Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Look at the Internet Backbone Map of the USA
Related Articles: Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Look at the Internet Backbone Map of the USA
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Look at the Internet Backbone Map of the USA. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Look at the Internet Backbone Map of the USA
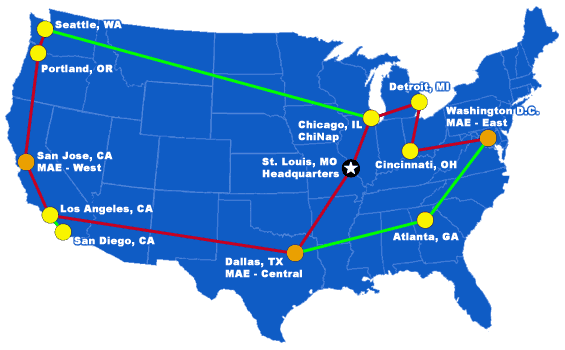
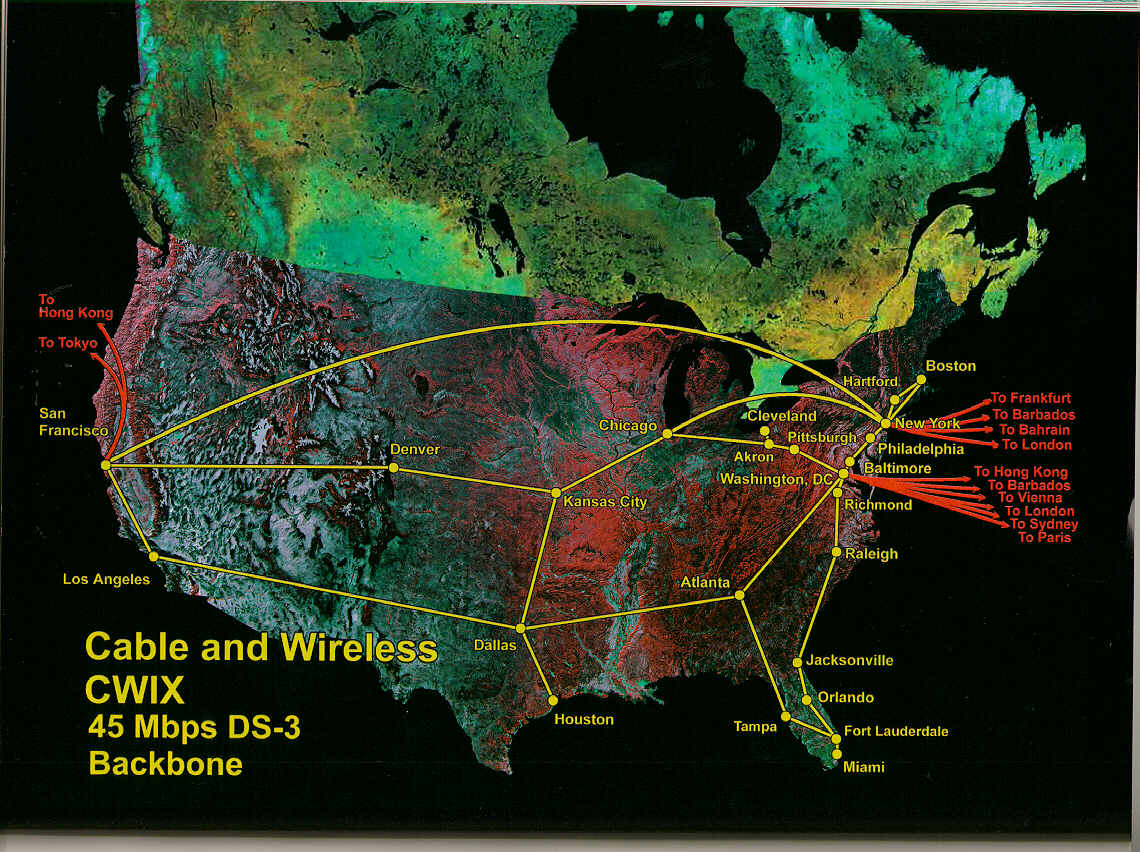
The internet, a vast and intricate web of interconnected networks, operates on a complex infrastructure that allows for seamless communication and information sharing across the globe. At the heart of this digital landscape lies the internet backbone, a high-speed network of fiber optic cables that serves as the primary pathway for data transmission. Understanding the intricate network of the internet backbone map of the USA is crucial for comprehending the flow of information within the country and its global reach.
Mapping the Information Superhighway: A Look at the Internet Backbone Map of the USA
The internet backbone map of the USA visually represents the physical infrastructure that underpins the internet’s operations. This map displays the major fiber optic cable routes that traverse the country, connecting major cities, data centers, and internet exchange points (IXPs). These cables, buried underground or suspended on towers, act as the arteries of the digital world, carrying massive volumes of data at lightning speed.
