Unveiling Iraq’s Landscape: A Topographic Journey
Related Articles: Unveiling Iraq’s Landscape: A Topographic Journey
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Iraq’s Landscape: A Topographic Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Iraq’s Landscape: A Topographic Journey
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Iraq’s Landscape: A Topographic Journey
- 3.1 A Tapestry of Topography
- 3.2 Understanding the Significance
- 3.3 Delving Deeper: Key Features and Their Significance
- 3.4 Navigating the Landscape: Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.5 Navigating the Landscape: Tips for Understanding Topographic Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Iraq’s Landscape: A Topographic Journey

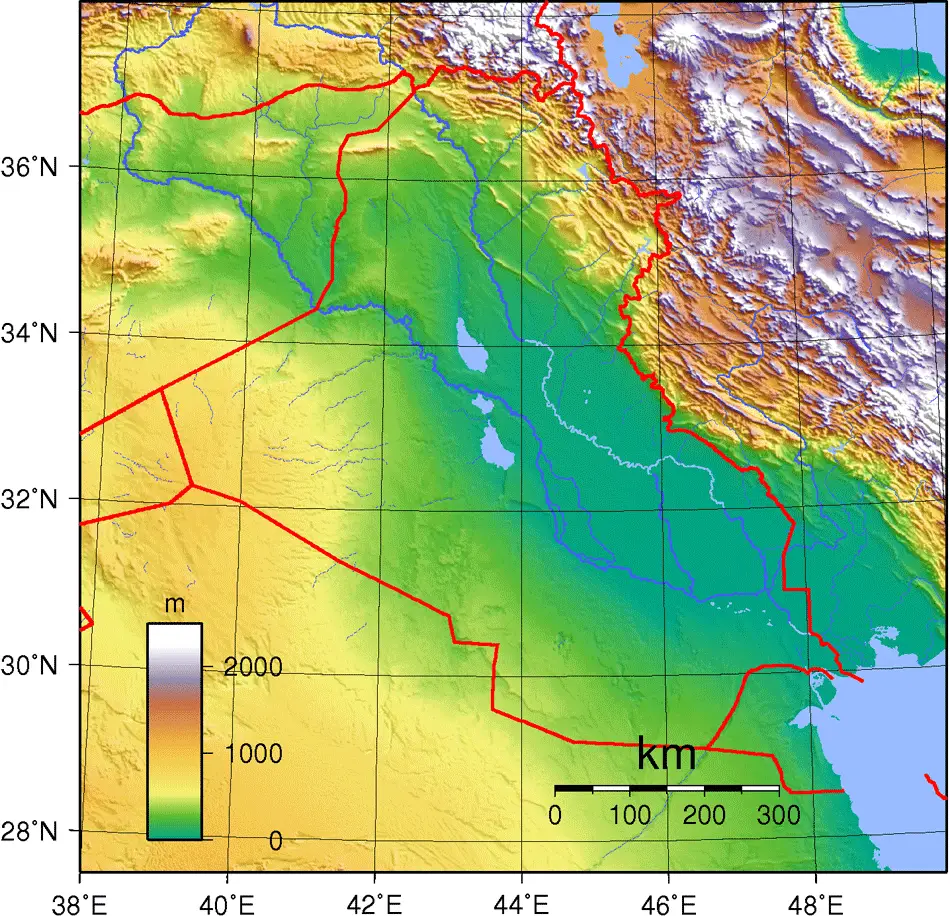
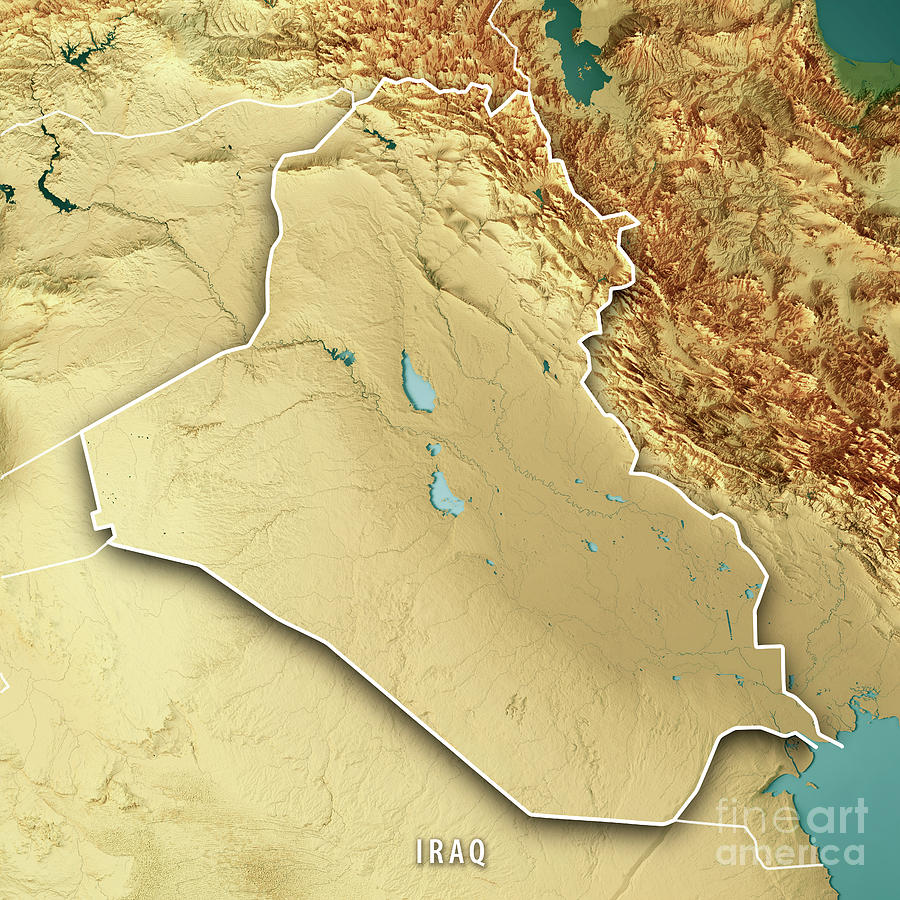
Iraq, a nation steeped in history and diverse cultures, boasts a landscape as varied and captivating as its past. To truly understand its geography, one must delve into the intricate details revealed by topographic maps. These maps, with their contours and elevations, paint a vivid picture of Iraq’s physical features, revealing the subtle interplay of mountains, deserts, plains, and rivers that shape the nation’s identity.
A Tapestry of Topography
Iraq’s topographic map tells a story of contrasts. The country is largely defined by its vast, low-lying plains, primarily the Mesopotamian Plain, which stretches from the Persian Gulf to the foothills of the Zagros Mountains. This fertile plain, historically the cradle of civilization, is traversed by the mighty Tigris and Euphrates rivers, lifeblood of the region.
To the east, the Zagros Mountains rise dramatically, forming a natural barrier between Iraq and Iran. These rugged peaks, reaching heights of over 3,000 meters, provide a stark contrast to the flat plains, offering a breathtaking tapestry of diverse landscapes.
In the west, the Syrian Desert stretches across the border, a vast expanse of sand and rock. This arid region, characterized by its harsh climate and sparse vegetation, serves as a stark reminder of the challenges posed by Iraq’s geography.
Understanding the Significance
Topographic maps of Iraq provide invaluable insights into the nation’s physical geography, revealing its strengths and challenges. They highlight:
- Resource Distribution: The location of rivers, plains, and mountains reveals the distribution of vital resources like water, arable land, and minerals. This understanding is crucial for sustainable development and resource management.
- Infrastructure Development: Topographic maps guide infrastructure development, ensuring roads, bridges, and pipelines are strategically placed to overcome geographic challenges and maximize efficiency.
- Environmental Management: Understanding the topography allows for effective environmental management, mitigating risks like flooding and drought, and promoting sustainable land use practices.
