Unveiling the Ancient Earth: A Journey Through the Supercontinent Pangaea
Related Articles: Unveiling the Ancient Earth: A Journey Through the Supercontinent Pangaea
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Ancient Earth: A Journey Through the Supercontinent Pangaea. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Ancient Earth: A Journey Through the Supercontinent Pangaea
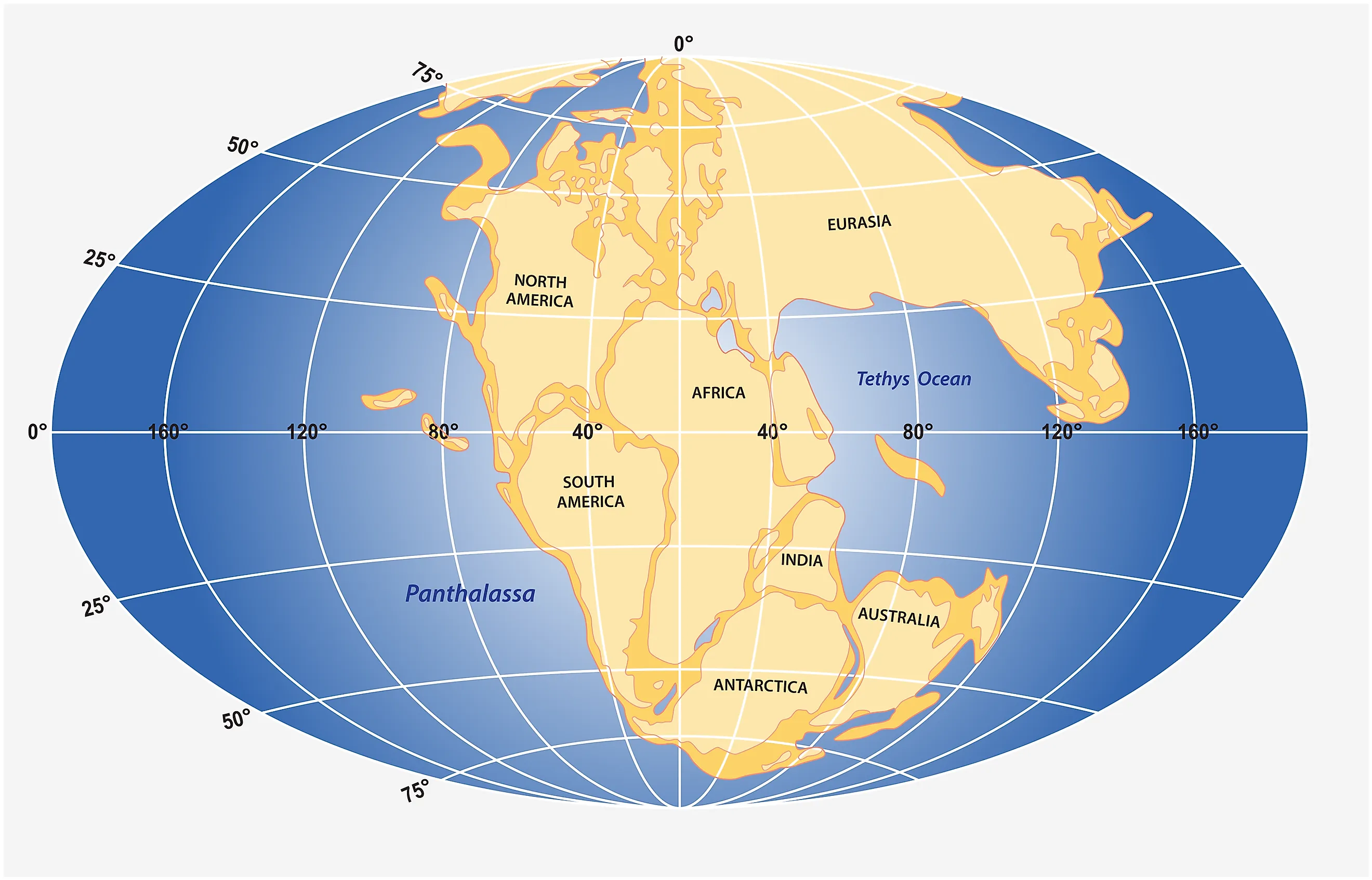
The Earth’s surface is in constant motion, a dynamic landscape sculpted by the relentless forces of plate tectonics. This geological ballet has shaped the continents we know today, but billions of years ago, the Earth’s landmasses were unified in a single, colossal supercontinent known as Pangaea. Understanding Pangaea’s existence and its eventual breakup is crucial for comprehending the geological history of our planet, the distribution of life, and even the climate patterns we experience today.
