Understanding the Power of Heat Map Scales: A Guide to Visualizing Data and Driving Insights
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Heat Map Scales: A Guide to Visualizing Data and Driving Insights
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Heat Map Scales: A Guide to Visualizing Data and Driving Insights. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Heat Map Scales: A Guide to Visualizing Data and Driving Insights
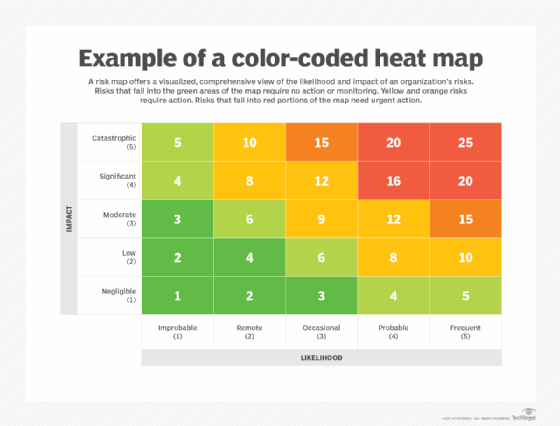
Heat maps, ubiquitous in data visualization, offer a powerful way to represent data visually, revealing patterns and trends that might otherwise remain hidden. A critical component of this visualization technique is the heat map scale, which plays a crucial role in interpreting the information presented.
Defining the Heat Map Scale
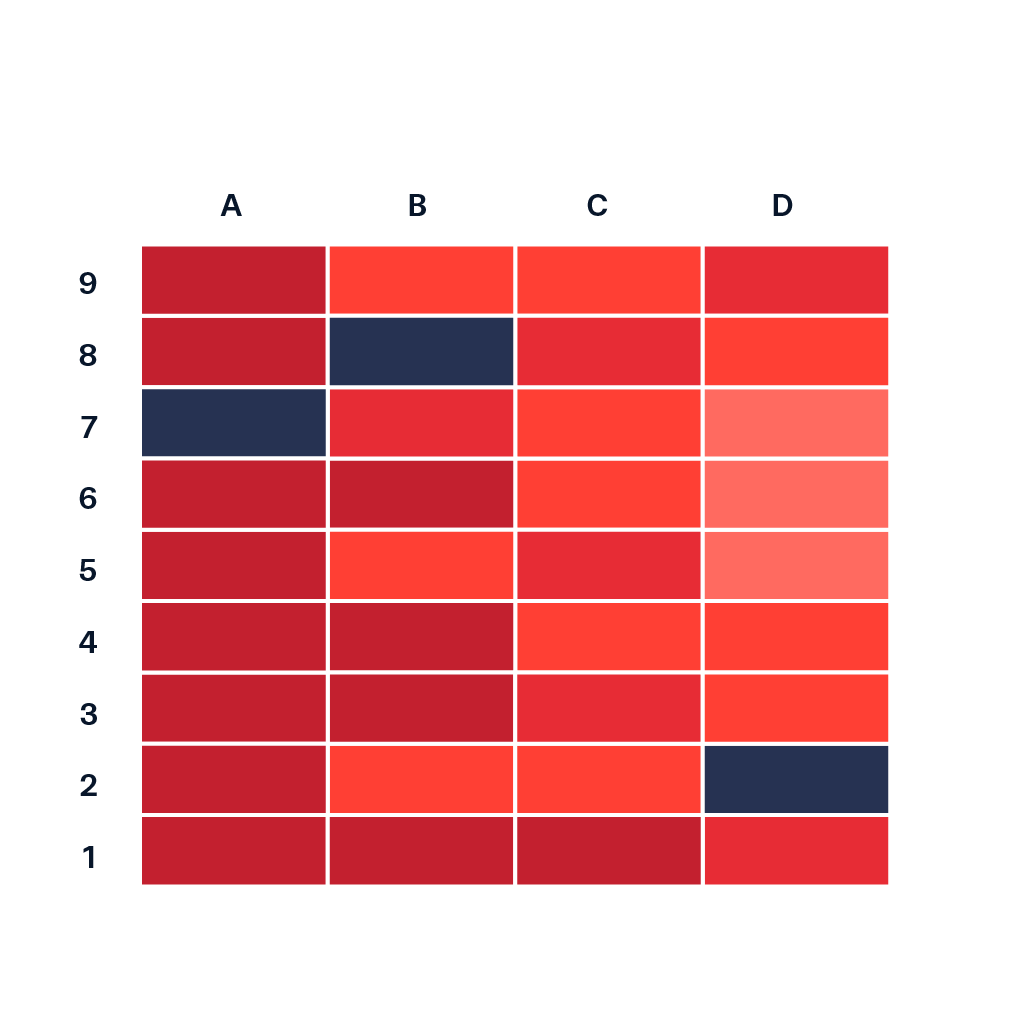
The heat map scale, also known as a color scale or legend, acts as a visual key, translating numerical data into a spectrum of colors. It establishes a clear relationship between the intensity of a color and the corresponding data value. This visual correspondence allows for swift and intuitive comprehension of the data, enabling users to quickly identify areas of high or low activity, concentration, or value.