- Military Strategy: Topographic maps have long been vital for military planning and operations, providing crucial information about terrain, elevation, and potential obstacles.
- Disaster Response: In the face of natural disasters, topographic maps aid in swift and efficient relief efforts, guiding rescue teams and enabling accurate assessments of affected areas.
Delving Deeper: Key Features and Their Significance
1. The Mesopotamian Plain:
This fertile plain, cradled between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, has been the heart of Iraqi civilization for millennia. Its fertile soil, fed by the rivers, has sustained agriculture and supported dense populations. The plain’s flat topography facilitated the development of early irrigation systems, laying the foundation for the rise of ancient Mesopotamian empires.
2. The Zagros Mountains:
These mountains, a formidable barrier between Iraq and Iran, play a crucial role in the nation’s climate, water resources, and biodiversity. The Zagros Mountains act as a rain shadow, creating a drier climate on their western slopes, while their eastern slopes receive significant rainfall. They are also home to diverse flora and fauna, including endangered species.
3. The Syrian Desert:
This vast expanse of sand and rock covers a significant portion of western Iraq. The desert’s harsh climate and limited resources pose significant challenges to human habitation and development. However, it also holds potential for resource extraction, such as oil and gas, and offers unique opportunities for eco-tourism.
4. The Persian Gulf:
Iraq’s coastline along the Persian Gulf is a vital economic asset, providing access to international trade routes and supporting a significant fishing industry. However, the shallow waters and potential for environmental pollution require careful management.
Navigating the Landscape: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the highest point in Iraq?
The highest point in Iraq is Chekdar Kuh in the Zagros Mountains, reaching a height of 3,607 meters (11,834 feet).
Q2. What is the lowest point in Iraq?
The lowest point in Iraq is the Persian Gulf, which has a depth of 0 meters (0 feet).
Q3. What are the major rivers in Iraq?
The two major rivers in Iraq are the Tigris and the Euphrates, which converge in the south to form the Shatt al-Arab waterway.
Q4. What is the climate like in Iraq?
Iraq experiences a hot, arid climate with significant variations in temperature and rainfall. The country is generally divided into three climatic zones:
- The Mediterranean Zone: Located in the north, characterized by mild winters and hot, dry summers.
- The Steppe Zone: Located in the central region, characterized by hot summers and cold winters with limited rainfall.
- The Desert Zone: Located in the western and southern regions, characterized by extremely hot summers, cold winters, and very low rainfall.
Q5. What are the major geological formations in Iraq?
Iraq’s geology is characterized by:
- Mesozoic and Cenozoic sedimentary rocks: Predominantly found in the Mesopotamian Plain, these rocks are rich in oil and gas reserves.
- Paleozoic sedimentary rocks: Found in the Zagros Mountains, these rocks are rich in minerals like gypsum and sulfur.
- Igneous and metamorphic rocks: Found in the Zagros Mountains, these rocks are remnants of ancient volcanic activity.
Navigating the Landscape: Tips for Understanding Topographic Maps
- Understanding Contour Lines: Contour lines connect points of equal elevation. The closer the lines, the steeper the terrain.
- Identifying Elevation: The elevation of a point can be determined by the contour line it lies on.
- Interpreting Relief: The spacing and shape of contour lines reveal the topography, whether it’s a mountain, valley, or plain.
- Utilizing Symbols: Topographic maps use symbols to represent various features like rivers, roads, forests, and settlements.
Conclusion
Topographic maps of Iraq provide a vital lens through which to understand the nation’s physical geography. They reveal the intricate interplay of mountains, plains, rivers, and deserts, shaping the nation’s resources, climate, and challenges. By understanding the nuances of Iraq’s topography, we gain a deeper appreciation for its rich history, diverse culture, and the enduring spirit of its people. This knowledge is essential for sustainable development, environmental management, and ensuring the well-being of future generations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Iraq’s Landscape: A Topographic Journey. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!