The Birth of a Supercontinent:
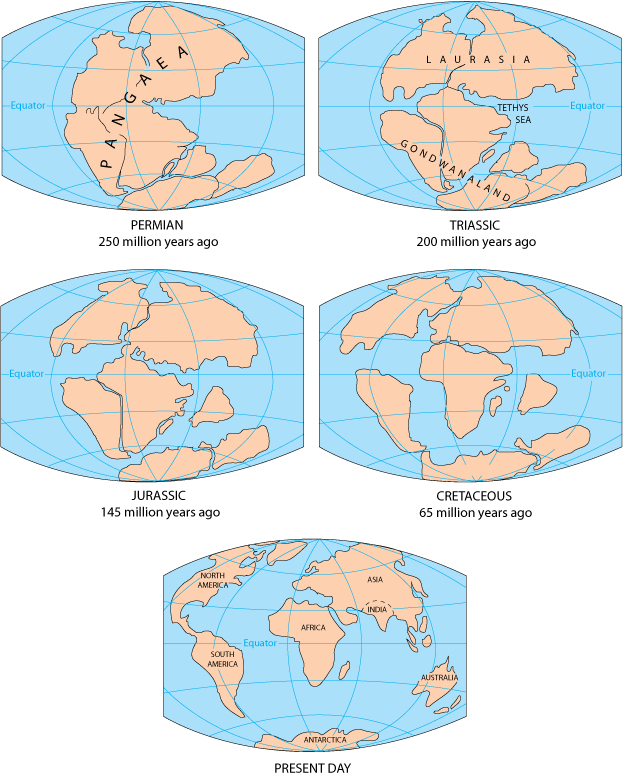
Pangaea, meaning "all lands" in Greek, formed approximately 335 million years ago during the late Paleozoic Era. This monumental event was the culmination of a long process of continental drift, where Earth’s tectonic plates, carrying the continents on their backs, slowly converged over millions of years. The continents that eventually coalesced into Pangaea included:
- Laurasia: Composed of North America, Greenland, Europe, and Asia.
- Gondwana: Comprised of South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia, and the Indian subcontinent.
As these landmasses collided, the immense pressure and heat generated by the convergence of tectonic plates caused the Earth’s crust to buckle and fold, forming massive mountain ranges. The Appalachian Mountains in North America and the Ural Mountains in Russia are remnants of this ancient mountain-building event.
A World Transformed:
The formation of Pangaea had a profound impact on the Earth’s environment and the evolution of life. The vast landmass created a single, interconnected ecosystem with unique climatic conditions. The interior of Pangaea, far from the moderating influence of oceans, experienced extreme temperature fluctuations, leading to the development of arid deserts. The formation of Pangaea also led to the rise of new animal and plant species, as the interconnectedness of continents allowed for greater migration and diversification.
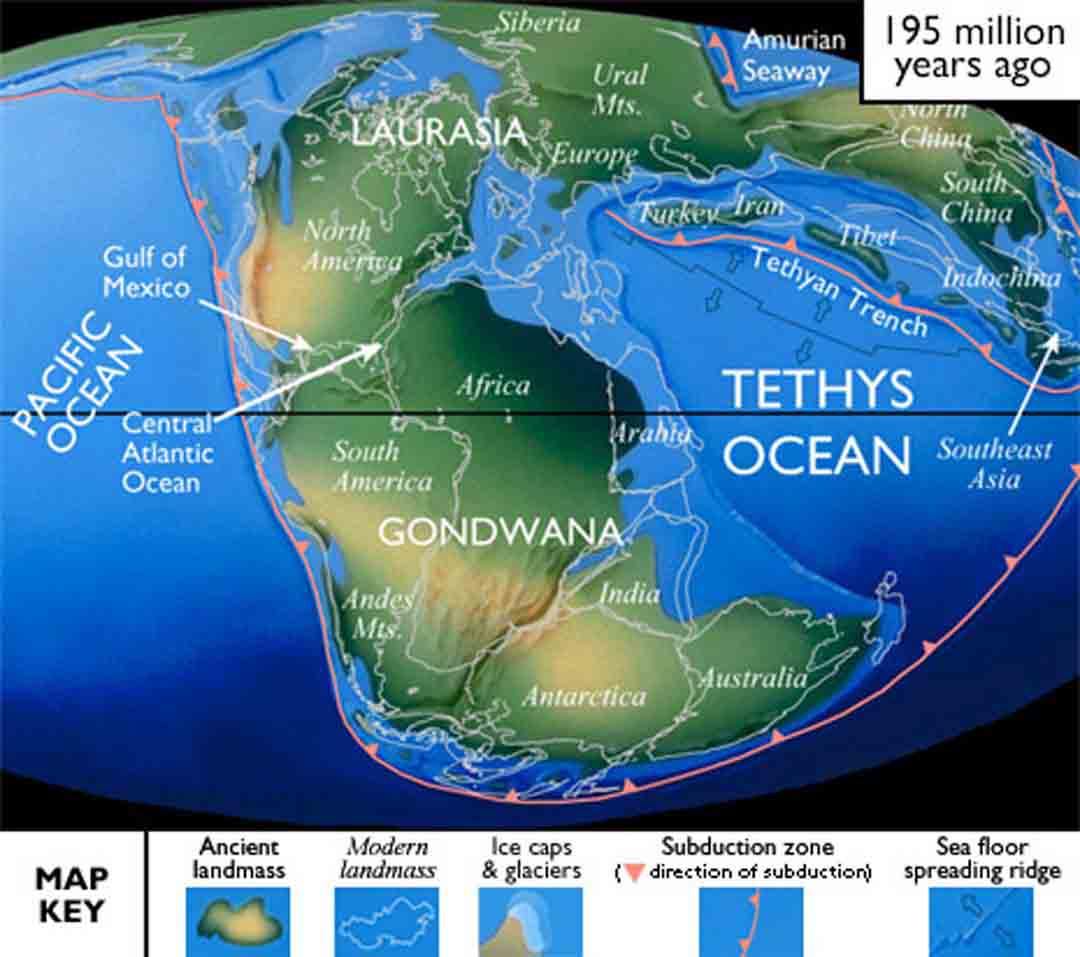
The Great Breakup:
Pangaea’s reign as a supercontinent was not to last. Around 200 million years ago, during the early Mesozoic Era, the supercontinent began to break apart. This process, driven by the relentless forces of plate tectonics, was characterized by the gradual separation of the continents along deep rifts and the formation of new ocean basins. The breakup of Pangaea had a profound impact on the Earth’s geography, climate, and the evolution of life.