Key Components of the Internet Backbone Map
-
Fiber Optic Cables: These cables form the backbone of the internet, transmitting data as pulses of light. Their high bandwidth capacity allows for the transmission of vast amounts of information, including streaming videos, downloading files, and facilitating online communication.
-
Internet Exchange Points (IXPs): These physical locations serve as meeting points for different internet service providers (ISPs) and content delivery networks (CDNs). IXPs facilitate the exchange of internet traffic between various networks, ensuring efficient data routing and reducing latency.
-
Data Centers: These facilities house servers and other computing equipment, storing and processing vast amounts of data. Data centers are connected to the internet backbone through high-speed fiber optic cables, ensuring fast and reliable access to information.
-
Network Operators: These companies own and operate the physical infrastructure of the internet backbone, including fiber optic cables, network equipment, and data centers. Major network operators in the USA include AT&T, Verizon, Comcast, and Lumen Technologies.
The Significance of the Internet Backbone Map
The internet backbone map holds significant importance for various stakeholders, including:
-
Internet Service Providers (ISPs): Understanding the network topology allows ISPs to optimize their routing strategies, ensuring efficient data delivery and minimizing latency for their customers.
-
Businesses and Organizations: Companies rely on the internet backbone for their operations, including communication, data storage, and online services. A robust backbone infrastructure is essential for businesses to maintain uninterrupted operations and ensure data security.
-
Government Agencies: The internet backbone is critical for national security and disaster response. Government agencies rely on a reliable and resilient network infrastructure for communication, data sharing, and emergency services.
-
Researchers and Academics: The internet backbone map provides valuable insights into the structure and evolution of the internet, facilitating research on network performance, security, and the impact of new technologies.
Benefits of a Well-Developed Internet Backbone
-
High-Speed Data Transmission: The internet backbone’s fiber optic cables enable the transmission of data at exceptionally high speeds, facilitating seamless online experiences, including video streaming, online gaming, and cloud computing.
-
Low Latency: The efficient routing and high bandwidth capacity of the internet backbone minimize delays in data transmission, resulting in faster response times and improved user experience.
-
Network Resilience: The redundant nature of the internet backbone, with multiple pathways for data transmission, ensures network resilience against outages and disruptions.
-
Global Connectivity: The internet backbone connects the USA to the global internet network, facilitating communication and information sharing with other countries.
Challenges Facing the Internet Backbone
Despite its vital role, the internet backbone faces several challenges, including:
-
Capacity Constraints: The increasing demand for data transmission due to the proliferation of online services and devices puts pressure on the capacity of the internet backbone.
-
Security Threats: The internet backbone is a prime target for cyberattacks, posing threats to data security and network stability.
-
Infrastructure Aging: The aging infrastructure of the internet backbone requires constant maintenance and upgrades to ensure its reliability and efficiency.
-
Digital Divide: Uneven access to high-speed internet connectivity across the country, particularly in rural areas, highlights the need for investments in expanding the internet backbone infrastructure.
FAQs about the Internet Backbone Map of the USA
Q: What are the major internet backbone providers in the USA?
A: Major internet backbone providers in the USA include AT&T, Verizon, Comcast, Lumen Technologies, and Google.
Q: How does the internet backbone map impact internet speeds?
A: The internet backbone’s high bandwidth capacity and efficient routing significantly contribute to faster internet speeds.
Q: What is the role of IXPs in the internet backbone?
A: IXPs facilitate the exchange of internet traffic between different networks, reducing latency and improving network efficiency.
Q: How does the internet backbone contribute to national security?
A: A robust internet backbone is essential for government agencies to maintain communication, data sharing, and emergency services during national crises.
Q: What are the future trends in internet backbone development?
A: Future trends include the expansion of fiber optic cable networks, the adoption of 5G technology, and the development of more secure and resilient network infrastructure.
Tips for Understanding the Internet Backbone Map
-
Explore interactive maps: Several online resources provide interactive maps of the internet backbone, allowing users to visualize the network’s structure and identify key routes.
-
Focus on major cities and data centers: Pay attention to the locations of major cities and data centers, as they represent key hubs for internet traffic.
-
Learn about network operators: Research the major network operators in the USA and their role in providing internet services.
-
Stay updated on industry trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in internet backbone infrastructure, including new technologies and advancements in network security.
Conclusion
The internet backbone map of the USA provides a crucial window into the intricate network that underpins the digital world. Understanding the map’s components, significance, and challenges is vital for navigating the complexities of the internet and appreciating its impact on our lives. As technology continues to evolve, the internet backbone will undoubtedly play an even more critical role in shaping our future.

