Unveiling the Hidden Network: A Comprehensive Look at the United States Nuclear Bunkers Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Hidden Network: A Comprehensive Look at the United States Nuclear Bunkers Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Hidden Network: A Comprehensive Look at the United States Nuclear Bunkers Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Hidden Network: A Comprehensive Look at the United States Nuclear Bunkers Map

The United States, like many nations, has a complex and often shrouded history of nuclear preparedness. At the heart of this preparedness lies a network of underground bunkers, strategically dispersed across the country. These bunkers, designed to withstand the catastrophic effects of nuclear war, represent a crucial element of national security and disaster response planning. While their exact locations remain classified, understanding their significance and the factors influencing their distribution is crucial for comprehending the nation’s historical and present-day approach to nuclear threats.
This article delves into the intricacies of the United States’ nuclear bunker network, exploring its history, purpose, and the factors that shape its geographical distribution. We will examine the evolution of these bunkers, their varying levels of security and functionality, and the ongoing debate surrounding their relevance in the 21st century.
A Historical Perspective: From Cold War Fear to Modern Challenges
The genesis of the United States’ nuclear bunker network can be traced back to the height of the Cold War. Fueled by the escalating tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union, the threat of nuclear annihilation loomed large, prompting the construction of numerous underground facilities designed to provide shelter and command centers in the event of a nuclear attack. These early bunkers, often referred to as "control centers," were strategically located near major cities and military installations, ensuring the continuity of government operations and the ability to launch retaliatory strikes.
The construction of these bunkers was driven by a combination of factors, including:
- The Need for Continuity of Government: In the event of a nuclear attack, the ability to maintain a functioning government was paramount. Bunkers provided a secure location for key government officials and military leaders to continue operations and coordinate a response.
- Command and Control Centers: These bunkers served as critical command centers, allowing military leaders to monitor the situation, coordinate defense efforts, and manage the use of nuclear weapons.
- Protection of Critical Resources: Bunkers were also designed to safeguard vital resources, including communication networks, infrastructure, and critical supplies, ensuring the nation’s ability to recover from a nuclear attack.
Mapping the Network: Factors Influencing Bunker Locations
The distribution of nuclear bunkers across the United States is not random. Several factors influence their location, including:
- Proximity to Major Cities and Military Bases: Bunkers are often located near major population centers and strategic military installations, ensuring their proximity to key assets and personnel.
- Geological Stability: Bunkers are typically constructed in areas with stable geological formations, minimizing the risk of collapse during an earthquake or other natural disaster.
- Accessibility: Proximity to major transportation routes, including highways, railroads, and airfields, ensures easy access for personnel and supplies.
- Secrecy: The location of nuclear bunkers remains highly classified, with the government actively working to conceal their exact locations. This secrecy is essential for maintaining the security and effectiveness of these facilities.
Types of Bunkers: From Simple Shelters to Advanced Command Centers
The United States’ nuclear bunker network encompasses a wide range of facilities, each tailored to specific needs and functions. These bunkers can be broadly categorized into three main types:
- Emergency Operations Centers (EOCs): These bunkers are designed for government officials and military leaders, providing a secure location for decision-making and coordinating response efforts. They are typically equipped with advanced communication systems, data processing capabilities, and secure access to information.
- Strategic Command Centers: These bunkers serve as the nerve center for the nation’s nuclear arsenal, providing the ability to monitor and control nuclear weapons. They are highly fortified and equipped with sophisticated technology for communication, surveillance, and weapon control.
- Population Shelters: Designed to provide refuge for a large number of people in the event of a nuclear attack, these bunkers are typically located in remote areas and offer basic survival necessities, including food, water, and medical supplies.
The Debate Continues: The Relevance of Bunkers in the 21st Century
The relevance of the United States’ nuclear bunker network in the 21st century is a subject of ongoing debate. While the threat of nuclear war has diminished somewhat since the end of the Cold War, concerns remain about the potential for accidental or deliberate nuclear attacks, as well as the use of nuclear weapons by rogue states or terrorist organizations.
Proponents of maintaining the bunker network argue that it remains a vital component of national security, providing a crucial layer of protection against the catastrophic consequences of a nuclear attack. They emphasize the importance of ensuring the continuity of government, maintaining command and control capabilities, and safeguarding critical resources.
Critics, however, argue that the focus on nuclear bunkers represents an outdated approach to national security, one that is both expensive and ineffective in the face of modern threats. They contend that the focus should shift towards diplomacy, arms control, and non-proliferation efforts, rather than relying on outdated and potentially costly bunker systems.
FAQs Regarding the US Nuclear Bunkers Map
1. Are the locations of all US nuclear bunkers publicly known?
No, the exact locations of most US nuclear bunkers are classified information. The government actively works to maintain the secrecy of these facilities, recognizing their importance for national security.
2. How many nuclear bunkers are there in the United States?
The exact number of US nuclear bunkers is classified information. However, it is estimated that there are hundreds, if not thousands, of these facilities spread across the country.
3. Are all nuclear bunkers equally secure?
No, US nuclear bunkers vary in their level of security and functionality. Some are designed for specific purposes, such as command and control, while others are intended to provide basic shelter for a large number of people.
4. Are nuclear bunkers still relevant in the 21st century?
The relevance of nuclear bunkers in the 21st century is a subject of debate. While the threat of a large-scale nuclear war has diminished, concerns remain about the potential for accidental or deliberate attacks, as well as the use of nuclear weapons by rogue states or terrorist organizations.
5. What is the future of the US nuclear bunker network?
The future of the US nuclear bunker network is uncertain. Some experts believe that these facilities will continue to play a role in national security, while others argue that they are outdated and should be phased out.
Tips for Understanding the US Nuclear Bunkers Map
- Consult Historical Sources: Researching historical documents and accounts of the Cold War can provide valuable insights into the development of the US nuclear bunker network.
- Examine Government Reports: Government reports on national security, defense, and emergency preparedness often contain information about the role of nuclear bunkers in US strategy.
- Engage with Experts: Seek out the perspectives of experts in nuclear security, military history, and disaster preparedness to gain a deeper understanding of the complex issues surrounding the US nuclear bunker network.
- Stay Informed: Follow developments in international relations, nuclear proliferation, and national security to stay informed about the evolving role of nuclear bunkers in the 21st century.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Cold War Preparedness
The United States’ nuclear bunker network is a testament to the nation’s historical anxieties about nuclear war. These facilities, designed to provide shelter, command and control, and continuity of government in the event of a nuclear attack, represent a crucial aspect of the nation’s Cold War defense strategy. While the threat of nuclear war has evolved, the legacy of these bunkers continues to shape the nation’s approach to national security and disaster preparedness. Understanding the history, purpose, and distribution of these facilities is essential for comprehending the United States’ evolving relationship with nuclear threats and the ongoing debate about the role of nuclear bunkers in the 21st century.