Types of Heat Map Scales
The choice of heat map scale directly influences the clarity and effectiveness of the visualization. Understanding the different types available is crucial for selecting the most appropriate option for the data being presented:
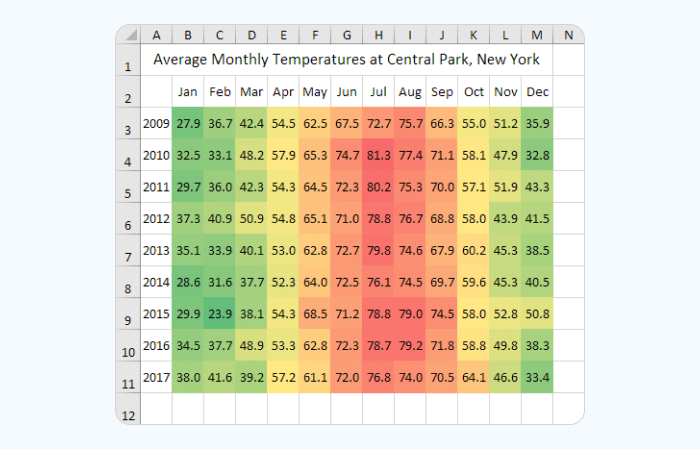
- Sequential Scales: These scales use a single color that gradually transitions from light to dark, representing a continuous range of data values. For example, a scale might transition from light blue to dark blue, representing increasing values of temperature. Sequential scales are ideal for representing data with a clear directionality, such as time series or magnitude.
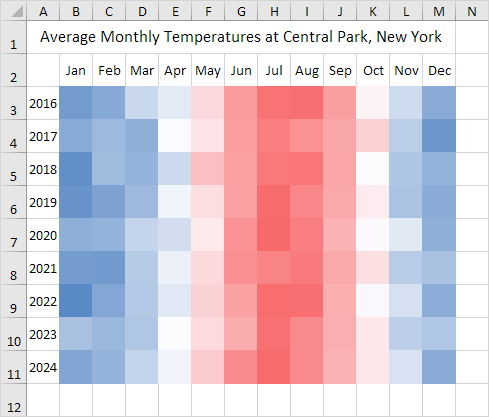
- Diverging Scales: Diverging scales utilize two distinct colors, usually with a neutral midpoint, to represent data that diverges from a central value. For instance, a scale might use red for high values, green for low values, and yellow for the midpoint, indicating positive, negative, or neutral values. These scales are effective for highlighting deviations from a baseline or average.
- Qualitative Scales: These scales use distinct colors to represent different categories or groups. For example, a scale might use red for one group, blue for another, and green for a third, representing different product types or customer segments. Qualitative scales are best suited for visualizing categorical data, where the focus is on distinguishing between groups rather than on the magnitude of values.
Choosing the Right Heat Map Scale
Selecting the appropriate heat map scale is essential for creating a clear and effective visualization. Several factors should be considered:
- Data Type: The type of data being visualized will determine the most suitable scale. Sequential scales are ideal for continuous data, while diverging scales are well-suited for data that diverges from a central value. Qualitative scales are used for categorical data.
- Data Range: The range of data values should be considered when choosing a scale. A scale with a wider range can accommodate larger variations in data, while a narrower range provides more detail for smaller variations.
- Target Audience: The intended audience should also be taken into account. A scale that is easy to understand and interpret will be more effective in communicating the intended message.
Benefits of Using a Heat Map Scale
The use of heat map scales offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Data Visualization: Heat maps provide a visually appealing and intuitive way to represent data, making it easier for users to understand and interpret trends and patterns.