![United States Backbone, Internet2 [1] Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/A-Zincir-Heywood/publication/326241163/figure/fig5/AS:645567294218251@1530926645632/United-States-Backbone-Internet2-1.png)

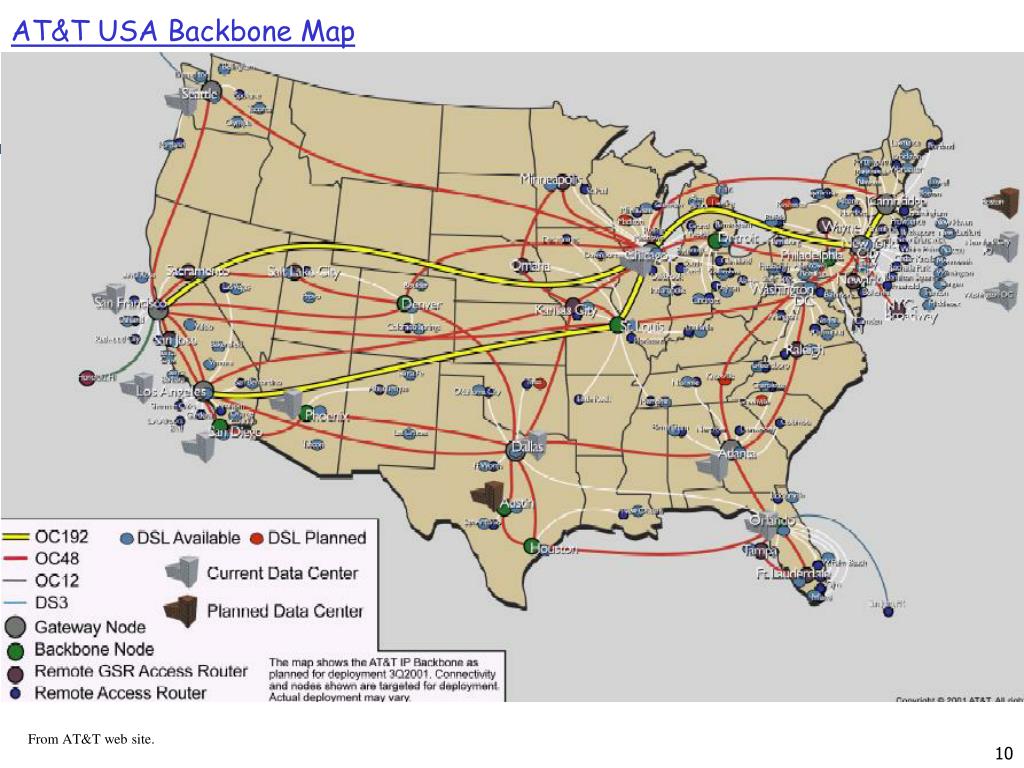

