Understanding the Power of Leg Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Your Supply Chain
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Leg Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Your Supply Chain
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Leg Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Your Supply Chain. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Leg Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Your Supply Chain
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Power of Leg Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Your Supply Chain
- 3.1 What is a Leg Map?
- 3.2 The Importance of Leg Maps
- 3.3 Constructing a Leg Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.4 Types of Leg Maps
- 3.5 Tools and Resources for Leg Map Creation
- 3.6 FAQs about Leg Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Creating Effective Leg Maps
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Power of Leg Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Your Supply Chain
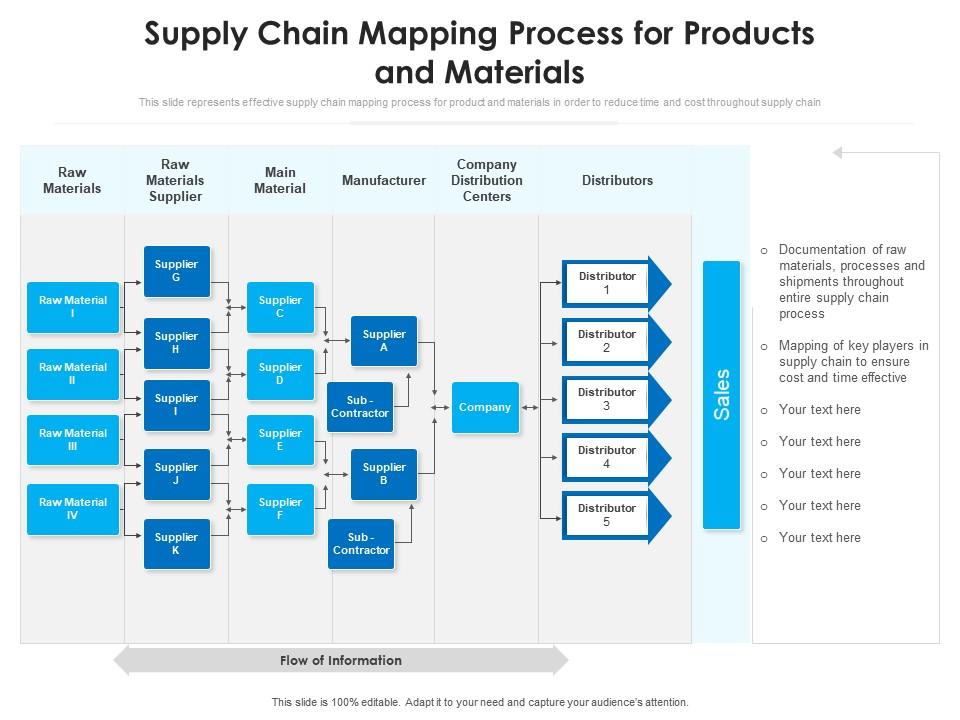
In the complex and intricate world of supply chain management, visibility is paramount. The ability to track goods, materials, and resources throughout their journey from origin to destination is crucial for maintaining efficiency, mitigating risks, and optimizing costs. This is where the concept of a "legs map" comes into play, offering a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding the intricate flow of goods within a supply chain.
What is a Leg Map?
A leg map, also known as a "supply chain map" or "logistics map," is a visual representation of the various stages and processes involved in moving goods from their source to their final destination. It encompasses the entire journey, including transportation modes, warehousing, processing, and distribution. Essentially, it provides a detailed blueprint of the supply chain, highlighting key touchpoints, potential bottlenecks, and areas for improvement.
The Importance of Leg Maps
The value of leg maps lies in their ability to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of the supply chain’s structure and dynamics. By mapping out the intricate network of processes and relationships, organizations gain insights that can significantly impact their operations.
Key Benefits of Leg Maps:
- Enhanced Visibility: Leg maps offer a clear and concise overview of the entire supply chain, enabling organizations to track the movement of goods, identify potential delays, and proactively address challenges.
- Improved Efficiency: By pinpointing bottlenecks and inefficiencies, leg maps facilitate optimization efforts, streamlining processes and reducing costs.