- Improved Data Analysis: By highlighting areas of high and low activity, heat maps facilitate data analysis and enable users to identify key areas of interest.
- Enhanced Decision Making: Heat map visualizations can provide valuable insights that inform decision-making, leading to better outcomes.
- Effective Communication: Heat maps are effective tools for communicating data insights to stakeholders, enabling them to understand complex data in a clear and concise manner.
Applications of Heat Map Scales
Heat map scales find applications across various domains, including:
- Business Analytics: Heat maps are widely used in business analytics to visualize customer behavior, website traffic, sales performance, and other key metrics.
- Marketing: Marketers utilize heat maps to understand user engagement with websites and marketing campaigns, optimizing content and strategies.
- Finance: Heat maps are employed in finance to analyze market trends, identify investment opportunities, and assess risk.
- Healthcare: Heat maps are used in healthcare to visualize patient data, track disease outbreaks, and monitor patient outcomes.
- Research: Researchers utilize heat maps to analyze data from experiments, surveys, and other research activities.
Frequently Asked Questions about Heat Map Scales
Q: What is the purpose of a heat map scale?
A: The heat map scale serves as a visual key, translating numerical data into a spectrum of colors, enabling users to understand the relationship between color intensity and data values.
Q: How do I choose the right heat map scale?
A: The choice of scale depends on the type of data, the data range, and the intended audience. Consider using sequential scales for continuous data, diverging scales for data that deviates from a central value, and qualitative scales for categorical data.
Q: What are some common heat map scale types?
A: Common types include sequential scales, diverging scales, and qualitative scales.
Q: How do heat maps benefit data analysis?
A: Heat maps provide a visual representation of data, highlighting areas of high and low activity, enabling users to quickly identify patterns and trends, facilitating data analysis.
Q: What are some applications of heat map scales?
A: Heat map scales are used in business analytics, marketing, finance, healthcare, and research to visualize data and gain insights.
Tips for Using Heat Map Scales Effectively
- Use a Clear and Consistent Scale: Ensure the scale is easy to understand and interpret, using clear labels and consistent color gradients.
- Choose Appropriate Colors: Select colors that are visually appealing and effectively convey the data. Consider using contrasting colors to highlight important areas.
- Provide Context: Include a legend or key to explain the meaning of different colors on the scale.
- Avoid Overcrowding: Ensure the heat map is not overcrowded with too much data. Use appropriate data aggregation or filtering techniques to simplify the visualization.
- Optimize for Accessibility: Ensure the heat map is accessible to users with visual impairments by providing alternative text descriptions and using color contrast ratios that meet accessibility standards.
Conclusion
Heat map scales play a crucial role in data visualization, enabling users to understand and interpret data visually. By translating numerical data into a spectrum of colors, heat map scales provide a clear and concise representation of data, highlighting areas of high and low activity, concentration, or value. Understanding the different types of scales and choosing the most appropriate option for the data being presented is essential for creating effective and insightful visualizations. By leveraging the power of heat map scales, users can gain valuable insights from data, make informed decisions, and effectively communicate data insights to stakeholders.
