Unveiling the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Spherical Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Spherical Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Spherical Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Spherical Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Spherical Maps
- 3.1 The Spherical Map: A Window to the World’s True Form
- 3.2 Types of Spherical Maps: A Spectrum of Representations
- 3.3 Applications of Spherical Maps: A World of Possibilities
- 3.4 FAQs: Demystifying the Spherical Map
- 3.5 Tips for Utilizing Spherical Maps Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion: A New Era of Mapping
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Spherical Maps
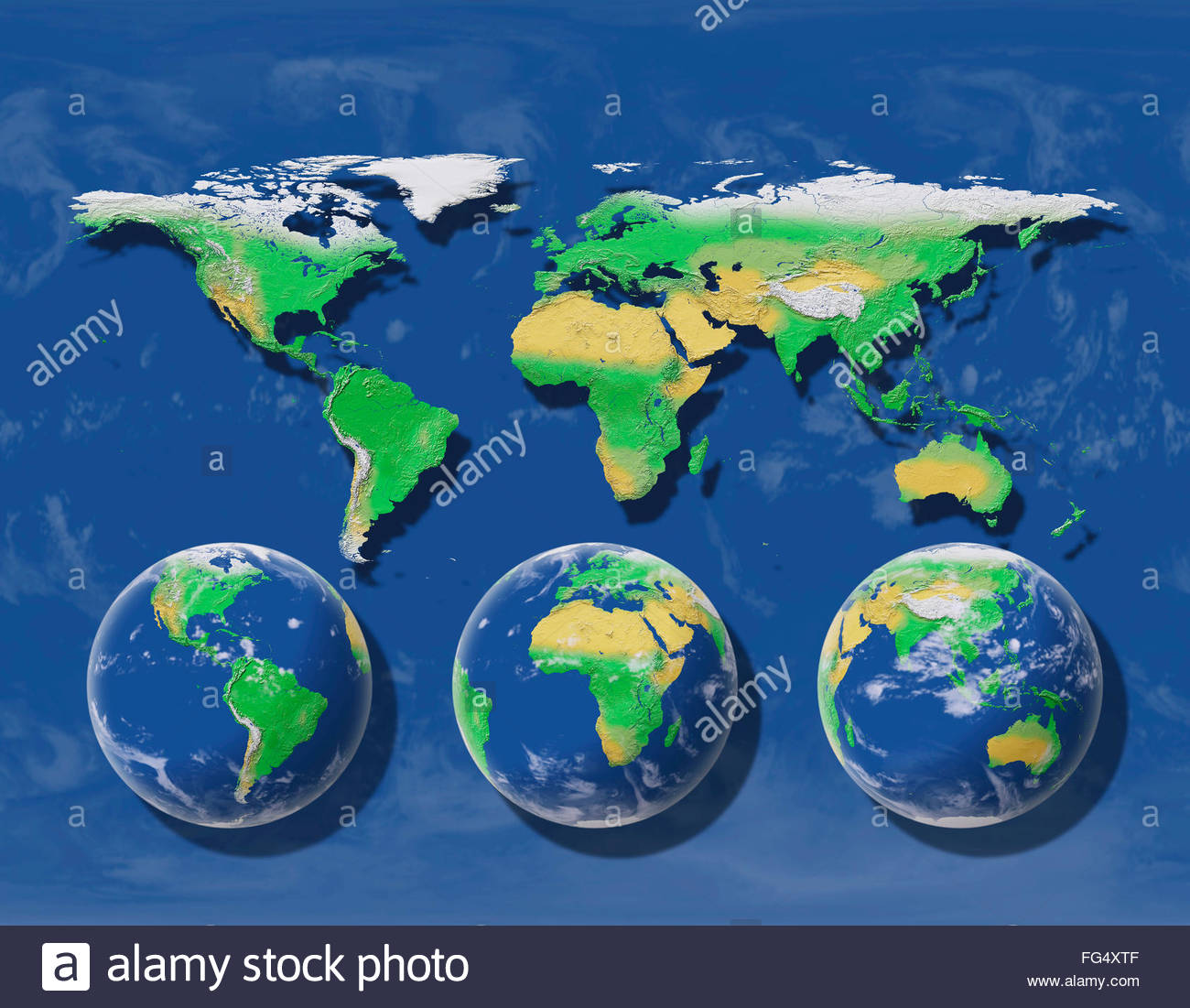
The world, in its entirety, is a complex tapestry of continents, oceans, and intricate geographical features. Accurately representing this intricate sphere on a flat surface has been a challenge for cartographers since antiquity. While traditional flat maps have served their purpose, they inevitably distort the true representation of the Earth’s curvature. Enter the spherical map, a revolutionary solution that offers a more accurate and immersive way to visualize our planet.
