Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of Virginia: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Fault Lines
Related Articles: Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of Virginia: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Fault Lines
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of Virginia: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Fault Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of Virginia: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Fault Lines
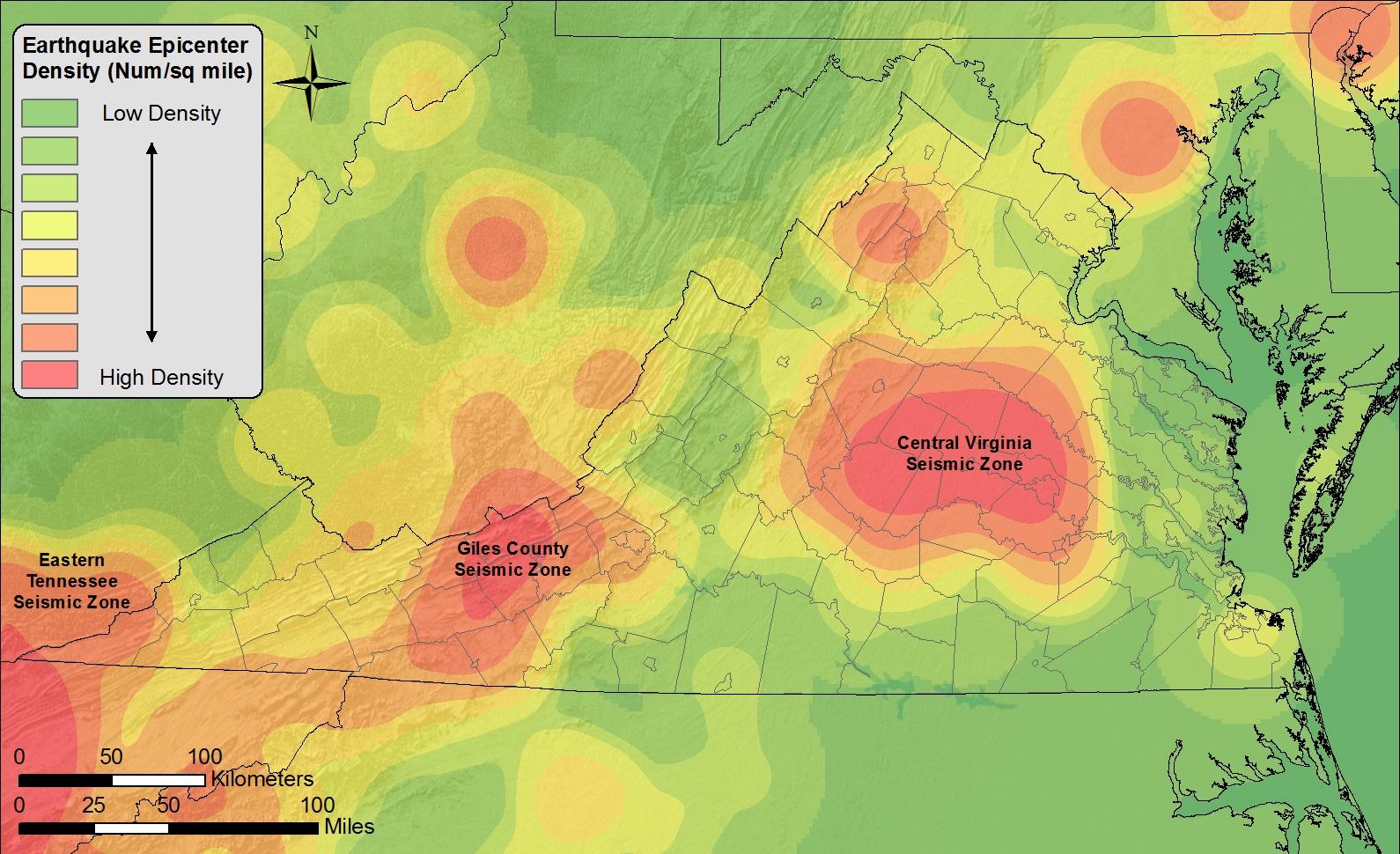
Virginia, a state steeped in history and natural beauty, sits atop a complex geological foundation. Beneath its rolling hills and coastal plains lies a network of faults, remnants of ancient tectonic activity that continue to shape the state’s landscape and influence its seismic potential. Understanding the location and characteristics of these faults is crucial for mitigating seismic risks and ensuring the safety of its residents and infrastructure.
