Unraveling the Topography of Eastern Europe: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unraveling the Topography of Eastern Europe: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Topography of Eastern Europe: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Topography of Eastern Europe: A Comprehensive Guide
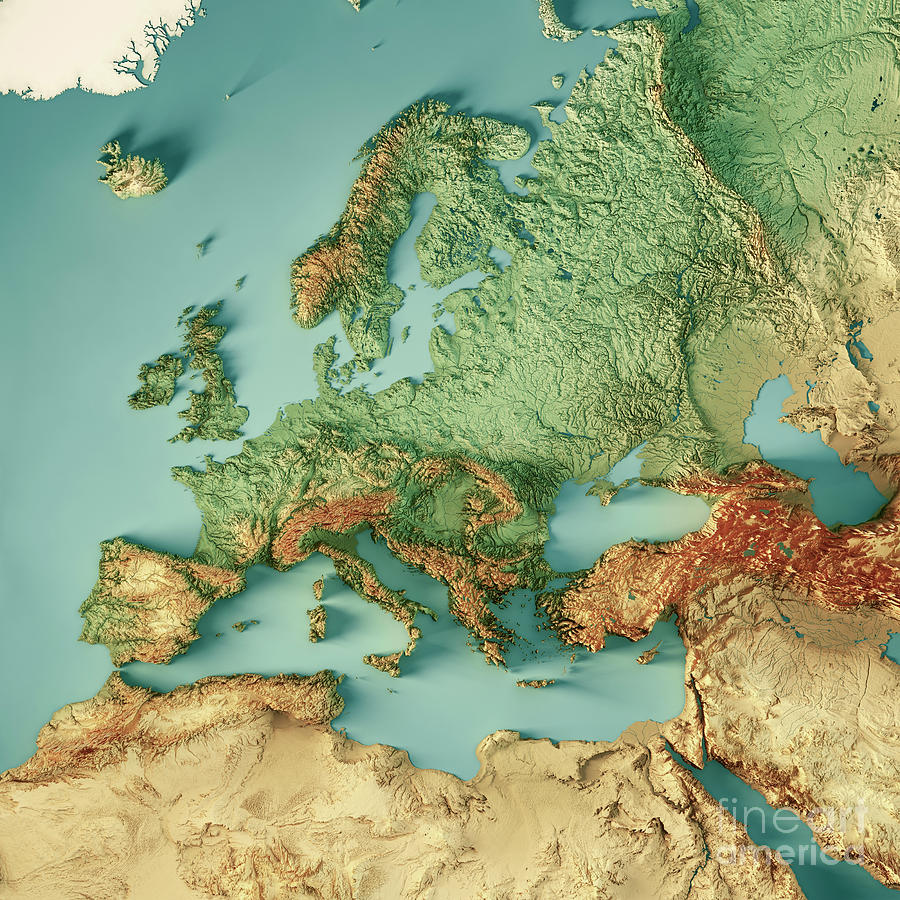
Eastern Europe, a region encompassing a diverse array of landscapes, cultures, and histories, presents a fascinating study in topography. Understanding its diverse terrain is crucial for comprehending its geological evolution, its impact on human settlements and infrastructure, and its significance in shaping the region’s economic and political landscape. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Eastern Europe’s topography, exploring its key features, their origins, and their implications for the region’s development.
A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring Eastern Europe’s Diverse Topography
Eastern Europe’s topography is a captivating mosaic of contrasting landscapes, each with its unique geological history and characteristics. From the towering Carpathian Mountains to the vast plains of the East European Plain, the region presents a diverse range of geographical features, each playing a significant role in shaping the region’s identity.
