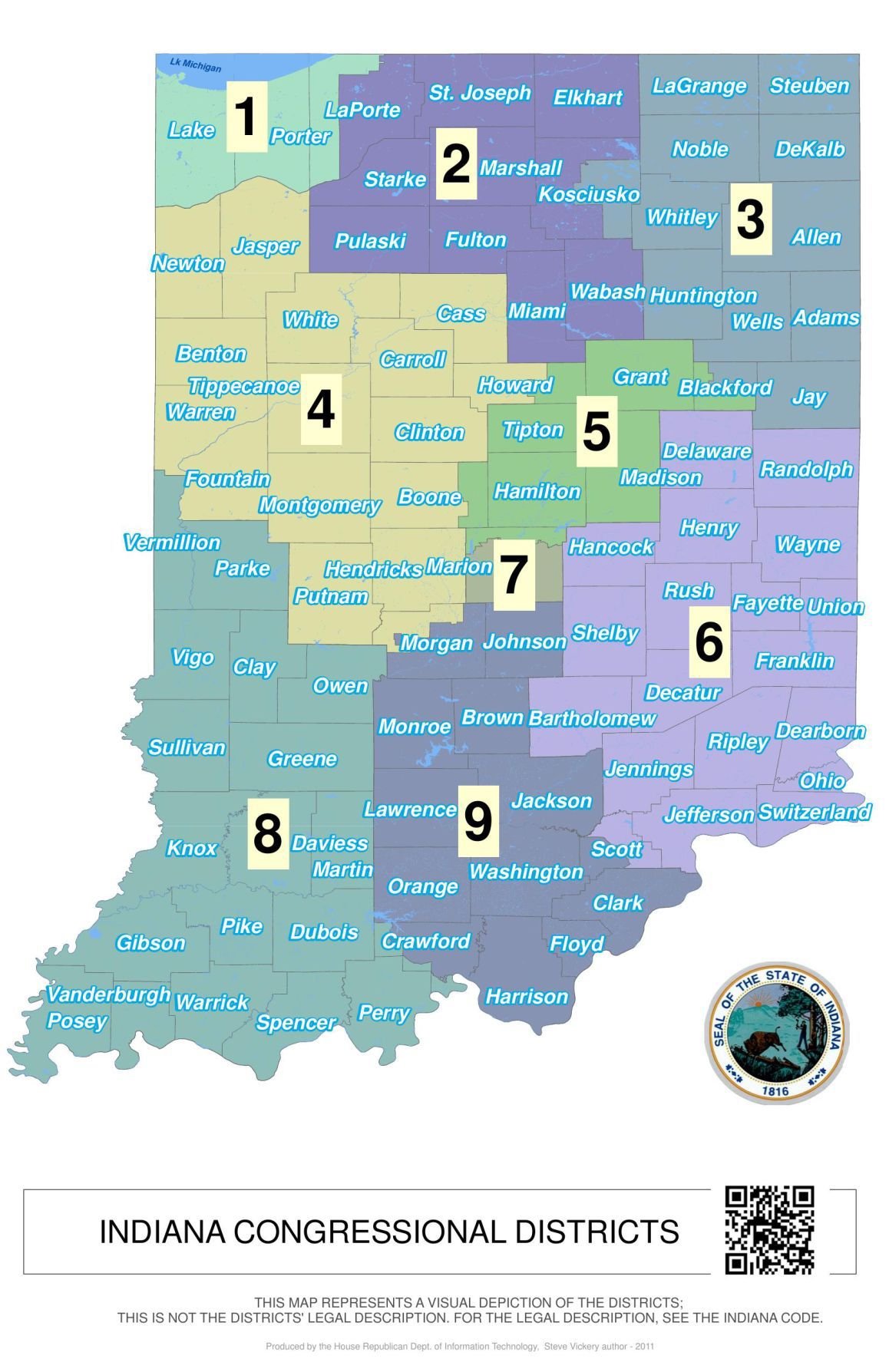
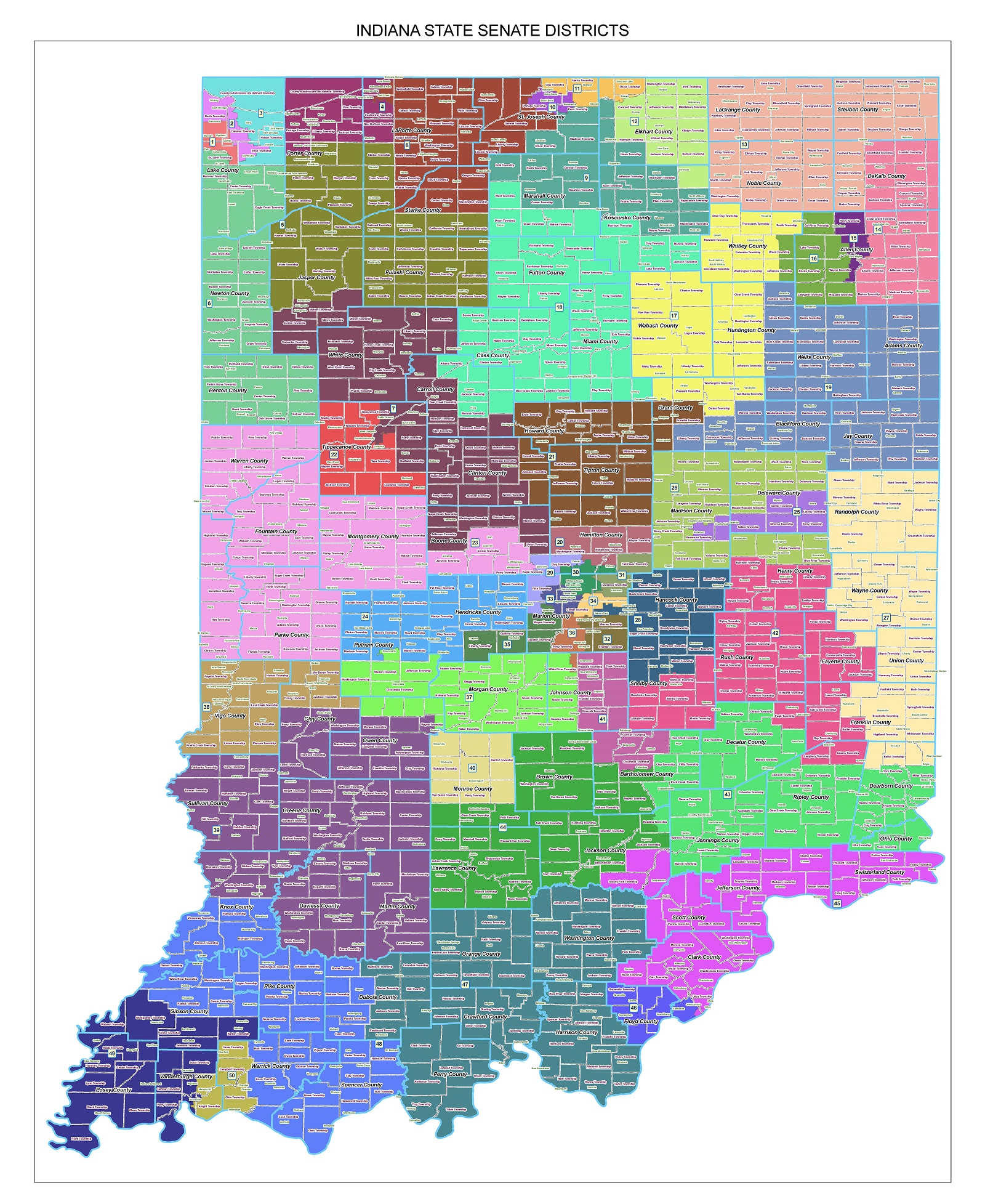
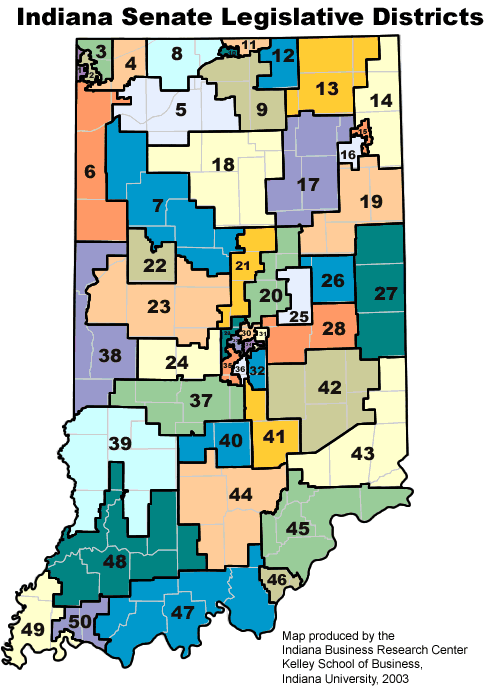
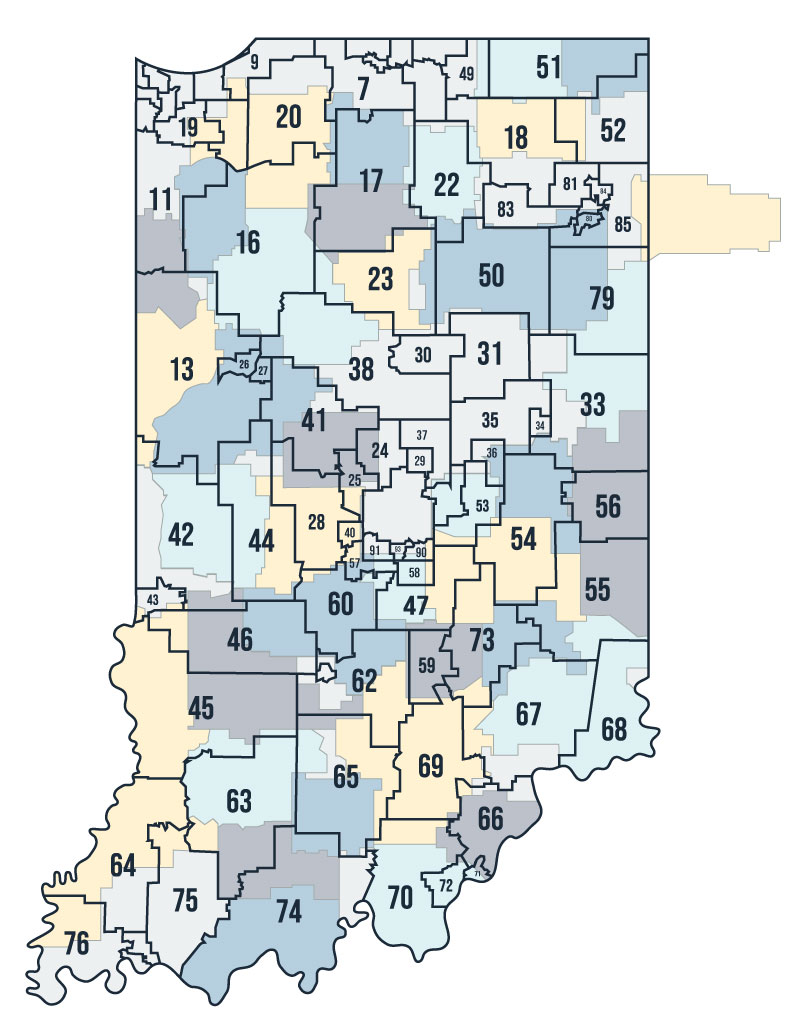
The Indiana House of Representatives District Map is a critical tool for understanding the state’s political landscape and the representation of its citizens. This map outlines the boundaries of the 100 districts that elect representatives to the Indiana House of Representatives, the lower chamber of the state legislature.
The Importance of District Maps
District maps play a crucial role in shaping the political landscape of any state. They determine the composition of the legislature by influencing which candidates are elected and the policies they prioritize. In Indiana, the House of Representatives is responsible for crafting and approving legislation on a wide range of issues, including education, healthcare, taxes, and infrastructure.
The boundaries of these districts directly impact the constituents each representative serves. A well-designed map ensures that districts are geographically compact, demographically similar, and represent the interests of their residents effectively.
Historical Context: The Evolution of Indiana’s District Map
The Indiana House of Representatives District Map has undergone significant changes over the years, reflecting shifts in population, demographics, and political trends.
- 1901: The first official district map was adopted, establishing the foundation for the state’s legislative structure.
- 1960s: The landmark Supreme Court case Reynolds v. Sims (1964) established the "one person, one vote" principle, requiring districts to be roughly equal in population. This led to significant redistricting efforts across the country, including Indiana.
- 1970s: Further redistricting occurred to comply with the Voting Rights Act of 1965, ensuring fair representation for minority groups.
- 1980s-Present: The map has continued to evolve with each decennial census, reflecting changes in population distribution and demographic shifts.
Key Features of the Indiana House of Representatives District Map
The current Indiana House of Representatives District Map, adopted after the 2020 census, incorporates several key features:
- Equal Population: Each district contains approximately the same number of residents, ensuring equal representation in the House.
- Compactness: Districts are designed to be geographically cohesive, avoiding sprawling or oddly shaped boundaries.