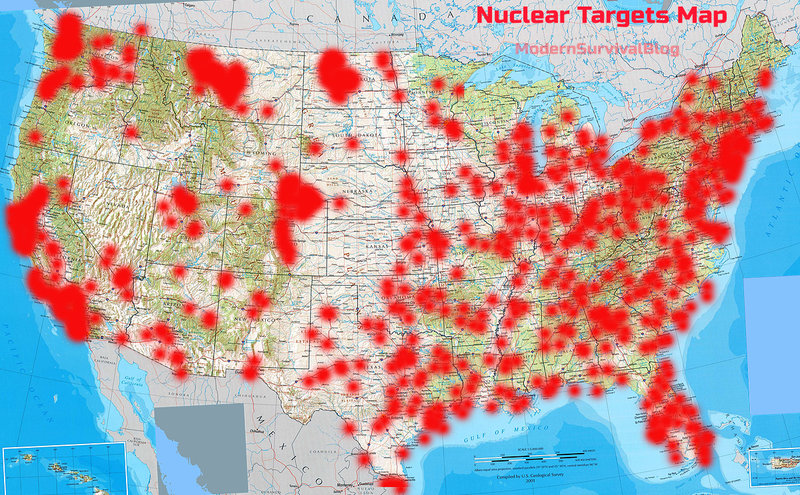
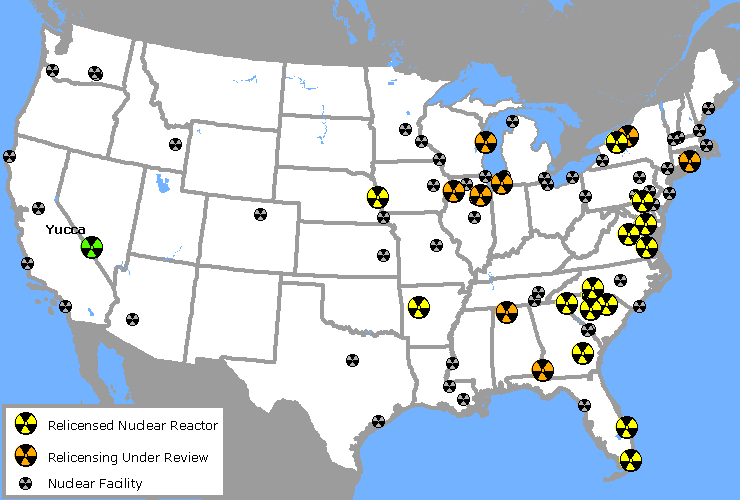
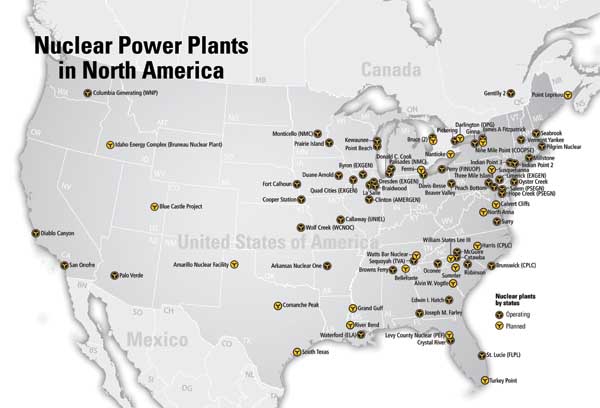

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Hidden Network: A Comprehensive Look at the United States Nuclear Bunkers Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!