The Spherical Map: A Window to the World’s True Form
A spherical map, as the name suggests, is a map that replicates the Earth’s spherical shape. Unlike flat maps, these maps maintain the true proportions and distances between locations, eliminating the distortions inherent in planar projections. This fidelity to the Earth’s curvature provides several key advantages:
- Accurate Representation: Spherical maps offer a more accurate portrayal of the Earth’s surface, preserving the true size and shape of continents, oceans, and other geographical features. This eliminates the distorted perspectives that can arise from flat maps, particularly at the poles and along the edges of continents.
- Enhanced Visual Understanding: The three-dimensional nature of spherical maps fosters a more intuitive understanding of the Earth’s interconnectedness. Users can easily grasp the relative positions of continents, oceans, and countries, fostering a deeper appreciation for the planet’s global interconnectedness.
- Improved Spatial Awareness: By showcasing the Earth’s true curvature, spherical maps enhance spatial awareness, enabling users to visualize distances and directions more effectively. This is particularly beneficial for understanding global travel routes, weather patterns, and the distribution of resources.
Types of Spherical Maps: A Spectrum of Representations
While the fundamental principle of spherical maps remains consistent, various types exist, each tailored to specific purposes and aesthetic preferences. Here are some common categories:
- Globes: The most traditional and widely recognized form of spherical map, globes are physical representations of the Earth, often made of paper mache or plastic. They offer a tactile and immersive experience, allowing users to physically rotate and explore the globe.
- Interactive Digital Globes: Leveraging the power of computer technology, interactive digital globes offer a dynamic and engaging way to explore the Earth. These virtual representations allow users to zoom in and out, rotate the globe, and access various layers of information, such as elevation data, population density, and climate patterns.
- Projection-Based Spherical Maps: These maps utilize mathematical projections to translate the spherical Earth onto a flat surface, then wrap this flat surface around a sphere. While this approach introduces some distortion, it allows for the creation of spherical maps using readily available printing techniques.
Applications of Spherical Maps: A World of Possibilities
The accuracy and visual appeal of spherical maps have made them indispensable tools across diverse fields:
- Education: Spherical maps serve as invaluable learning aids in classrooms, providing students with a realistic representation of the Earth and facilitating a deeper understanding of geography, climate, and global connections.
- Navigation: Spherical maps are increasingly used in navigation systems, particularly for long-distance flights and maritime voyages. Their accurate representation of distances and directions improves route planning and enhances safety.
- Data Visualization: Spherical maps are powerful tools for visualizing global datasets, such as population distribution, environmental data, and economic indicators. Their three-dimensional nature allows for a more comprehensive and intuitive understanding of complex global patterns.
- Art and Design: Spherical maps are finding their way into contemporary art and design, inspiring innovative installations, sculptures, and interactive experiences. These artistic expressions showcase the beauty and complexity of our planet in new and captivating ways.
FAQs: Demystifying the Spherical Map
1. What are the limitations of spherical maps?
While spherical maps offer significant advantages over flat maps, they do have limitations. Due to their three-dimensional nature, spherical maps can be more challenging to store and transport compared to flat maps. Additionally, the creation and printing of spherical maps can be more complex and expensive.