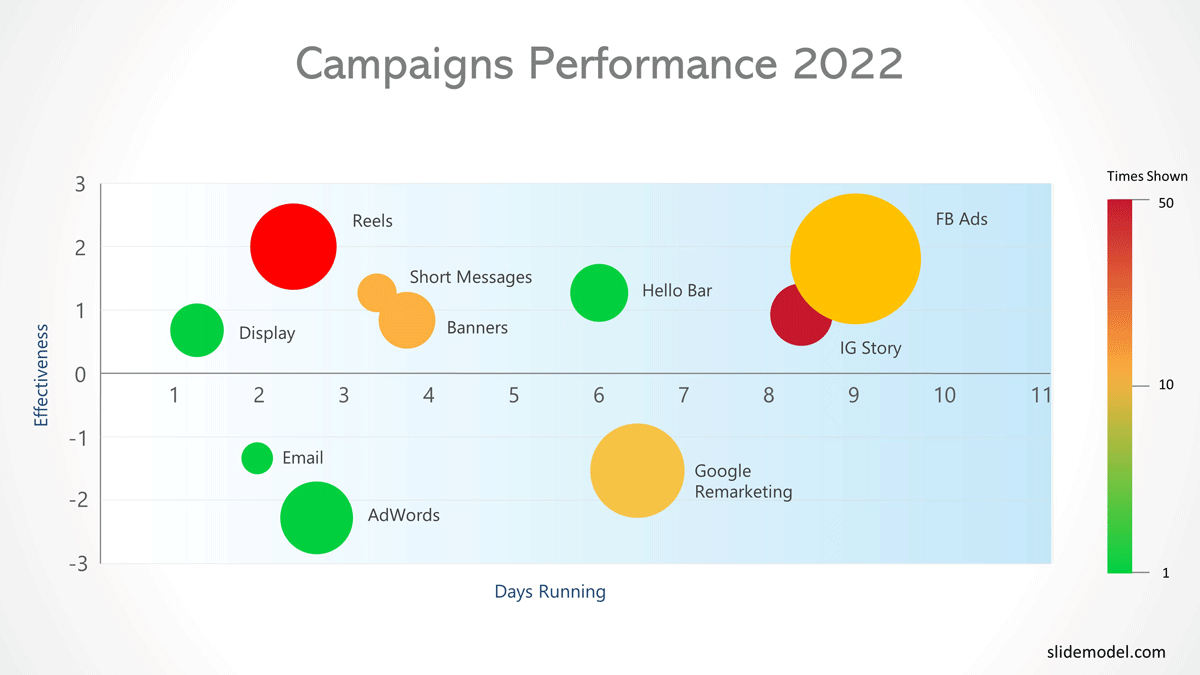

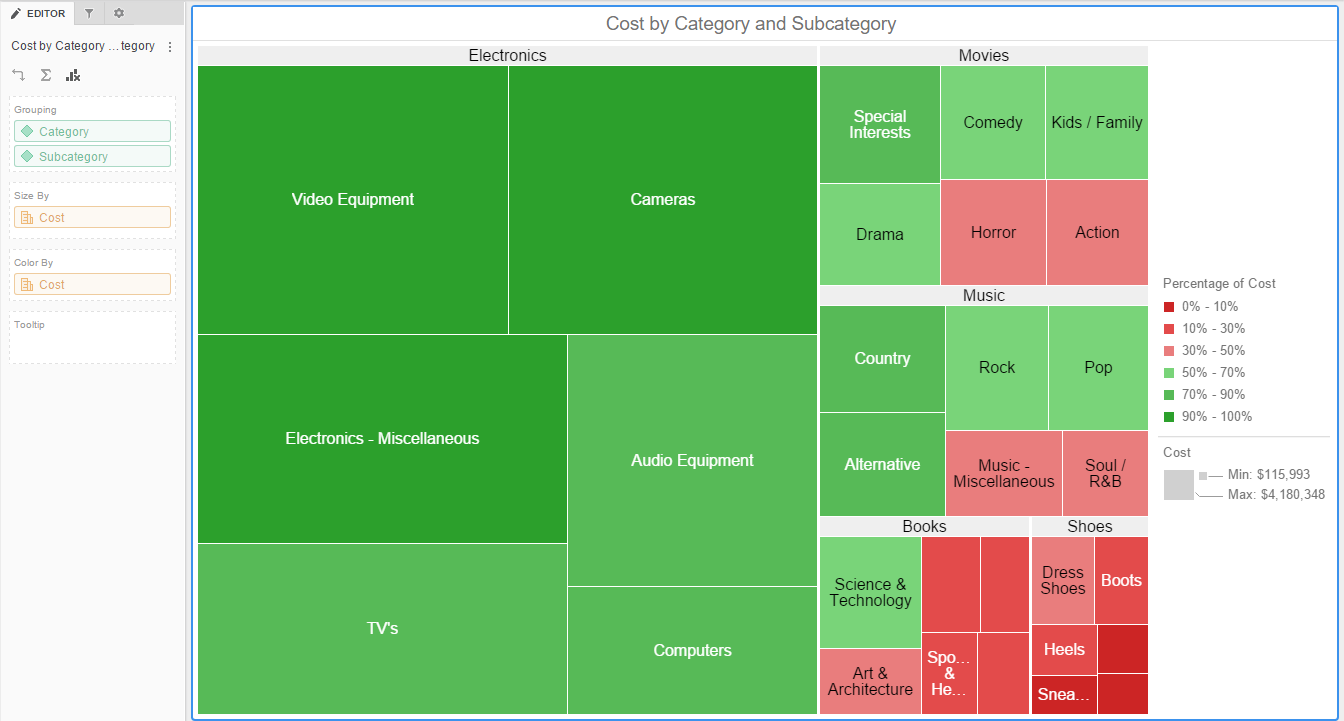
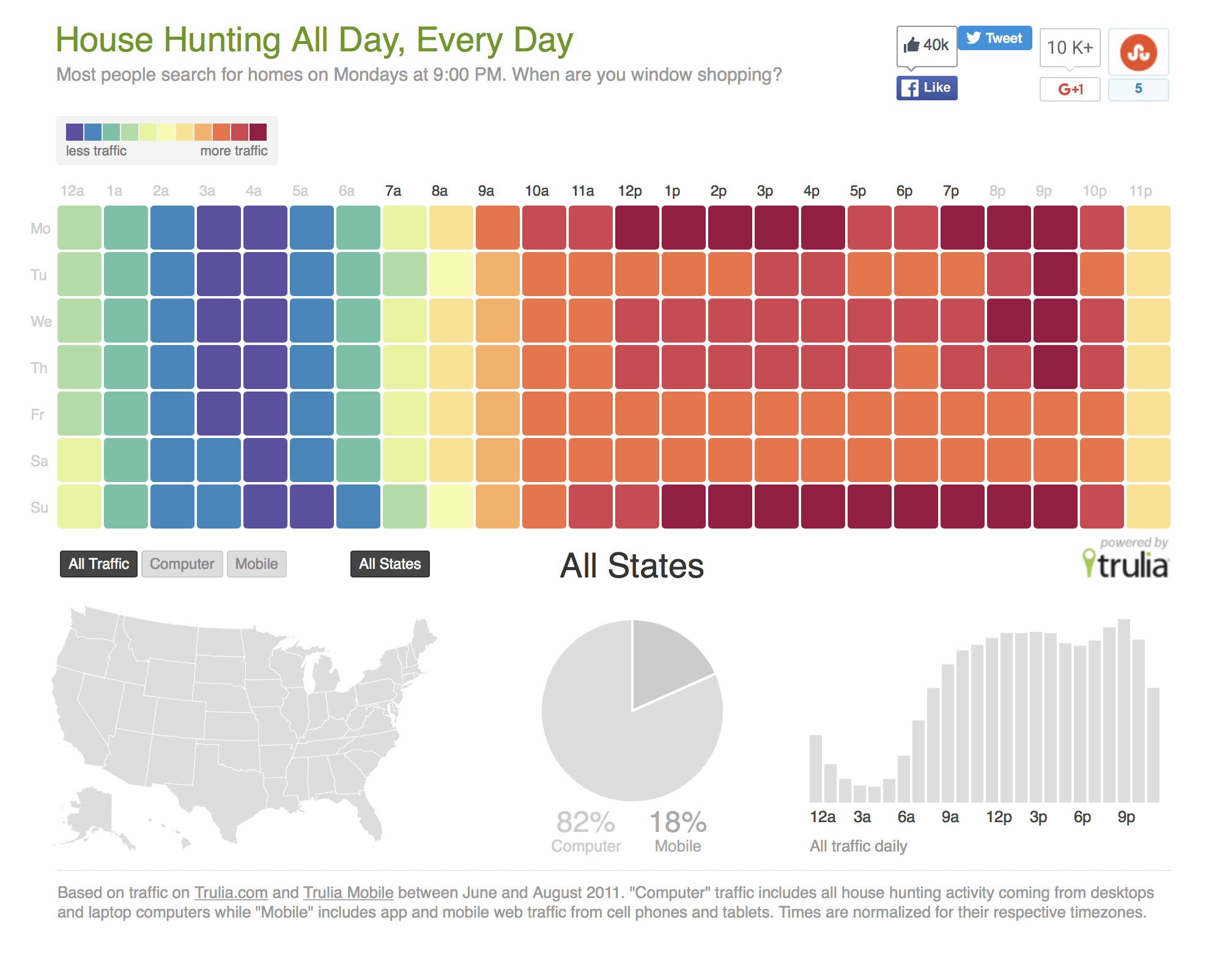
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Heat Map Scales: A Guide to Visualizing Data and Driving Insights. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!