Unveiling Asia: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Mapping
Related Articles: Unveiling Asia: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Mapping
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Asia: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Asia: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Asia: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Mapping
- 3.1 The Power of Satellite Mapping: A Glimpse into Asia’s Dynamic Landscape
- 3.2 Exploring the Landscape: A Look at Different Types of Satellite Maps
- 3.3 Navigating the Data: Essential Tools and Techniques for Asia Satellite Map Analysis
- 3.4 The Future of Asia Satellite Mapping: Trends and Innovations
- 3.5 FAQs about Asia Satellite Mapping
- 3.6 Tips for Utilizing Asia Satellite Mapping
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Asia: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Mapping

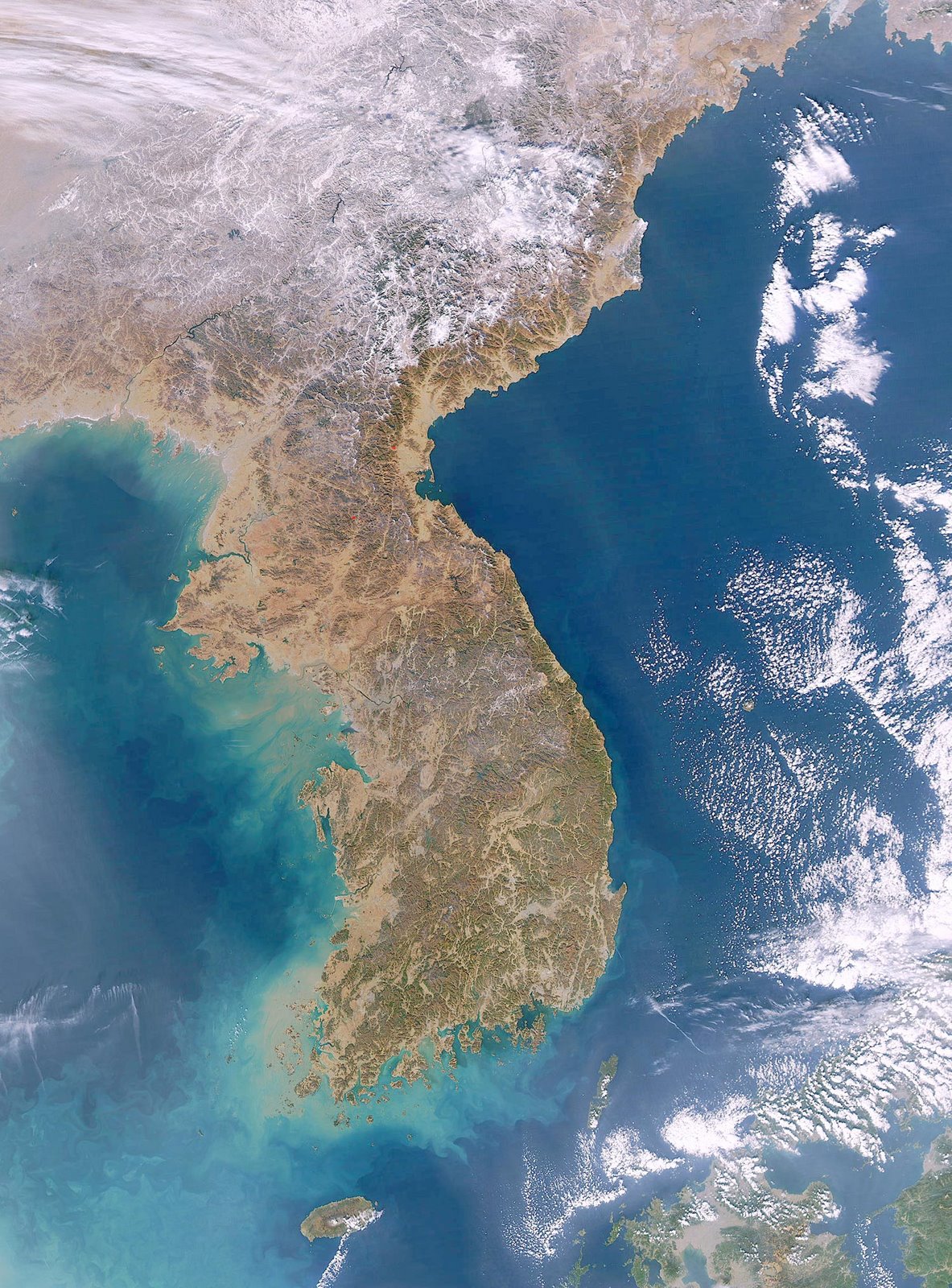
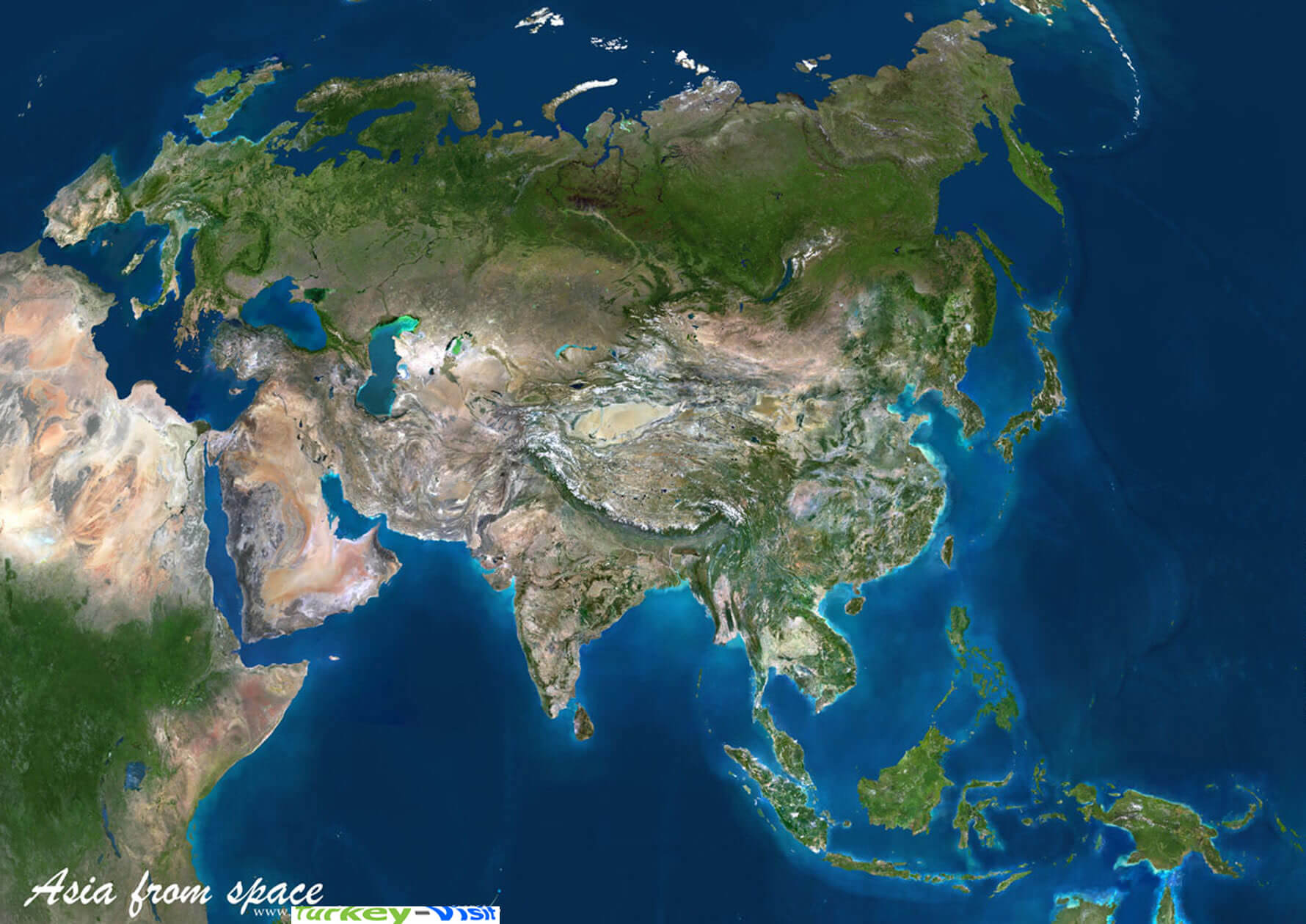
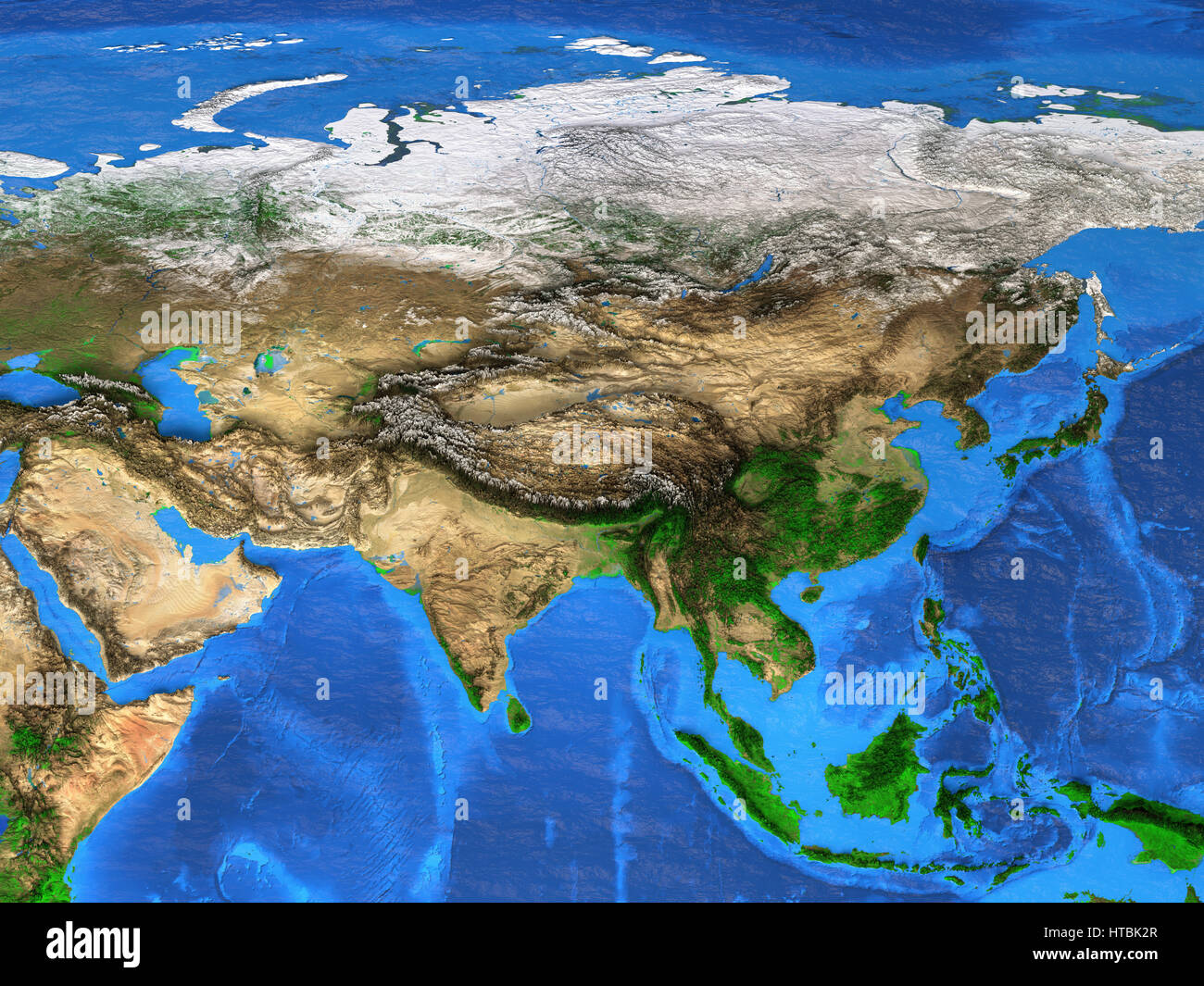
Asia, the largest and most populous continent, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and economies. Understanding its intricate geography and dynamic changes is crucial for various sectors, from environmental monitoring to disaster management, economic development, and even national security. Satellite mapping, a powerful tool in the realm of geospatial technology, provides an unprecedented window into Asia’s complexities, offering invaluable insights and data for informed decision-making.
The Power of Satellite Mapping: A Glimpse into Asia’s Dynamic Landscape
Satellite mapping, also known as remote sensing, employs satellites equipped with specialized sensors to capture images and data of the Earth’s surface. These images, processed and analyzed, reveal a wealth of information about the planet’s physical and human features. In the context of Asia, satellite mapping offers a unique perspective on:
1. Environmental Monitoring and Management:
- Deforestation and Land Use Change: Satellite imagery provides a comprehensive view of forest cover changes, deforestation rates, and land use patterns. This data is vital for monitoring forest health, managing natural resources, and implementing sustainable land management practices.