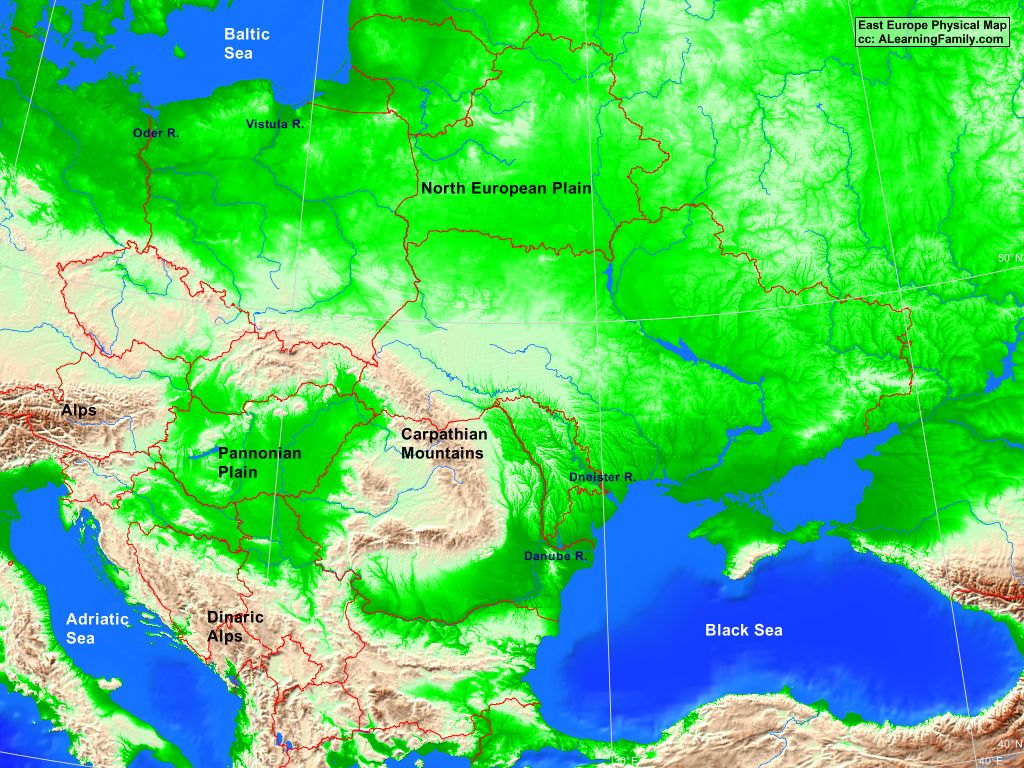
1. The Carpathian Mountains: A Majestic Spine
The Carpathian Mountains, stretching across a vast arc from the Czech Republic to Romania, form the backbone of Eastern Europe’s topography. This mountain range, a product of tectonic activity and volcanic eruptions, is a testament to the region’s dynamic geological past. The Carpathians are characterized by their rugged peaks, deep valleys, and dense forests, offering a haven for diverse flora and fauna.
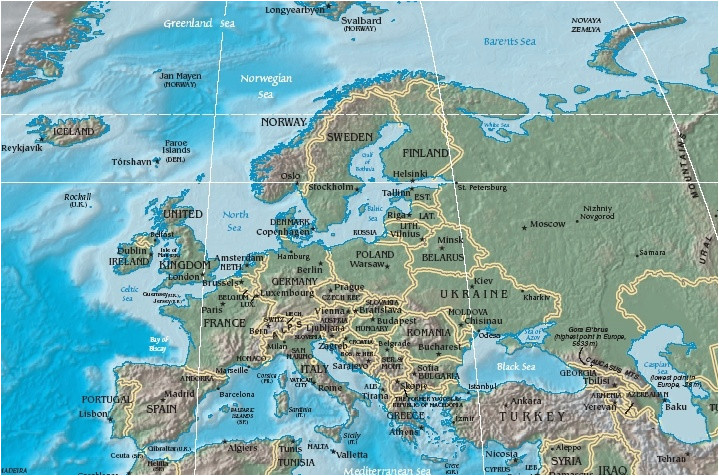
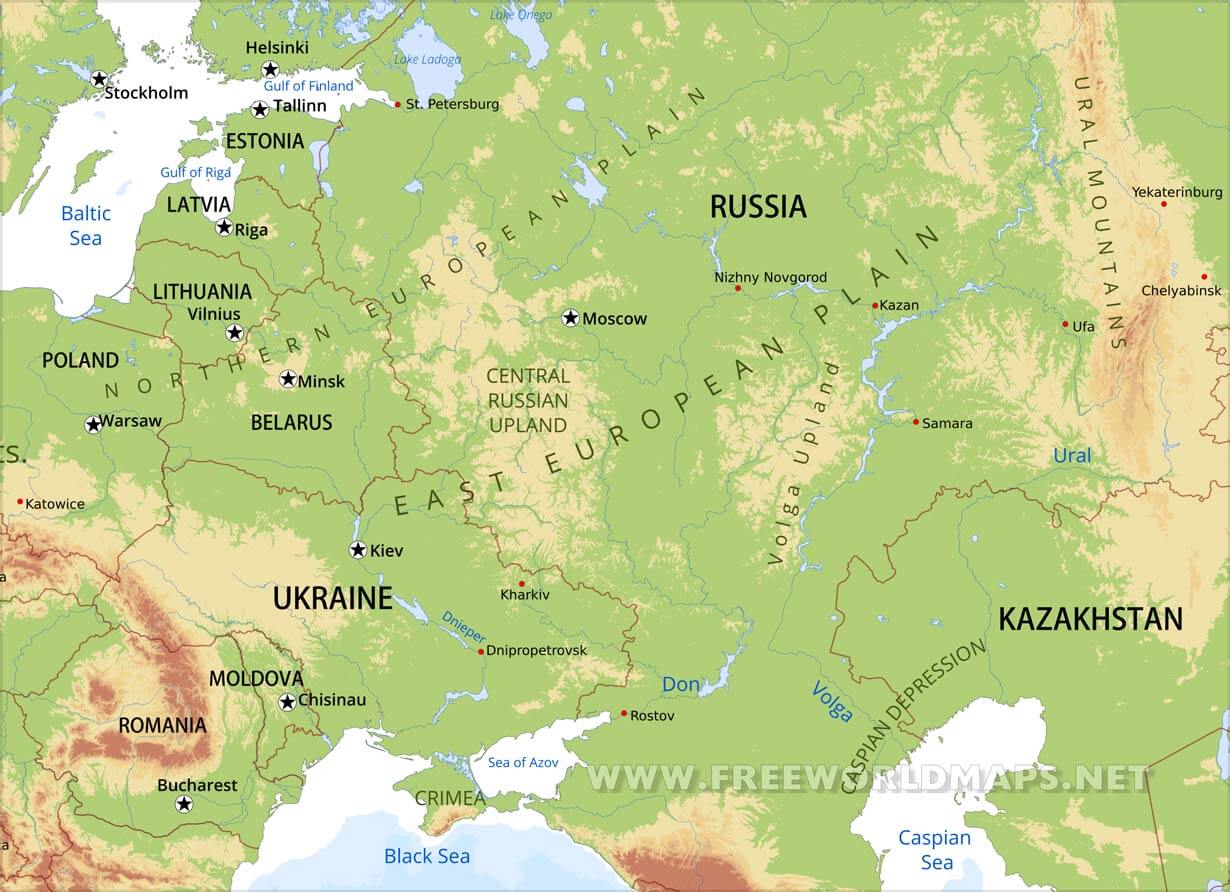
2. The East European Plain: A Vast and Fertile Realm
The East European Plain, sprawling across vast swathes of Eastern Europe, is a testament to the region’s sedimentary past. This vast expanse of flat land, formed over millions of years by the deposition of sediments, is characterized by its fertile soils and its role as a major agricultural hub. The plain’s flat topography has also facilitated the development of extensive transportation networks, connecting major cities and fostering trade.
3. The Caucasus Mountains: A Bridge Between Continents
The Caucasus Mountains, a formidable range spanning the border between Europe and Asia, mark a significant topographic transition. This mountain range, formed by the collision of the Eurasian and Arabian tectonic plates, is home to some of the highest peaks in Europe, including Mount Elbrus, the highest peak in Europe. The Caucasus Mountains, with their rugged terrain and diverse ecosystems, are a testament to the region’s geological dynamism.
4. The Balkan Mountains: A Rugged and Historic Landscape
The Balkan Mountains, a rugged range extending from the Danube River to the Aegean Sea, are a defining feature of Southeastern Europe. This mountain range, formed by the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates, is known for its steep slopes, deep gorges, and rich history. The Balkans, with their strategic location and diverse terrain, have played a pivotal role in shaping the region’s political and cultural landscape.
