Unpacking the Story of Sweden: A Comprehensive Look at its Population Distribution
Related Articles: Unpacking the Story of Sweden: A Comprehensive Look at its Population Distribution
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unpacking the Story of Sweden: A Comprehensive Look at its Population Distribution. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unpacking the Story of Sweden: A Comprehensive Look at its Population Distribution

Sweden, a Scandinavian nation renowned for its scenic beauty, progressive policies, and high standard of living, boasts a population distribution that reflects its unique history, geography, and socio-economic development. Understanding the nuances of this distribution is crucial for gaining insights into the country’s demographic trends, urban planning challenges, and the overall well-being of its citizens.
This article delves into the intricacies of Sweden’s population map, providing a comprehensive overview of its key features, historical context, and the factors influencing its current state.
A Glimpse into the Landscape:
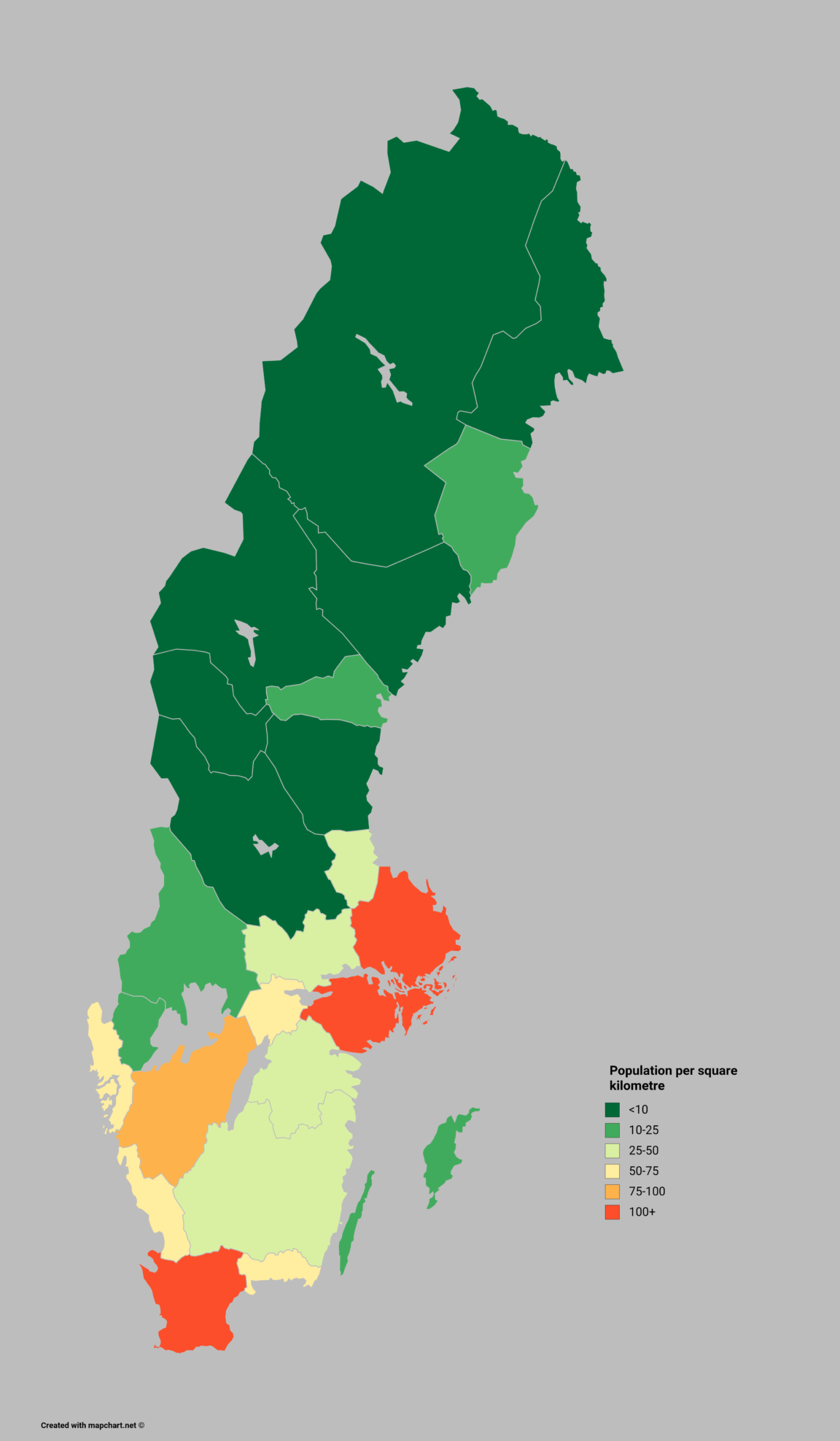
The Swedish population map, at a glance, reveals a striking pattern: a concentration of people in the southern and eastern regions, with a gradual decrease in density towards the north. This pattern is largely attributed to the country’s geography and historical development. The southern and eastern regions offer a more favorable climate, fertile land, and proximity to major trade routes, making them ideal for settlement and economic activity.