- Water Resource Management: Satellite-based observations track water bodies, monitor water quality, and assess the impact of climate change on water availability. This information is crucial for managing water resources, ensuring water security, and addressing water scarcity issues.
- Natural Disaster Monitoring: Satellite imagery plays a critical role in disaster response and mitigation by providing real-time data on floods, earthquakes, landslides, and other natural disasters. This allows for rapid assessment of damage, efficient resource allocation, and coordinated relief efforts.
- Climate Change Impacts: Satellite data provides crucial insights into the impact of climate change on Asia’s environment, including rising sea levels, glacial retreat, and changes in vegetation patterns. This information is vital for understanding the long-term consequences of climate change and developing adaptation strategies.
2. Urban Planning and Development:
- Urban Growth and Sprawl: Satellite images provide a comprehensive overview of urban areas, allowing for the analysis of urban growth patterns, infrastructure development, and the impact of urbanization on the environment.
- Infrastructure Development: Satellite mapping assists in identifying suitable locations for infrastructure projects, optimizing transportation networks, and managing urban development.
- Population Distribution and Density: Satellite data can be used to estimate population distribution and density, providing valuable insights for urban planning, resource allocation, and service delivery.
3. Economic Development and Agriculture:
- Agricultural Monitoring: Satellite images can track crop health, monitor irrigation patterns, and assess the impact of weather conditions on agricultural production. This data is essential for improving agricultural practices, optimizing yields, and ensuring food security.
- Resource Exploration: Satellite mapping assists in identifying potential mineral deposits, oil and gas reserves, and other valuable resources. This information is crucial for economic development and resource management.
- Trade and Transportation: Satellite data supports the monitoring of trade routes, shipping lanes, and transportation infrastructure, enabling efficient logistics and economic growth.
4. Security and Defense:
- Border Security and Surveillance: Satellite imagery enhances border security by providing real-time monitoring of border regions, detecting illegal activities, and supporting border patrol operations.
- Military Intelligence: Satellite data provides valuable intelligence for military planning, operations, and defense strategies.
- Disaster Response and Relief: Satellite imagery facilitates rapid assessment of damage during natural disasters, enabling effective disaster response and relief efforts.
Exploring the Landscape: A Look at Different Types of Satellite Maps
Satellite mapping utilizes diverse types of sensors and imaging techniques to capture different aspects of Asia’s landscape. Some common types include:
1. Optical Satellite Imagery:
- Multispectral Imagery: This type captures images in multiple bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, revealing different information about the Earth’s surface. For example, vegetation appears in different shades of red, while water bodies appear in shades of blue.
- Hyperspectral Imagery: This advanced technique captures images in hundreds of spectral bands, providing a highly detailed analysis of the Earth’s surface. It is particularly useful for identifying specific minerals, vegetation types, and environmental pollutants.
- Panchromatic Imagery: This type captures images in a single band of the electromagnetic spectrum, providing high-resolution grayscale images. It is often used for mapping terrain features and creating detailed base maps.
2. Radar Satellite Imagery:
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR): This technique uses radar waves to penetrate clouds and darkness, allowing for imaging even under adverse weather conditions. SAR is particularly useful for mapping terrain features, monitoring deforestation, and detecting changes in land cover.
- Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR): This technique uses two radar signals to create three-dimensional images, allowing for the detection of subtle changes in the Earth’s surface, such as ground deformation and subsidence.
3. Thermal Infrared Satellite Imagery:
- Thermal Infrared Sensors: These sensors detect the heat emitted by objects on the Earth’s surface, allowing for the identification of heat sources, monitoring wildfires, and assessing urban heat islands.
4. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging):
- LiDAR Sensors: These sensors emit laser pulses to measure the distance to the Earth’s surface, creating highly detailed three-dimensional models of the terrain. LiDAR is particularly useful for mapping vegetation, urban areas, and natural disasters.
Navigating the Data: Essential Tools and Techniques for Asia Satellite Map Analysis
Interpreting and analyzing satellite data requires specialized tools and techniques:
1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software allows for the visualization, analysis, and management of geospatial data. It enables the creation of maps, the overlaying of different data layers, and the analysis of spatial relationships.