The Legacy of Pangaea:
The breakup of Pangaea gave rise to the continents we know today, each with its unique geological history and biodiversity. The process of continental drift continues to reshape the Earth’s surface, albeit at a much slower pace than the dramatic events that led to the formation and breakup of Pangaea.
Evidence of Pangaea:
The existence of Pangaea is not just a theoretical construct. Numerous geological and biological observations provide compelling evidence for this ancient supercontinent:
- Matching Coastlines: The shapes of the continents, particularly those of South America and Africa, fit together like pieces of a puzzle. This suggests that they were once joined.
- Fossil Distribution: Similar fossils of ancient plants and animals are found on continents now separated by vast oceans. This distribution pattern points to a time when these continents were connected.
- Geological Formations: Similar rock formations and mountain ranges found on different continents provide further evidence of their past connection.
- Paleomagnetic Data: The Earth’s magnetic field leaves a record in rocks, and by studying this record, scientists can reconstruct the past positions of continents. This data aligns with the concept of Pangaea.
The Importance of Understanding Pangaea:
Understanding Pangaea’s formation, existence, and eventual breakup provides insights into:
- Earth’s Geological History: The study of Pangaea helps us understand the dynamics of plate tectonics, the processes that shape our planet, and the evolution of continents.
- The Distribution of Life: The interconnectedness of continents in Pangaea facilitated the migration and diversification of species, shaping the distribution of life we see today.
- Climate Patterns: The formation and breakup of Pangaea influenced global climate patterns, contributing to the development of deserts, ice ages, and other climatic events.
- Resource Exploration: Understanding the geological history of Pangaea can aid in the exploration of resources like oil, gas, and minerals, as these deposits often reflect the geological processes that shaped the Earth’s crust.
FAQs about Pangaea:
Q: How long did Pangaea exist?
A: Pangaea existed for approximately 160 million years, from about 335 million years ago to 175 million years ago.
Q: What caused Pangaea to break apart?
A: The breakup of Pangaea was driven by the forces of plate tectonics. Convection currents in the Earth’s mantle caused the tectonic plates to move, and the immense pressure generated by this movement eventually led to the separation of the supercontinent.
Q: What happened to the animals and plants that lived on Pangaea?
A: As Pangaea broke apart, the continents separated, isolating populations of animals and plants. This isolation led to the evolution of new species, contributing to the diversity of life we see today.
Q: What is the significance of Pangaea in understanding the Earth’s history?
A: Pangaea is a pivotal point in Earth’s history. Its formation and breakup profoundly impacted the Earth’s geography, climate, and the evolution of life. Studying Pangaea provides a window into the dynamic processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
Tips for Visualizing Pangaea:
- Use Interactive Maps: Explore online maps that allow you to manipulate the continents to visualize how they fit together in Pangaea.
- Study Paleogeographic Maps: Examine maps that depict the Earth’s geography at different points in time, including the period when Pangaea existed.
- Engage with Visualizations: Seek out animations and videos that illustrate the formation and breakup of Pangaea, providing a dynamic perspective on this geological event.
Conclusion:
Pangaea, the ancient supercontinent, serves as a powerful testament to the dynamic nature of our planet. Its formation and breakup, driven by the forces of plate tectonics, have shaped the Earth’s geography, influenced the distribution of life, and left an indelible mark on the history of our planet. By studying Pangaea, we gain a deeper understanding of the geological processes that have shaped the Earth we live on and the interconnectedness of life across our planet.


/GettyImages-476873389-5c44fc6146e0fb0001afe477.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Ancient Earth: A Journey Through the Supercontinent Pangaea. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!