Unveiling the World Through IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Guide to Location Mapping
Related Articles: Unveiling the World Through IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Guide to Location Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World Through IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Guide to Location Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the World Through IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Guide to Location Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the World Through IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Guide to Location Mapping
- 3.1 Understanding IP Addresses and Their Role in Location Mapping
- 3.2 IP Geolocation: How It Works
- 3.3 Applications of IP Address Location Mapping
- 3.4 Benefits of Utilizing IP Address Location Mapping
- 3.5 Limitations of IP Address Location Mapping
- 3.6 FAQs Regarding IP Address Location Mapping
- 3.7 Tips for Utilizing IP Address Location Mapping Effectively
- 3.8 Conclusion: Navigating the Digital World with IP Geolocation
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the World Through IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Guide to Location Mapping
In the vast digital landscape, where information flows freely across borders and continents, understanding the geographical origins of online activity becomes increasingly crucial. This is where IP address location mapping emerges as a powerful tool, offering insights into the physical locations associated with internet traffic. This guide provides a comprehensive exploration of IP address location mapping, delving into its workings, applications, benefits, and limitations.
Understanding IP Addresses and Their Role in Location Mapping
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) serves as a unique identifier for every device connected to the internet. It acts as a virtual postal address, enabling communication between computers and servers. IP addresses are broadly categorized into two types:
- IPv4: The older version, using a 32-bit system, representing addresses as four numbers separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- IPv6: The newer, 128-bit system, addressing the depletion of IPv4 addresses, using a more complex hexadecimal format.
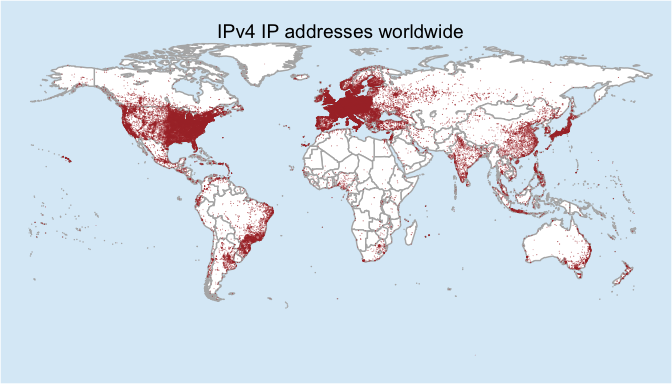
While IP addresses are designed for network communication, they can also be used to infer the approximate geographical location of a device. This is achieved through a process known as IP geolocation.
IP Geolocation: How It Works
IP geolocation relies on databases that map IP address ranges to geographical locations. These databases are compiled through various methods, including:
- ISP (Internet Service Provider) Information: ISPs provide information about the geographical regions they serve, which can be linked to IP address ranges.
- GeoIP Databases: Companies like MaxMind and IP-API maintain extensive databases, constantly updated with information from various sources.
- Reverse DNS Lookups: This process involves querying a DNS server to retrieve the hostname associated with an IP address. The hostname can often provide clues about the device’s location.
It’s important to note that IP geolocation is not an exact science. While it can provide a general idea of a device’s location, it may not always be precise. Factors contributing to this imprecision include:
- Dynamic IP Addresses: Many internet users have dynamic IP addresses, which can change frequently.
- Proxy Servers: Users can route their internet traffic through proxy servers, masking their actual location.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs encrypt internet traffic and route it through servers in different locations, further obscuring the user’s true location.
Applications of IP Address Location Mapping
IP geolocation finds applications in various fields, including:
- Security and Fraud Detection: Identifying the geographical origins of suspicious activity can help detect fraudulent transactions, malware attacks, and other security threats.
- Marketing and Advertising: Targeting advertisements based on user location enhances campaign effectiveness and improves ROI.
- Website Analytics: Understanding the geographical distribution of website visitors provides insights into audience demographics and interests.
- Network Management: Monitoring network traffic based on location helps identify potential bottlenecks and optimize network performance.
- Law Enforcement: IP geolocation assists in investigations by providing leads on the location of suspects or cybercrime origins.
Benefits of Utilizing IP Address Location Mapping
Leveraging IP geolocation offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Security: By identifying potential threats based on location, organizations can implement targeted security measures and mitigate risks.
- Improved Customer Experience: Tailoring content and services based on user location enhances user experience and increases engagement.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Understanding the geographical distribution of data allows for more informed business decisions based on real-time insights.
- Streamlined Operations: Optimizing network infrastructure based on location data improves efficiency and reduces operational costs.
Limitations of IP Address Location Mapping
While IP geolocation offers valuable insights, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations:
- Accuracy Concerns: IP geolocation is not always accurate, especially with dynamic IP addresses, proxy servers, and VPNs.
- Privacy Implications: Using IP geolocation to track user location raises privacy concerns, necessitating responsible data handling practices.
- Legal Considerations: In some jurisdictions, using IP geolocation for specific purposes may require legal compliance.
FAQs Regarding IP Address Location Mapping
Q: How accurate is IP geolocation?
A: The accuracy of IP geolocation varies based on the factors discussed above. While it can provide a general idea of a device’s location, it may not be precise.
Q: Is IP geolocation legal?
A: The legality of using IP geolocation depends on the specific context and jurisdiction. It’s essential to consult relevant laws and regulations before implementing IP geolocation solutions.
Q: How can I protect my privacy when using IP geolocation?
A: Consider using a VPN to mask your IP address and protect your location information. Be mindful of the privacy policies of websites and services that utilize IP geolocation.
Q: What are the ethical considerations of IP geolocation?
A: Ethical considerations include ensuring transparency, obtaining consent, and safeguarding user privacy. It’s crucial to use IP geolocation responsibly and ethically.
Tips for Utilizing IP Address Location Mapping Effectively
- Verify Accuracy: Always verify the accuracy of IP geolocation data before making decisions based on it.
- Respect Privacy: Ensure compliance with privacy regulations and obtain user consent before collecting and using location data.
- Use Reputable Providers: Choose reputable IP geolocation providers with accurate and up-to-date databases.
- Consider Context: Understand the limitations of IP geolocation and consider the specific context before relying on it.
Conclusion: Navigating the Digital World with IP Geolocation
IP address location mapping plays a pivotal role in understanding the geographical origins of online activity. It offers valuable insights for security, marketing, website analytics, and other applications. However, it’s essential to acknowledge its limitations, address privacy concerns, and utilize it responsibly. By understanding the workings, benefits, and limitations of IP geolocation, individuals and organizations can navigate the digital world with greater awareness and insight.


![]()



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World Through IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Guide to Location Mapping. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!