5. The Dinaric Alps: A Limestone Frontier
The Dinaric Alps, a limestone mountain range extending along the Adriatic coast, are a distinctive feature of Southeastern Europe. This range, formed by the uplift of the Adriatic Plate, is characterized by its steep slopes, karst formations, and abundant caves. The Dinaric Alps, with their unique topography, have played a significant role in shaping the region’s biodiversity and cultural identity.
Understanding the Significance of Eastern Europe’s Topography
Eastern Europe’s topography is not merely a collection of geographical features; it is a powerful force that has shaped the region’s history, culture, and development.
1. Shaping Human Settlements
The region’s topography has played a pivotal role in influencing the location and development of human settlements. Mountains have provided natural barriers, shaping the boundaries of empires and fostering distinct cultural identities. Plains, on the other hand, have facilitated the growth of agriculture, trade, and urban centers.
2. Influencing Infrastructure Development
Eastern Europe’s topography has presented both challenges and opportunities for infrastructure development. Mountains have posed obstacles to transportation networks, while plains have facilitated the construction of roads, railways, and pipelines. The region’s diverse terrain has also influenced the development of hydroelectric power, mining, and forestry industries.
3. Impacting Climate and Biodiversity
Eastern Europe’s topography has a profound impact on its climate and biodiversity. Mountains create rain shadows, influencing precipitation patterns and shaping distinct microclimates. The region’s diverse terrain supports a wide range of ecosystems, from alpine meadows to temperate forests and coastal wetlands, contributing to its remarkable biodiversity.
4. Defining Political and Economic Landscapes
Eastern Europe’s topography has played a significant role in shaping the region’s political and economic landscapes. Mountains have served as natural boundaries, influencing the formation of nation-states and fostering regional identities. The region’s diverse terrain has also influenced its economic development, shaping its agricultural, industrial, and tourism sectors.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into Eastern Europe’s Topography
Q1: What are the major topographic features of Eastern Europe?
A: Eastern Europe’s topography is characterized by a diverse array of features, including the Carpathian Mountains, the East European Plain, the Caucasus Mountains, the Balkan Mountains, and the Dinaric Alps.
Q2: How has Eastern Europe’s topography influenced its history?
A: Eastern Europe’s topography has played a pivotal role in shaping its history, influencing the location of settlements, the development of trade routes, and the formation of empires.
Q3: What are the major challenges and opportunities presented by Eastern Europe’s topography?
A: Eastern Europe’s topography presents both challenges and opportunities. Mountains can pose obstacles to infrastructure development, while plains facilitate transportation and agriculture. The region’s diverse terrain also presents opportunities for tourism, hydroelectric power, and mining.
Q4: How does Eastern Europe’s topography impact its climate and biodiversity?
A: Eastern Europe’s topography influences its climate and biodiversity. Mountains create rain shadows, shaping precipitation patterns and fostering diverse microclimates. The region’s diverse terrain supports a wide range of ecosystems, contributing to its remarkable biodiversity.
Q5: What are the future implications of Eastern Europe’s topography?
A: Understanding Eastern Europe’s topography is crucial for sustainable development, resource management, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. The region’s diverse terrain presents challenges and opportunities for infrastructure development, resource utilization, and conservation efforts.
Tips: Exploring Eastern Europe’s Topography Further
- Utilize topographic maps: Topographic maps, with their detailed representation of elevation and terrain, provide invaluable insights into Eastern Europe’s landscape.
- Explore satellite imagery: Satellite imagery offers a comprehensive view of the region’s topography, revealing its major features and their relationships.
- Engage with local communities: Local communities possess a wealth of knowledge about the region’s topography, its impact on their lives, and its cultural significance.
- Explore historical records: Historical records, including maps, documents, and archaeological evidence, provide valuable insights into how Eastern Europe’s topography has shaped its history.
Conclusion: A Landscape of Diversity and Opportunity
Eastern Europe’s topography is a testament to the region’s dynamic geological history, its diverse landscapes, and its rich cultural heritage. Understanding its diverse terrain is crucial for comprehending the region’s development, its environmental challenges, and its potential for sustainable growth. By appreciating the intricacies of Eastern Europe’s topography, we gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating region and its unique place in the world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Topography of Eastern Europe: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!