2. Remote Sensing Software: Specialized remote sensing software facilitates the processing, analysis, and interpretation of satellite imagery. These tools allow for the extraction of information, such as land cover classification, change detection, and object recognition.
3. Image Processing Techniques: Techniques like image enhancement, filtering, and classification are applied to improve the quality of satellite images, enhance their interpretability, and extract meaningful information.
4. Data Analysis and Modeling: Statistical analysis, machine learning, and other data analysis techniques are used to extract insights from satellite data, identify trends, and develop predictive models.
The Future of Asia Satellite Mapping: Trends and Innovations
The field of satellite mapping is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for geospatial data. Some key trends and innovations shaping the future of Asia satellite mapping include:
1. High-Resolution Imaging: Advancements in satellite technology are enabling the acquisition of higher-resolution images, providing more detailed insights into the Earth’s surface. This is particularly important for urban planning, infrastructure development, and environmental monitoring.
2. CubeSats and Microsatellites: These smaller, more affordable satellites are becoming increasingly popular for remote sensing applications. They offer flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for specific applications like environmental monitoring and disaster response.
3. Big Data and Cloud Computing: The vast amounts of data generated by satellites require robust data processing and storage capabilities. Cloud computing platforms offer scalable and cost-effective solutions for managing and analyzing satellite data.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms are being integrated into satellite data analysis, enabling automated image processing, object recognition, and predictive modeling. This allows for faster and more accurate analysis of satellite data.
5. Open-Source Data and Platforms: The increasing availability of open-source satellite data and platforms is democratizing access to geospatial information, enabling researchers, policymakers, and the public to utilize satellite data for various applications.
FAQs about Asia Satellite Mapping
1. What are the limitations of satellite mapping?
While satellite mapping offers invaluable insights, it does have limitations:
- Cloud Cover: Clouds can obscure the Earth’s surface, hindering data acquisition.
- Atmospheric Interference: The atmosphere can distort satellite signals, affecting image quality.
- Data Accuracy: Satellite data is not always perfectly accurate, and errors can occur due to various factors.
- Data Availability: Data availability can be limited, especially for historical periods or specific geographic locations.
- Cost: Acquiring and processing satellite data can be expensive, especially for high-resolution imagery.
2. How can I access and utilize satellite data?
Numerous sources provide access to satellite data:
- Government Agencies: National space agencies like NASA, ESA, and ISRO provide free or low-cost access to satellite data.
- Commercial Satellite Operators: Companies like Planet Labs, Maxar Technologies, and DigitalGlobe offer high-resolution imagery and data services.
- Open-Source Platforms: Platforms like Google Earth Engine and Sentinel Hub provide access to free and open-source satellite data.
3. What are some ethical considerations related to satellite mapping?
Ethical considerations in satellite mapping include:
- Privacy: Satellite imagery can capture sensitive information about individuals and their activities, raising privacy concerns.
- Security: Satellite data can be used for military intelligence and surveillance, potentially impacting national security.
- Data Ownership and Access: Determining ownership and access rights to satellite data is crucial for ensuring fair and responsible use.
4. How can I contribute to the advancement of Asia satellite mapping?
You can contribute to the advancement of Asia satellite mapping by:
- Supporting research and development: Contribute to research projects or organizations focused on satellite mapping and geospatial technology.
- Promoting awareness and education: Share knowledge and resources about satellite mapping to promote its understanding and applications.
- Advocating for responsible and ethical use: Advocate for the responsible and ethical use of satellite data, ensuring privacy, security, and equitable access.
Tips for Utilizing Asia Satellite Mapping
- Define your objectives: Clearly define your goals and the specific information you need from satellite data.
- Choose the right data source: Select the appropriate type of satellite imagery based on your needs and budget.
- Process and analyze data effectively: Utilize appropriate tools and techniques for data processing, analysis, and interpretation.
- Validate your findings: Ensure the accuracy and reliability of your results through data validation and comparison with other sources.
- Communicate your findings effectively: Clearly communicate your findings through maps, reports, and presentations.
Conclusion
Satellite mapping is a transformative technology that provides unprecedented insights into Asia’s diverse and dynamic landscape. By harnessing the power of satellite data, we can better understand environmental challenges, manage resources, plan urban development, and promote sustainable growth. As technology continues to advance, the use of satellite mapping will become even more integral in shaping Asia’s future, enabling informed decision-making and a more sustainable and prosperous continent.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Asia: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!