Historical Influences Shaping the Map:
The current population distribution is deeply rooted in Sweden’s historical journey.
- Early Settlement Patterns: The first settlers in Sweden gravitated towards the southern and eastern regions, attracted by their fertile land and access to resources. This established a foundation for population growth in these areas.
- Industrial Revolution: The Industrial Revolution, which began in the 18th century, further concentrated population in the southern and eastern regions, as industries flourished in these areas. This created a pull factor for people seeking employment opportunities.
- Urbanization: The 20th century witnessed a significant shift towards urbanization in Sweden. This led to the growth of major cities like Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö, further concentrating population in the southern and eastern regions.
Key Features of the Map:
- Densely Populated Regions: The southern and eastern regions, particularly the area around Stockholm, exhibit high population density. This area is home to major cities, industrial centers, and a significant portion of the country’s economic activity.
- Sparsely Populated Regions: The northern and western regions are characterized by low population density. These areas are dominated by forests, mountains, and vast stretches of wilderness, making them less suitable for large-scale settlements.
- Coastal Concentration: Sweden’s coastline, especially in the southern and eastern regions, is a major hub of population. This is driven by historical factors, maritime trade, and the availability of resources.
Factors Influencing Population Distribution:
Several factors, both historical and contemporary, influence the distribution of population in Sweden:
- Climate: The temperate climate of the southern and eastern regions provides a more favorable environment for human habitation, contributing to higher population density in these areas.
- Economic Opportunities: The concentration of industries, businesses, and employment opportunities in the southern and eastern regions attracts people seeking better livelihoods.
- Infrastructure: The development of infrastructure, including transportation networks, communication systems, and public services, is more concentrated in the southern and eastern regions, further attracting population.
- Education and Healthcare: The availability of high-quality education and healthcare facilities in the southern and eastern regions makes these areas more attractive to families and individuals.
- Cultural and Social Factors: The presence of vibrant cultural centers, diverse communities, and a higher concentration of social services in the southern and eastern regions attracts people seeking a more fulfilling lifestyle.
Implications of Population Distribution:
The current population distribution in Sweden has several implications:
- Urban Development Challenges: The concentration of population in major cities presents challenges in terms of housing, transportation, and infrastructure management.
- Regional Disparities: The disparity in population density between different regions can lead to economic and social inequalities, as resources and opportunities are concentrated in more densely populated areas.
- Environmental Impacts: The concentration of population in certain areas can exert pressure on natural resources and the environment, requiring sustainable development strategies.
- Social Cohesion: The distribution of population can impact social cohesion and integration, as different regions may experience varying levels of cultural diversity and social interaction.
Understanding the Map: A Vital Tool for Policymaking:
The Swedish population map serves as a valuable tool for policymakers, urban planners, and researchers, providing essential insights for:
- Developing Regional Development Strategies: Understanding the population distribution helps policymakers allocate resources and prioritize development initiatives to address regional disparities and promote equitable growth.
- Planning Urban Infrastructure: The map provides insights into the population density and distribution patterns, enabling urban planners to design infrastructure projects that meet the needs of the growing population.
- Addressing Social and Economic Issues: The map helps identify areas with high population density and potential social or economic challenges, enabling policymakers to develop targeted interventions to address these issues.
- Monitoring Demographic Trends: The map can be used to track changes in population distribution over time, providing insights into migration patterns, urbanization trends, and the impact of demographic shifts on the country’s development.
FAQs about Sweden’s Population Map:
Q: What is the current population of Sweden?
A: As of 2023, the population of Sweden is approximately 10.5 million.
Q: Which region of Sweden has the highest population density?
A: The region around Stockholm, the capital city, has the highest population density in Sweden.
Q: What are the main factors contributing to the concentration of population in the south and east?
A: The main factors include a more favorable climate, fertile land, proximity to trade routes, and the concentration of industries and economic opportunities.
Q: Are there any areas in Sweden experiencing population decline?
A: Yes, some rural areas in northern and western Sweden are experiencing population decline due to factors such as limited employment opportunities, lack of infrastructure, and outmigration.
Q: How does the population distribution in Sweden compare to other Scandinavian countries?
A: Compared to its Scandinavian neighbors, Sweden has a relatively more centralized population distribution, with a higher concentration in the southern and eastern regions.
Tips for Understanding Sweden’s Population Map:
- Visualize the Data: Use online maps and interactive tools to visualize the population distribution and identify key patterns and trends.
- Consider Historical Context: Understand the historical factors that have shaped the current population distribution, such as migration patterns, industrialization, and urbanization.
- Analyze Regional Differences: Compare population density, economic indicators, and social characteristics across different regions to identify areas with potential challenges and opportunities.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of the latest demographic trends and population projections to understand how the population distribution is evolving over time.
Conclusion:
The Swedish population map is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s demographic landscape and its implications for development, policymaking, and social well-being. By analyzing the distribution patterns, historical context, and influencing factors, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the unique dynamics of Sweden’s population and the challenges and opportunities it presents.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking the Story of Sweden: A Comprehensive Look at its Population Distribution. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!