- Reduced Risk: By identifying potential vulnerabilities in the supply chain, leg maps enable organizations to develop mitigation strategies and minimize disruptions.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Leg maps foster communication and collaboration among different stakeholders within the supply chain, ensuring everyone is aligned on processes and objectives.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leg maps provide a structured framework for collecting and analyzing data, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on real-time insights.
Constructing a Leg Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a comprehensive and effective leg map requires a systematic approach. The following steps provide a framework for developing a valuable tool for supply chain management:
- Define Scope and Objectives: Clearly define the scope of the leg map, specifying the specific products, regions, and timeframes covered. Determine the specific objectives, such as identifying bottlenecks, improving efficiency, or reducing costs.
- Identify Key Stakeholders: Identify all parties involved in the supply chain, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and customers.
- Map the Supply Chain Flow: Trace the movement of goods from their source to their final destination, identifying each stage and process involved. This includes transportation modes, warehousing, processing, and distribution.
-
Document Key Information: For each stage in the supply chain, document key information, including:
- Location: Identify the specific location of each facility, warehouse, or transportation hub.
- Processes: Detail the activities performed at each stage, such as manufacturing, packaging, or distribution.
- Resources: Identify the resources used at each stage, such as equipment, personnel, or technology.
- Lead Times: Determine the average time required to complete each stage, including transportation, processing, and warehousing.
- Costs: Capture the costs associated with each stage, including transportation, labor, and materials.
- Visualize the Supply Chain: Create a visual representation of the supply chain, utilizing a flowchart, network diagram, or other appropriate visualization tools.
- Analyze and Interpret Data: Analyze the data collected and identify key insights, such as bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or potential risks.
- Develop Improvement Strategies: Based on the analysis, develop strategies to improve the supply chain, such as optimizing processes, reducing lead times, or mitigating risks.
- Implement and Monitor: Implement the improvement strategies and monitor their impact on the supply chain. Regularly review and update the leg map to reflect changes in the supply chain environment.
Types of Leg Maps
Leg maps can be tailored to meet specific needs and objectives, leading to different types of maps:
- Basic Leg Map: A simple representation of the supply chain flow, highlighting key stages and processes.
- Detailed Leg Map: A comprehensive map that includes detailed information on each stage, including resources, costs, and lead times.
- Risk-Based Leg Map: A map that focuses on identifying and mitigating potential risks within the supply chain.
- Process-Oriented Leg Map: A map that focuses on the specific processes involved in the supply chain, such as procurement, manufacturing, or distribution.
- Geographic Leg Map: A map that visualizes the geographic locations of all stakeholders involved in the supply chain.
Tools and Resources for Leg Map Creation
Several tools and resources are available to assist in the creation and analysis of leg maps:
- Spreadsheet Software: Software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets can be used to create basic leg maps and organize data.
- Mapping Software: Specialized mapping software, such as ArcGIS or QGIS, can be used to create detailed geographic representations of the supply chain.
- Supply Chain Management Software: Advanced supply chain management software often includes features for creating and analyzing leg maps.
- Online Resources: Numerous online resources offer templates, examples, and guides for creating leg maps.
FAQs about Leg Maps
1. What are the key benefits of using a leg map?
Leg maps offer several benefits, including enhanced visibility, improved efficiency, reduced risk, enhanced collaboration, and data-driven decision-making.
2. How can a leg map help improve supply chain efficiency?
By identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, leg maps enable organizations to streamline processes, reduce lead times, and optimize resource utilization.
3. What are some common challenges in creating a leg map?
Challenges include data collection, stakeholder involvement, and maintaining accuracy and relevance over time.
4. How can a leg map be used to mitigate supply chain risks?
By identifying potential vulnerabilities, leg maps enable organizations to develop mitigation strategies, such as alternative suppliers or transportation routes.
5. How often should a leg map be reviewed and updated?
Leg maps should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in the supply chain environment, such as new suppliers, transportation routes, or regulatory requirements.
Tips for Creating Effective Leg Maps
- Start with a clear objective: Define the specific purpose and scope of the leg map before you begin.
- Involve key stakeholders: Ensure that all relevant parties contribute to the process, providing valuable insights and perspectives.
- Use clear and concise language: Utilize consistent terminology and avoid jargon to ensure everyone understands the information.