The Geological Underpinnings of Virginia’s Fault Lines
Virginia’s fault lines are primarily a result of the ongoing collision between the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates. This collision, occurring over millions of years, has generated immense forces that have fractured and shifted the Earth’s crust, creating the fault lines we see today.
Types of Faults in Virginia
Faults are classified based on the direction of movement between the rock masses on either side of the fracture. In Virginia, the most prominent types include:
-
Normal Faults: These faults form when the hanging wall (the rock mass above the fault) moves downward relative to the footwall (the rock mass below the fault). This type of movement is typically associated with extensional forces, where the Earth’s crust is being stretched apart.
-
Reverse Faults: Reverse faults occur when the hanging wall moves upward relative to the footwall. This movement is driven by compressional forces, where the Earth’s crust is being squeezed together.
-
Strike-Slip Faults: Strike-slip faults involve horizontal movement of the rock masses on either side of the fault, parallel to the fault’s strike (the direction of the fault line). This type of movement is associated with shearing forces, where the Earth’s crust is being pushed past each other laterally.
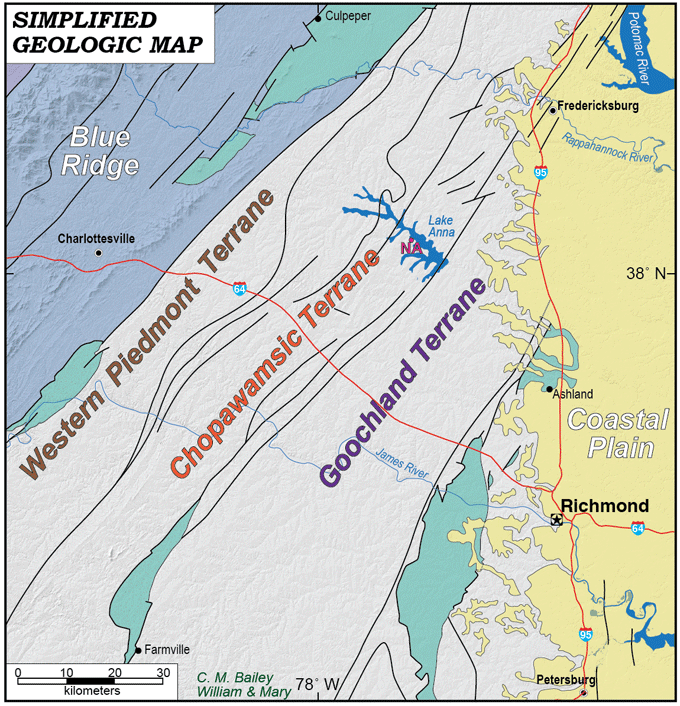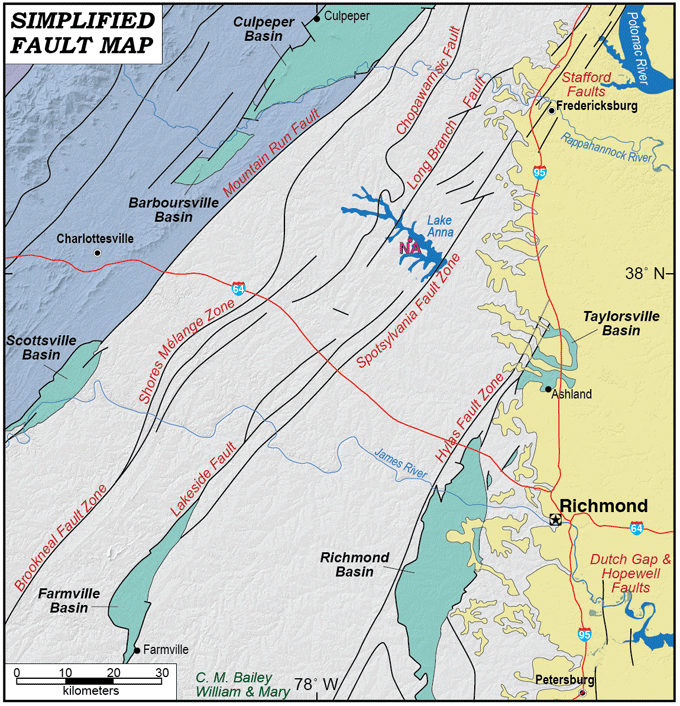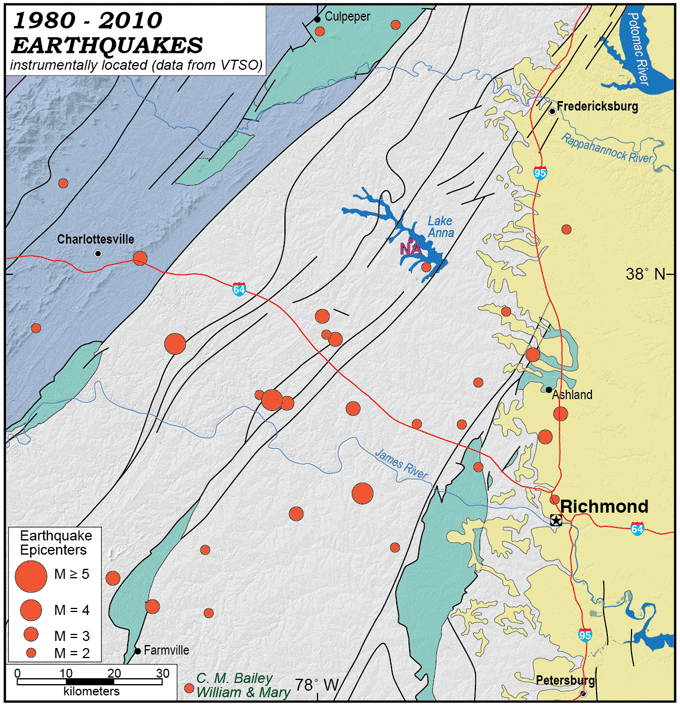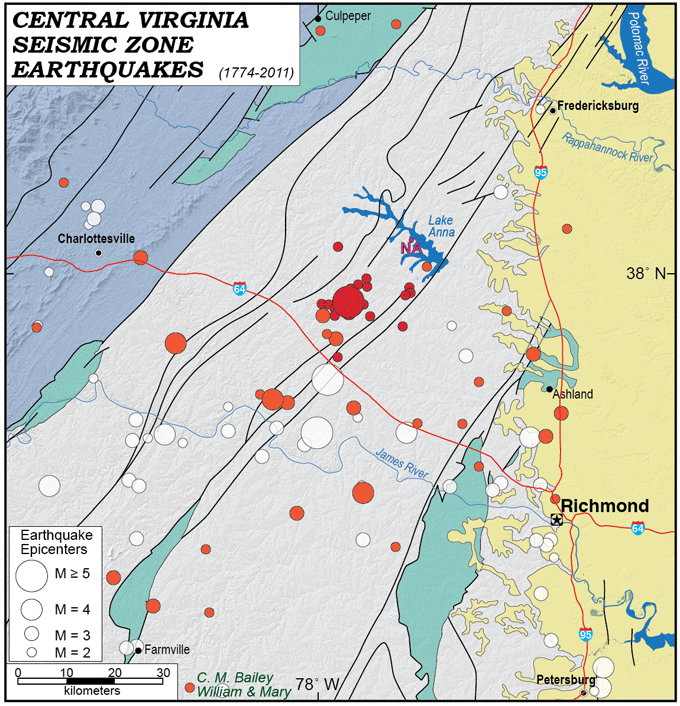
Key Fault Zones in Virginia
Several major fault zones traverse Virginia, each with its unique characteristics and seismic potential:
-
The Appalachian Thrust Belt: This belt, stretching from Pennsylvania to Alabama, represents a zone of significant compressional forces. The thrust faults within this belt have pushed older rocks over younger rocks, creating the prominent Appalachian Mountains. The Blue Ridge Mountains in Virginia are a direct result of this tectonic activity.