- Contiguity: All parts of a district must be connected, preventing districts from being fragmented.
- Respect for Communities of Interest: The map strives to avoid dividing communities with shared interests or characteristics, such as cities, towns, or neighborhoods.
The Redistricting Process: A Complex and Political Undertaking
The process of redrawing district maps is a complex and often politically charged endeavor. In Indiana, the state legislature is responsible for redistricting. This process involves:
- Data Collection: Gathering population data from the decennial census and other sources.
- Map Development: Creating proposed maps that meet legal requirements and political considerations.
- Public Input: Providing opportunities for citizens to review and provide feedback on proposed maps.
- Legislative Approval: The legislature debates, amends, and ultimately approves the final district map.
Understanding the Map: Tools and Resources
Several resources are available to help citizens understand and navigate the Indiana House of Representatives District Map:
- Indiana Legislative Services Agency: Provides access to official district maps, redistricting data, and legislative information.
- Indiana Election Division: Offers information on voting procedures, polling locations, and election results.
- Non-Partisan Redistricting Organizations: Independent groups, such as the League of Women Voters, provide analysis and advocacy related to redistricting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How can I find my district?
You can use the Indiana Legislative Services Agency website to search for your district by address or zip code.
2. Who represents my district?
The Indiana Legislative Services Agency website lists current representatives for each district.
3. How often are district maps redrawn?
District maps are redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census.
4. What are the criteria for drawing district maps?
District maps must adhere to legal requirements, including equal population, compactness, contiguity, and respect for communities of interest.
5. What are the potential impacts of redistricting?
Redistricting can impact the political landscape, influencing the outcome of elections and the policies adopted by the legislature.