- Visualize the data effectively: Use charts, graphs, and other visual elements to make the map easy to understand and interpret.
- Focus on key insights: Highlight the most important information and avoid overwhelming the audience with unnecessary details.
- Regularly review and update: Ensure the leg map remains accurate and relevant by regularly reviewing and updating it to reflect changes in the supply chain environment.
Conclusion
Leg maps serve as powerful tools for understanding, visualizing, and optimizing supply chain operations. By providing a comprehensive overview of the entire journey of goods, leg maps enable organizations to identify bottlenecks, mitigate risks, and make informed decisions. Implementing a robust leg map strategy can lead to significant improvements in efficiency, cost reduction, and overall supply chain resilience. As businesses navigate increasingly complex and dynamic supply chain landscapes, the importance of leg maps will only continue to grow.

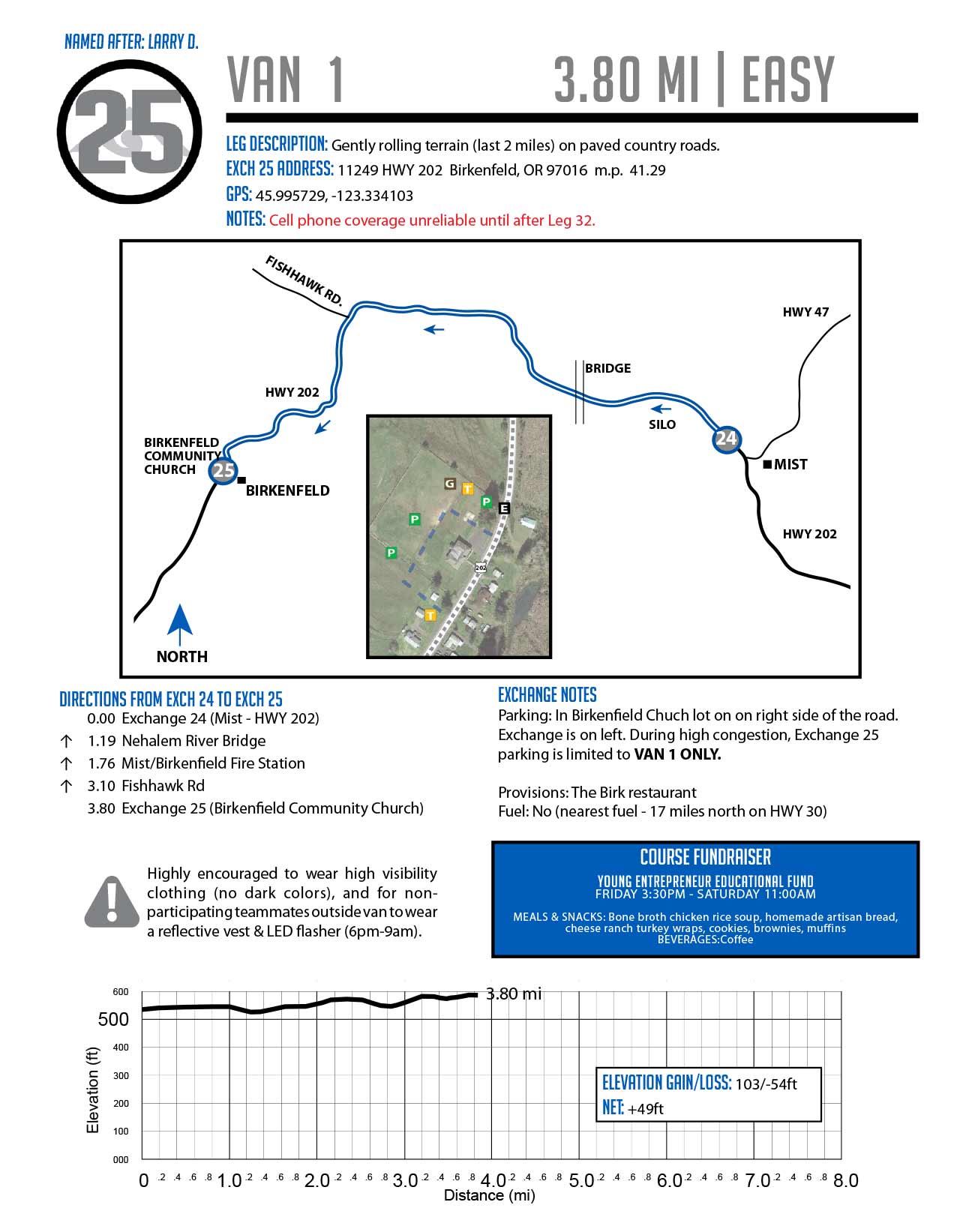

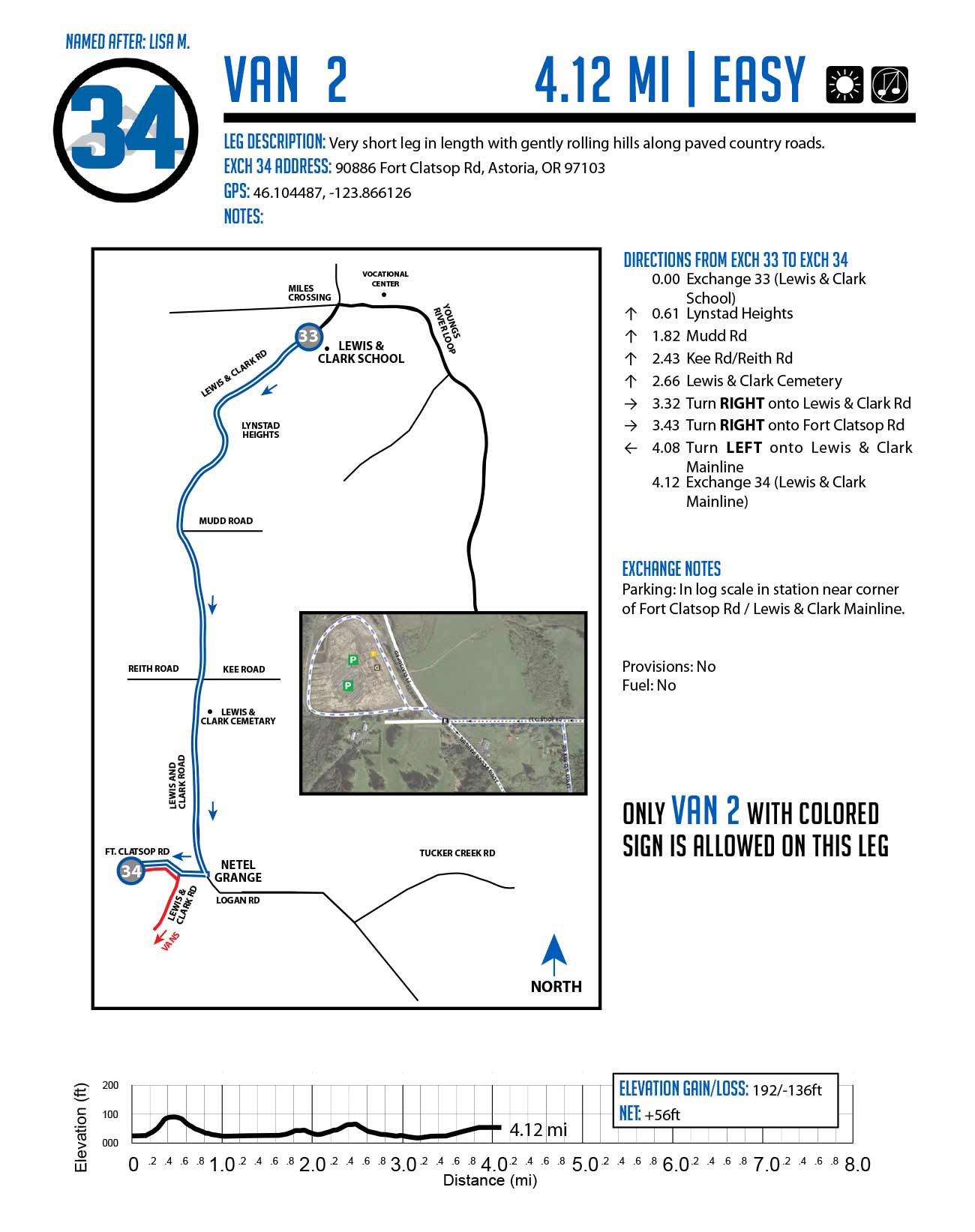



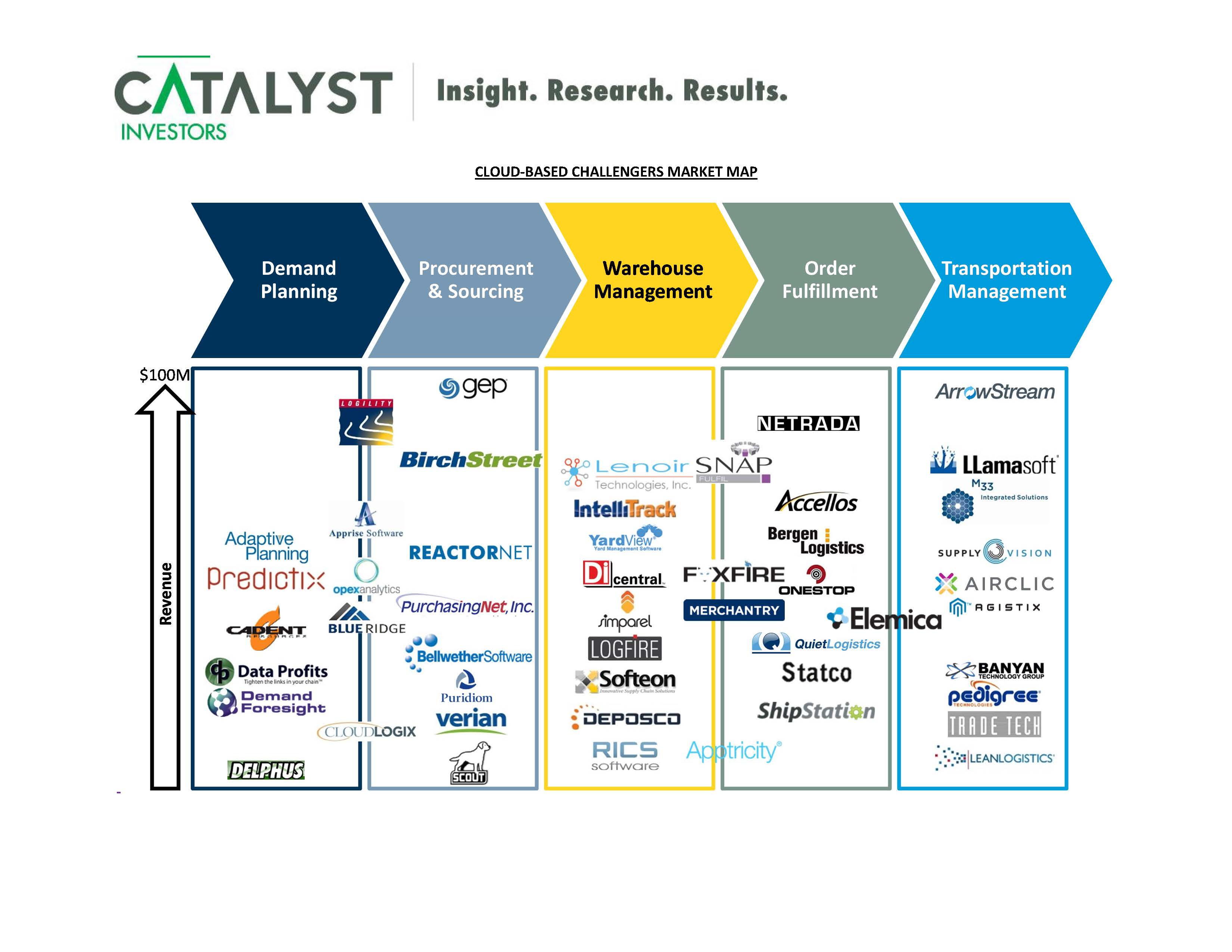
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Leg Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Your Supply Chain. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!