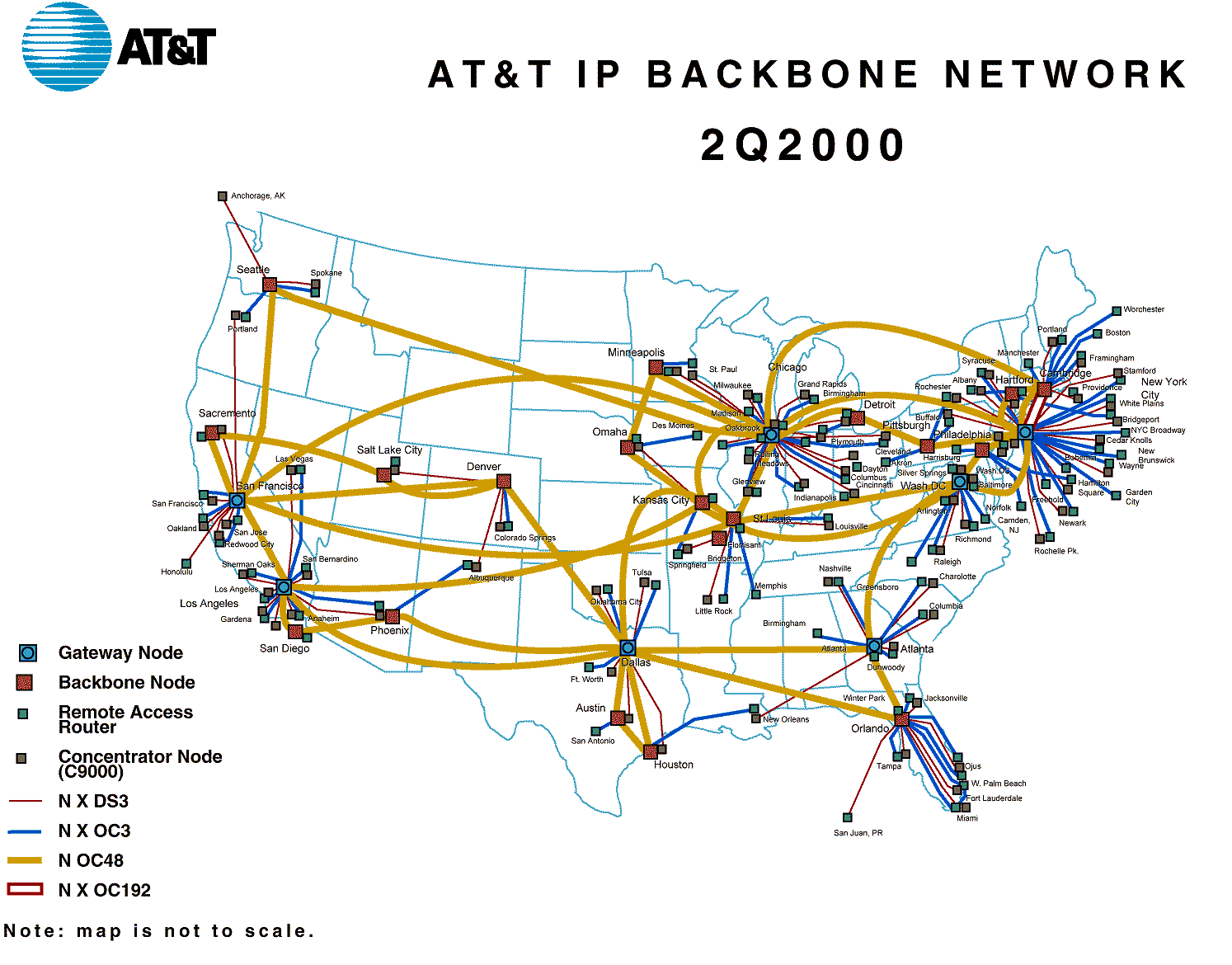
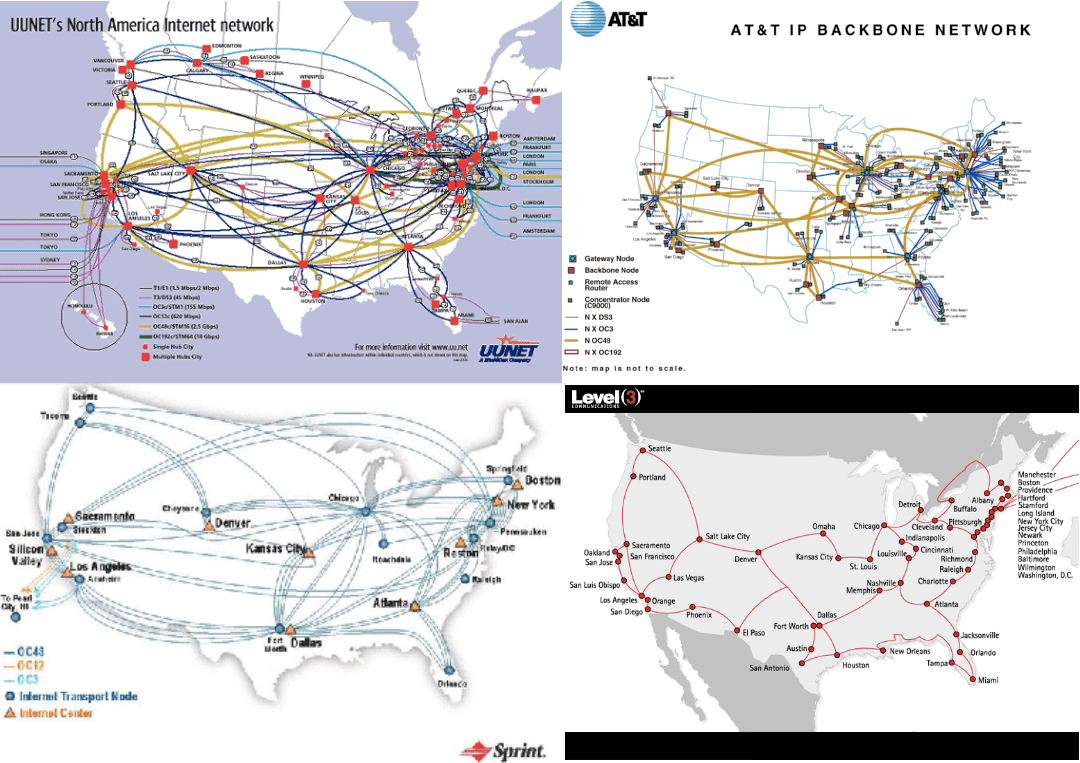
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Network: A Comprehensive Look at the Internet Backbone Map of the USA. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!