-
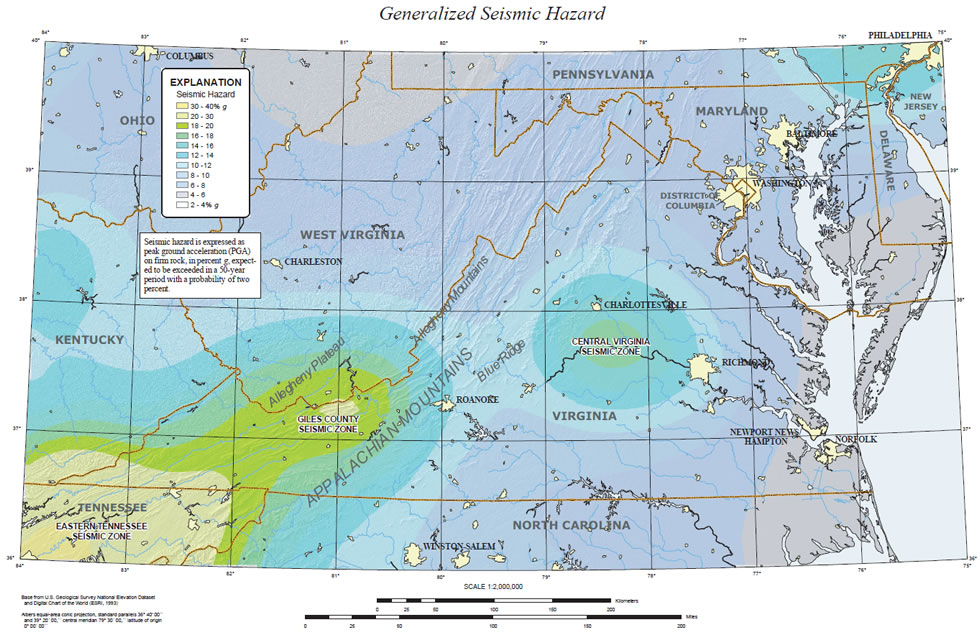
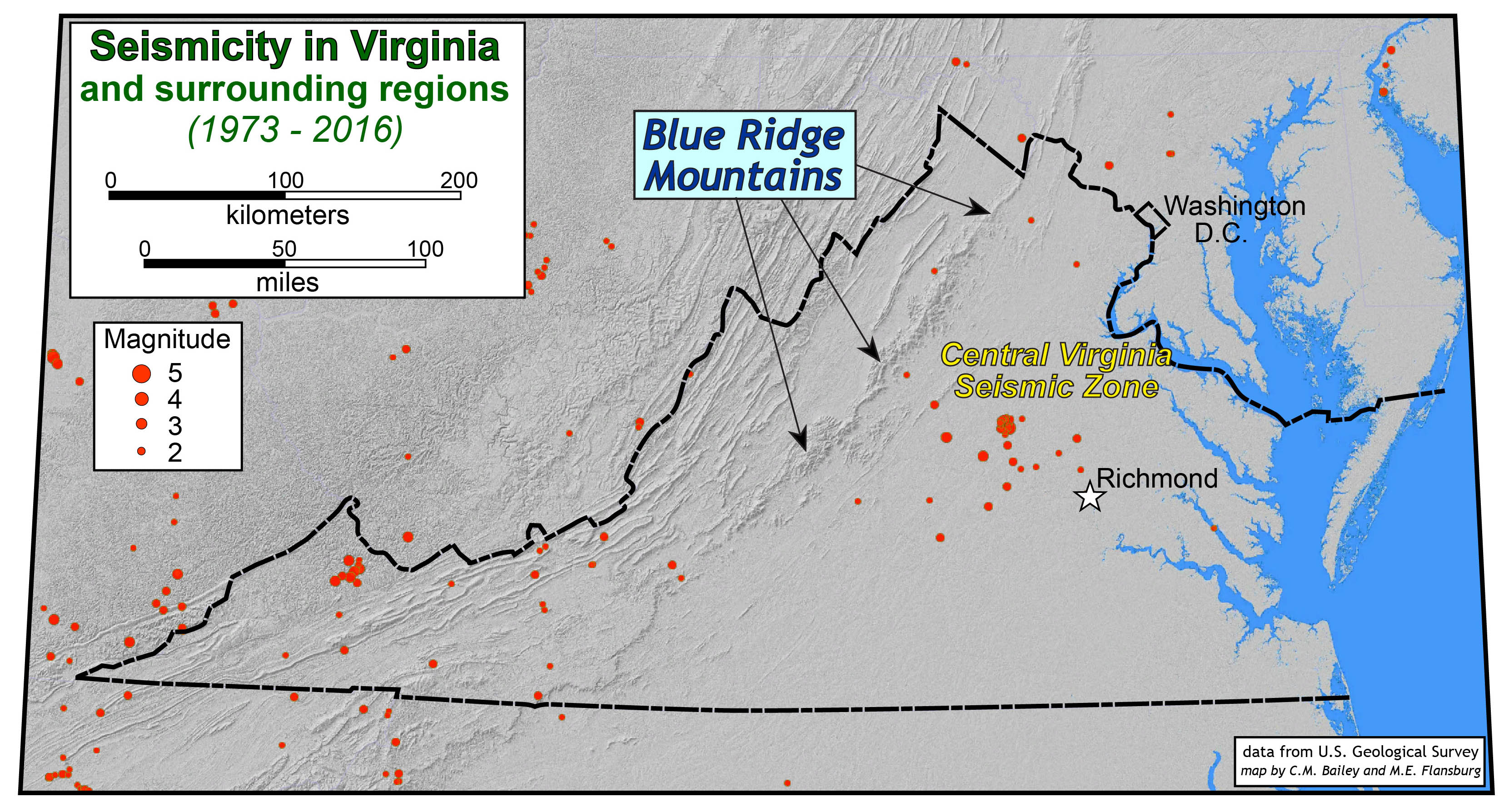
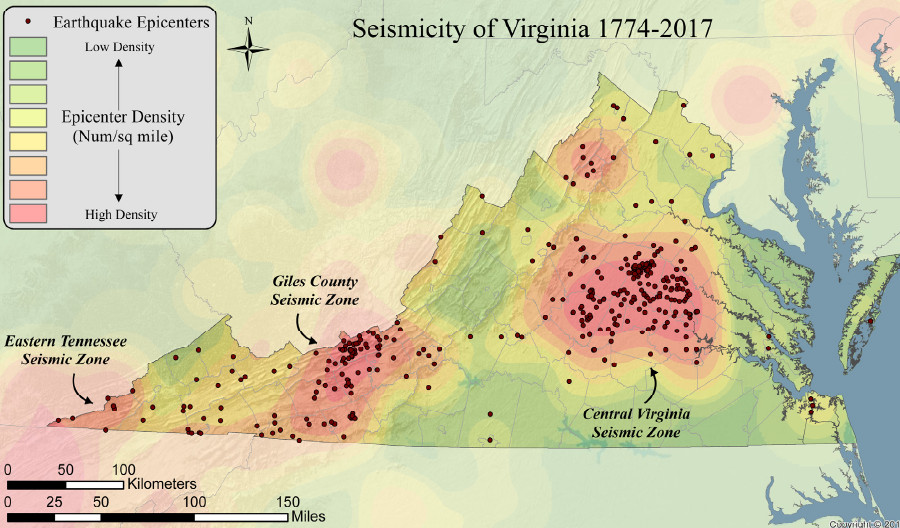
The Brevard Fault Zone: This major fault zone runs along the eastern edge of the Blue Ridge Mountains, extending from North Carolina into Virginia. It represents a zone of significant shear, with lateral movement of rock masses. The Brevard Fault Zone has been linked to several earthquakes throughout history, including the 1897 Giles County earthquake, the largest recorded earthquake in Virginia.