Tips for Engaging with the Redistricting Process
- Stay Informed: Follow redistricting news and updates from reputable sources.
- Participate in Public Input: Attend public hearings and provide feedback on proposed maps.
- Contact Your Representatives: Share your views and concerns with your elected officials.
- Support Non-Partisan Redistricting Organizations: Advocate for fair and transparent redistricting processes.
Conclusion
The Indiana House of Representatives District Map is a fundamental element of the state’s political system. It ensures fair representation for all citizens, reflects demographic changes, and shapes the legislative process. By understanding the map and engaging in the redistricting process, citizens can play an active role in shaping the future of their communities and the state as a whole.
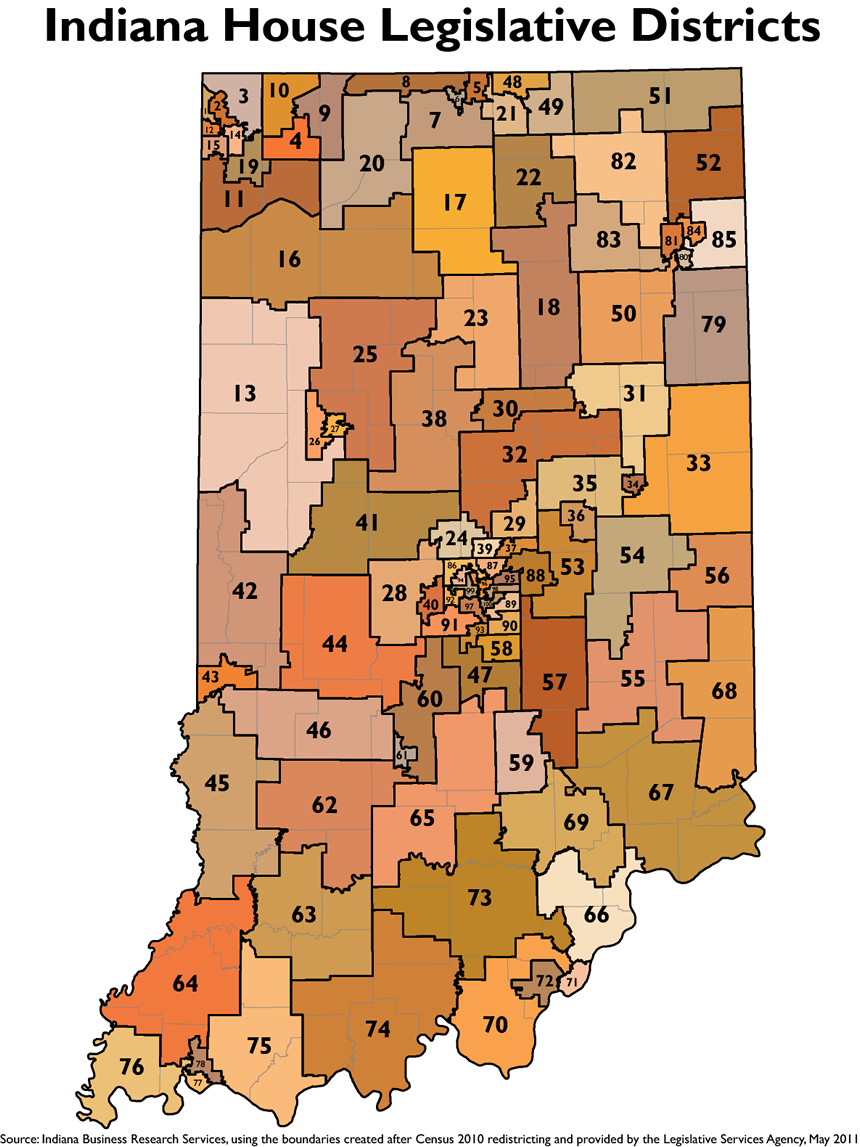
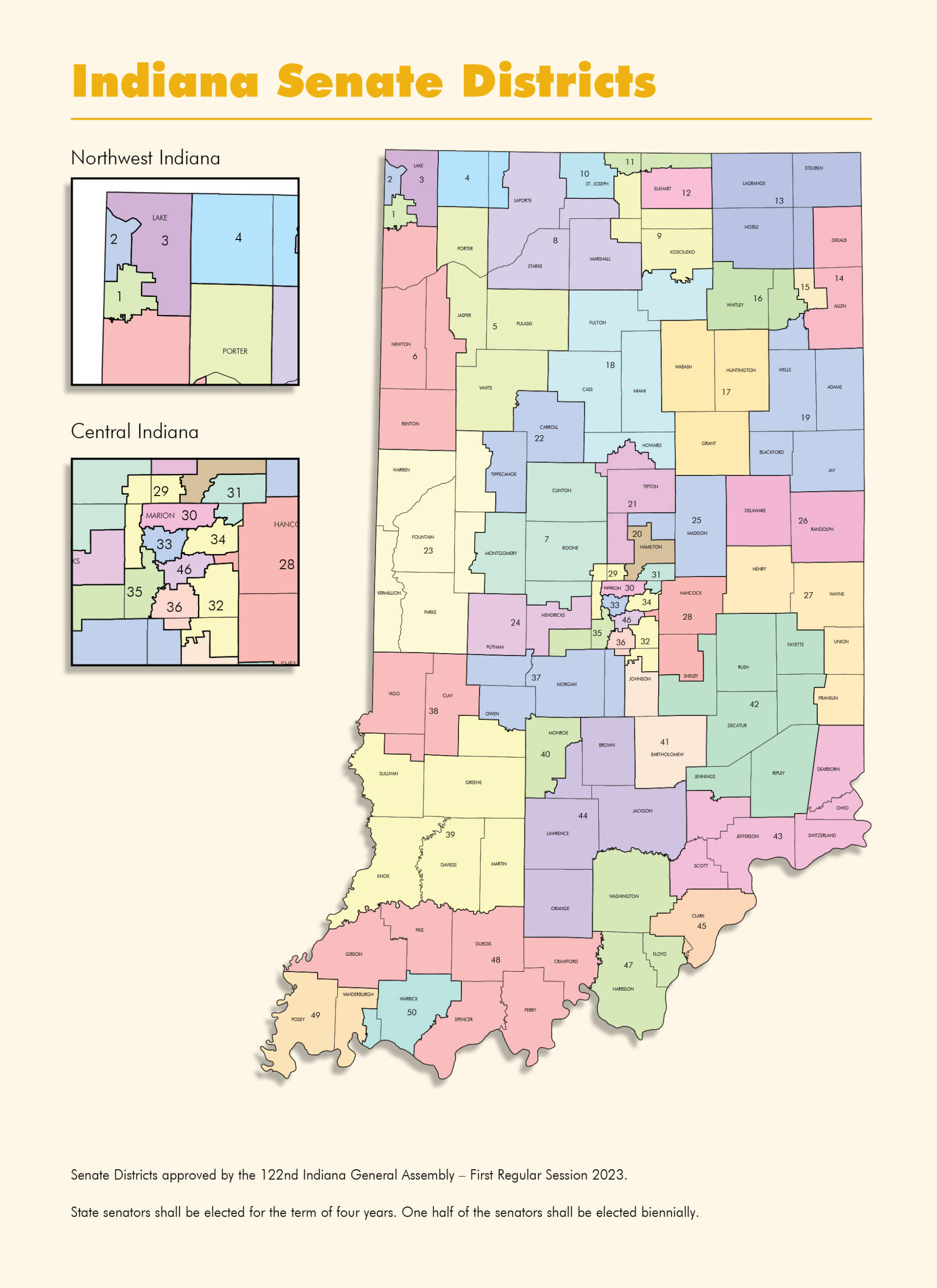
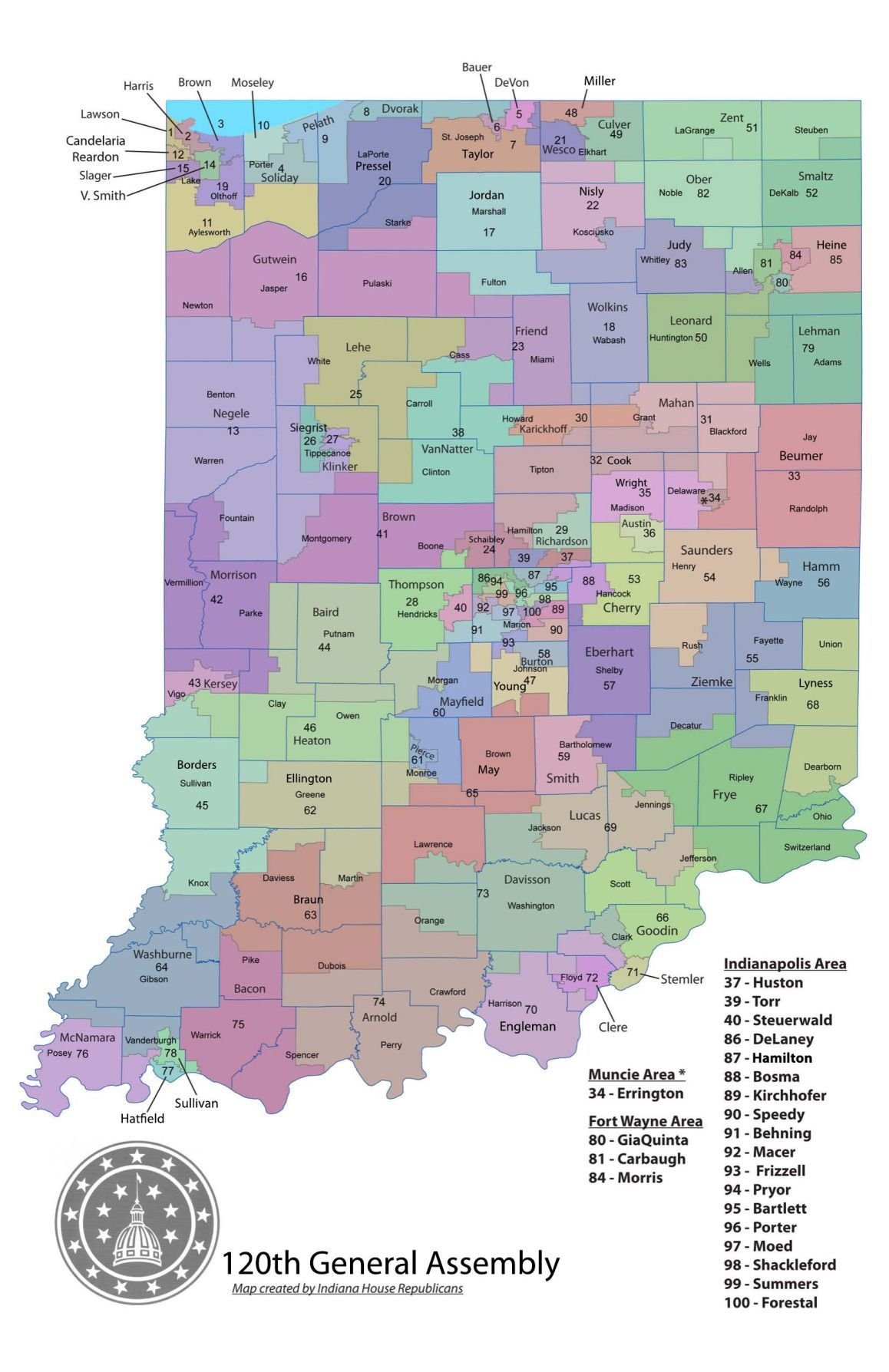


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Indiana House of Representatives District Map: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!