2. How accurate are spherical maps?
The accuracy of spherical maps depends on the specific type of projection used. Some projections, such as the Mollweide projection, maintain the relative areas of continents, while others, like the Mercator projection, preserve angles but distort areas. Ultimately, no spherical map can perfectly represent the Earth’s surface without some degree of distortion.
3. Can spherical maps be used for navigation?
Spherical maps are increasingly used in navigation systems, particularly for long-distance flights and maritime voyages. Their accurate representation of distances and directions improves route planning and enhances safety. However, it’s crucial to note that spherical maps are not a substitute for traditional navigation tools like GPS and compasses.
4. Are spherical maps only for professional use?
Spherical maps are becoming increasingly accessible to the general public. Interactive digital globes, for instance, are available online and through mobile apps, allowing anyone to explore the Earth in an immersive and engaging way.
Tips for Utilizing Spherical Maps Effectively
- Choose the right type of map: Consider the specific purpose and desired level of detail when selecting a spherical map. For general exploration, a traditional globe or an interactive digital globe might be suitable. For data visualization, a projection-based spherical map might be more appropriate.
- Explore different projections: Different projections offer different advantages and disadvantages. Familiarize yourself with the characteristics of various projections to choose the one that best suits your needs.
- Use interactive features: If using an interactive digital globe, take advantage of its features, such as zoom, rotate, and layer information to enhance your understanding.
- Engage with the map: Don’t simply look at a spherical map; interact with it. Rotate the globe, trace routes, and explore different locations to gain a deeper appreciation for the Earth’s interconnectedness.
Conclusion: A New Era of Mapping
Spherical maps represent a significant advancement in cartography, offering a more accurate and immersive way to visualize our planet. Their ability to preserve the Earth’s true curvature provides a deeper understanding of global geography, distances, and interconnectedness. As technology continues to evolve, spherical maps are poised to play an even more prominent role in education, navigation, data visualization, and art, fostering a deeper appreciation for our shared home in the cosmos.







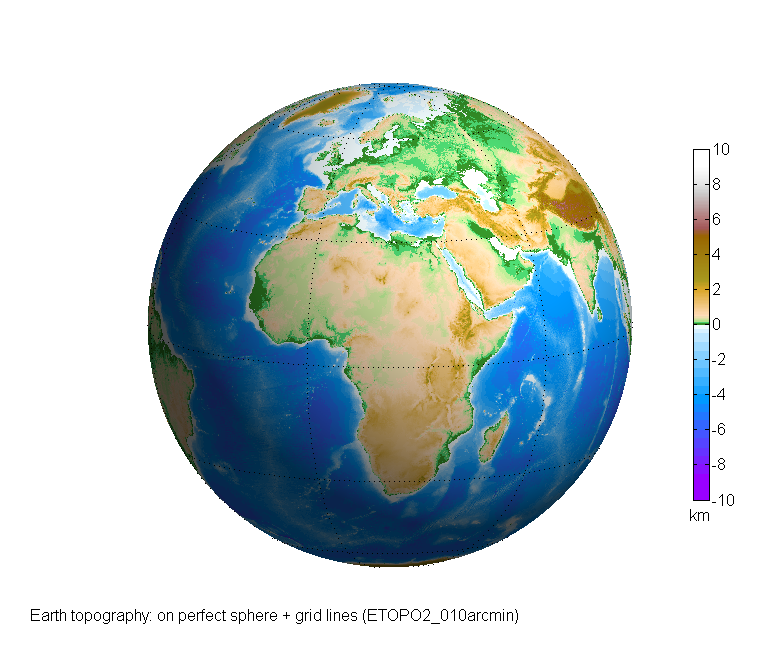
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Globe: A Comprehensive Guide to Spherical Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!