-
The Eastern Shore Fault Zone: This zone extends along the eastern coast of Virginia, running parallel to the Chesapeake Bay. It is associated with normal faulting, suggesting a zone of extensional forces. While this fault zone is less active than the Brevard Zone, it still poses a potential seismic hazard.
The Significance of Mapping Virginia’s Fault Lines
Mapping Virginia’s fault lines is crucial for several reasons:
-
Understanding Seismic Risk: Fault lines represent zones of weakness in the Earth’s crust, making them prone to earthquakes. Mapping these faults allows scientists to identify areas with higher seismic risk, enabling them to develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
-
Infrastructure Planning and Development: Knowledge of fault locations is essential for the planning and construction of critical infrastructure, such as dams, power plants, and bridges. By avoiding construction over or near active fault lines, engineers can minimize the risk of structural damage during earthquakes.
-
Land Use Planning: Mapping fault lines provides valuable information for land use planning, guiding the development of safe and sustainable communities. By avoiding development in high-risk areas, policymakers can reduce the potential for earthquake-related damage and casualties.
Navigating the Virginia Fault Line Map
Several resources are available to access and interpret Virginia’s fault line map:
-
The Virginia Department of Mines, Minerals and Energy (DMME): The DMME maintains a comprehensive geological database, including maps depicting major fault zones and seismic activity in Virginia.
-
The United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS provides a national earthquake hazard map, which includes information on fault locations and potential earthquake magnitudes.
-
Online Mapping Tools: Several online mapping tools, such as Google Earth and ArcGIS, allow users to overlay fault line data onto satellite imagery, providing a visual representation of the state’s seismic landscape.
Understanding the Data
Fault line maps typically depict the location and type of faults, along with their estimated age and activity. It’s important to note that:
-
Not all fault lines are active: While some fault lines are currently active and pose a seismic risk, others are inactive and represent remnants of past tectonic activity.
-
Fault lines can be complex: Fault lines are often interconnected and can extend for significant distances, making it challenging to map their exact boundaries.
-
Seismic risk is not uniform: While fault lines are important indicators of seismic risk, other factors, such as the type of rock, soil conditions, and building codes, also contribute to the overall earthquake vulnerability of a region.
FAQs about Virginia’s Fault Lines
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in Virginia?
A: Virginia experiences relatively infrequent earthquakes compared to other regions of the United States. However, the state has a history of significant seismic events, including the 1897 Giles County earthquake, which registered a magnitude of 5.8 on the Richter scale.
Q: Are Virginia’s fault lines a cause for concern?
A: While Virginia’s fault lines pose a potential seismic hazard, the risk of a major earthquake is relatively low. However, it’s important to be prepared for the possibility of earthquakes, particularly in areas near known fault zones.
Q: What steps can I take to prepare for an earthquake?
A: To prepare for an earthquake, it’s essential to:
-
Secure heavy objects: Secure heavy furniture and appliances to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
-
Develop an emergency plan: Create a family emergency plan, including evacuation routes and a designated meeting point.
-
Prepare an emergency kit: Assemble a kit containing essential supplies, such as food, water, first-aid supplies, and a flashlight.
Tips for Understanding and Navigating Virginia’s Fault Lines
-
Consult reliable sources: Refer to maps and information from reputable organizations like the DMME and USGS for accurate and up-to-date data on Virginia’s fault lines.
-
Stay informed about earthquake preparedness: Learn about earthquake safety measures and participate in community preparedness programs.
-
Consider the location of your home: If you are considering purchasing a home in Virginia, research the proximity of the property to known fault lines.
Conclusion
Virginia’s fault lines are a testament to the dynamic geological processes that have shaped the state over millions of years. Understanding these faults is crucial for mitigating seismic risks and ensuring the safety of Virginia’s residents and infrastructure. By utilizing available resources and staying informed about earthquake preparedness, Virginians can navigate the state’s seismic landscape with greater awareness and resilience. The ongoing study and mapping of these fault lines will continue to provide valuable insights into the state’s seismic potential, enabling us to build a safer and more sustainable future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of Virginia: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Fault Lines. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!